2026 Author: Howard Calhoun | calhoun@techconfronts.com. Last modified: 2025-01-24 13:10:28
Power supply stations today are operated in different variations. Thermal power plants are not the most common, but they also have many attractive qualities in terms of application. Equipment of this type is used to generate, convert and transmit electricity to consumers. But for the effective performance of these functions, thermal power plants must be properly serviced. This applies to basic technical preventive measures, to the organization of control systems, as well as to more responsible repair operations.

General information about thermal power plants
A power plant is a whole complex of systems, components and assemblies that work to generate electricity as a result of converting heat into mechanical energy. The basis of such stations is an electric generator with a rotating shaft. The complex also includes a combustion chamber in which the process of heat release takes place. It is important to note that the operation of thermal power plants and heating networks often involves the release of steam. This applies to those installations that are also supplied with hydrological communications, in which there is an increase in steam pressure, as a result of which the rotation of the turbine rotor is activated. The energy generated in this way is transmitted to the shaft of the main rotor of the engine, which leads to the generation of electric current. At the same time, the generated thermal energy is not always completely spent on generating electricity. Depending on the place of use and the needs of consumers, part of it can be used for the heating function.
Technical characteristics of thermal power plants

One of the key performance characteristics is the voltage with which the station operates. Typically, complexes are isolated with a potential of up to 1000 V or more. The former are used locally as a means of supplying energy to specific objects - as a rule, industrial ones. The second type of stations, maintaining a voltage of more than 1000 V, is used to serve certain areas and even cities. Most often, these are installations that implement transformative-distributive tasks. An equally important characteristic is the power, which varies in the range of 3-6 GW. This indicator largely depends on the type of fuel that is burned in the combustion chamber. Today, the rules for the operation of thermal power plants allow the use of diesel, fuel oil, natural gas, as well as traditional solid fuel cells.
Organization of heat networks
Most power plants are, to one degree or another,heating network infrastructure facilities. If, during the distribution of electrical energy, similar networks are formed by high-voltage lines, then in this case, the technical basis of communication is thermal pipelines that provide hot water supply. Each line is equipped with shut-off valves of appropriate size with gate valves and means of controlling the coolant. At the same time, thermal power plants can be interfaced with the same electrical networks. Thus, a combined network infrastructure is formed, in which distribution is carried out both through the heat supply channel and through the power transmission line.

In addition, the organization of the work of steam pipelines, which are part of the structure of thermal channels, is also practiced. In such cases, the operation of thermal power plants and heating networks involves the installation of more efficient condensate removal systems. Also, with a certain step along the entire laying line, devices for starting the drainage of the steam wire are installed.
Tasks of maintenance personnel
The list of functions performed by employees operating power plants can be divided into several groups. The basic tasks include the technical maintenance of equipment, which involves the control of operating parameters in accordance with design requirements. The next group of functions is due to security requirements. This applies to maintaining fire protection standards, compliance with labor protection standards, etc. In addition, thermalpower plants need regular preventive maintenance. This category of functions includes diagnostic and repair actions. The personnel must audit the components of the power plant, test it for compliance with technical and operational indicators, etc. Based on the results of the work done, documentation is formed in which acts of repair work, diagnostics, as well as accidents and accidents are recorded.
Admission of power plants for operation

The power plant is introduced into the infrastructure of the heat network after the completion of the admission measures. To assess the quality of equipment operation and check it for compliance with technical regulations, acceptance tests are carried out. Depending on the operating conditions, a test project is developed for thermal power plants. The admission rules require that this list of works, together with commissioning operations, be carried out by the contractor responsible for the design schemes of the specific heating network into which the facility is integrated.
Special attention deserves the process of technical organization of tests. At this stage, tools, protective equipment, spare components, fuel and other consumables are prepared. Also, the rules for the operation of thermal power plants require that the customer himself perform a comprehensive testing of the equipment before completing the acceptance certificate. This is necessary to check the already joint operation of the units and assemblies of the station in conjunction with an additionalequipment under load.
Equipment maintenance

Maintaining installations in good technical condition is the most responsible task of the staff. Specialists check the quality of functioning of individual parts of the station and its overall performance. Both the electronic filling and the mechanics with the body are tested. The integrity of the materials from which the parts of the power unit and the body are made is also evaluated. In accordance with the standards, the technical operation of thermal power plants is carried out with periodic monitoring of metals by non-destructive methods. That is, troubleshooting is carried out with devices that do not change the structure of the material, but make it possible to identify possible centers of destruction and deformation.
Installation control automation systems
Power plant management is gradually moving from traditional mechanical methods to automation systems. With the help of the controller, the operator can maintain optimal performance of all functional units of the power plant without leaving the control room. In this case, the operation of thermal power plants is closely associated with the function of sensors that record certain data about the operation of the station, sending information to the control panel. Based on this information, the system makes decisions about the correction of operating parameters.

Fuel facilities service
The power plant is notcan be considered as an autonomous object of electricity generation. Its function is provided by consumable fuel, which also requires maintenance measures. In particular, the fuel economy involves the organization of storage of products of future combustion. Modern rules for the technical operation of thermal power plants require that service companies maintain special storage facilities for such needs. Each such storage point provides equipment for loading and unloading fuel materials, their weighing, stacking and sorting.
Conclusion

The operation of power plants is necessarily focused on achieving optimal performance indicators. This is achieved by increasing the efficiency of working personnel, introducing new control systems and modernizing power units. However, thermal power plants do not always justify themselves financially. This is especially true for stations that have undergone a technological upgrade. Along with an increase in management efficiency, such facilities are generally more costly. For this reason, many operating companies strive to preserve the traditional principles of control and management of power plants.
Recommended:
Thermal imaging control of electrical equipment: concept, principle of operation, types and classification of thermal imagers, features of application and verification
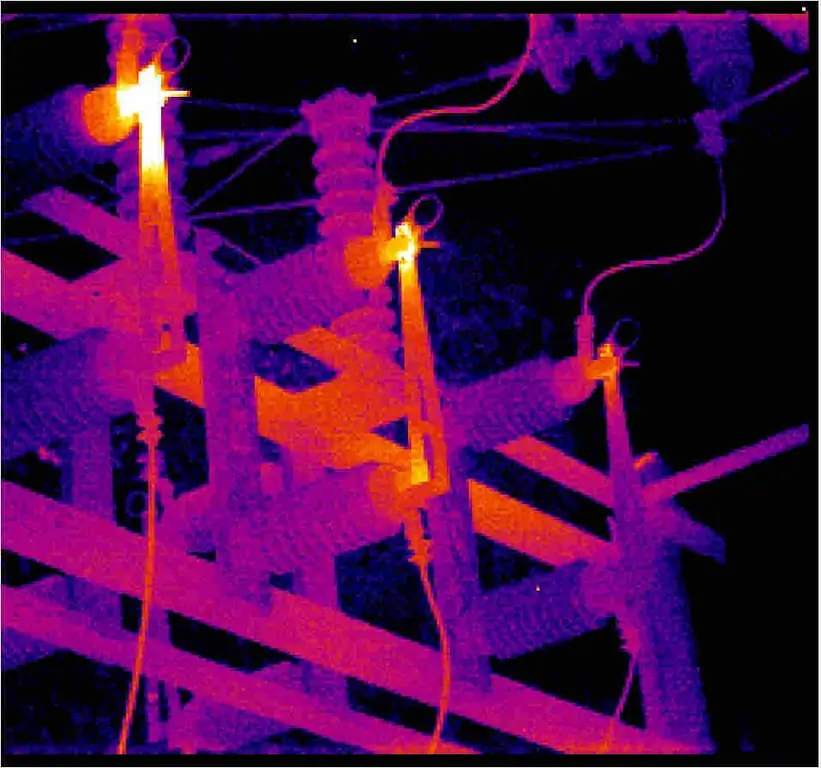
Thermal imaging control of electrical equipment is an effective way to identify defects in power equipment that are detected without shutting down the electrical installation. In places of poor contact, the temperature rises, which is the basis of the methodology
Nuclear power plants. Nuclear power plants of Ukraine. Nuclear power plants in Russia

Modern energy needs of mankind are growing at a gigantic pace. Its consumption for lighting cities, for industrial and other needs of the national economy is increasing. Accordingly, more and more soot from burning coal and fuel oil is emitted into the atmosphere, and the greenhouse effect increases. In addition, there has been more and more talk in recent years about the introduction of electric vehicles, which will also contribute to the increase in electricity consumption
Thermal conductivity of sandwich panels: concept, main characteristics, dimensions, thickness, thermal conductivity coefficient, installation rules, pros and cons of operation
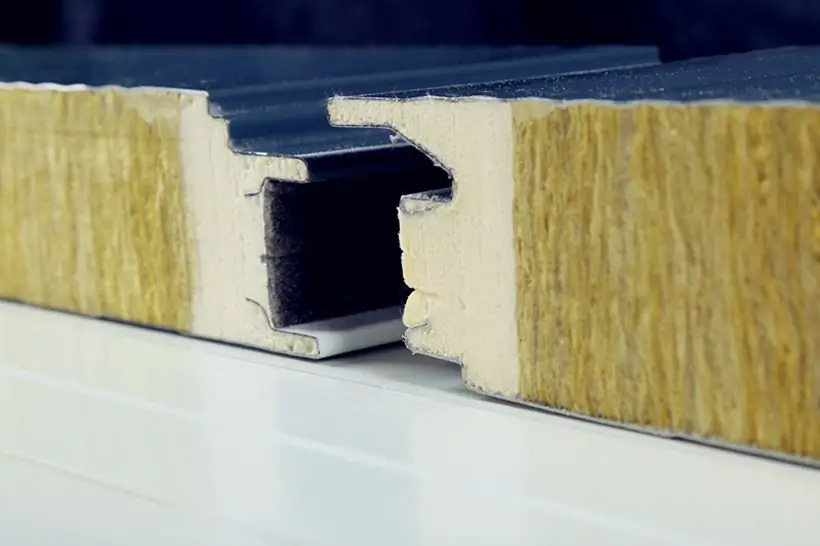
Thermal conductivity of sandwich panels will be the lowest if polyurethane foam is the basis. The parameter under consideration here varies from 0.019 to 0.25. The material is strong, dense and light. It is chemically resistant and does not absorb moisture. Rodents are indifferent to polyurethane foam, fungi and mold do not develop inside it. Working temperature reaches +160 ˚С
The largest power plants in Russia: list, types and features. Geothermal power plants in Russia
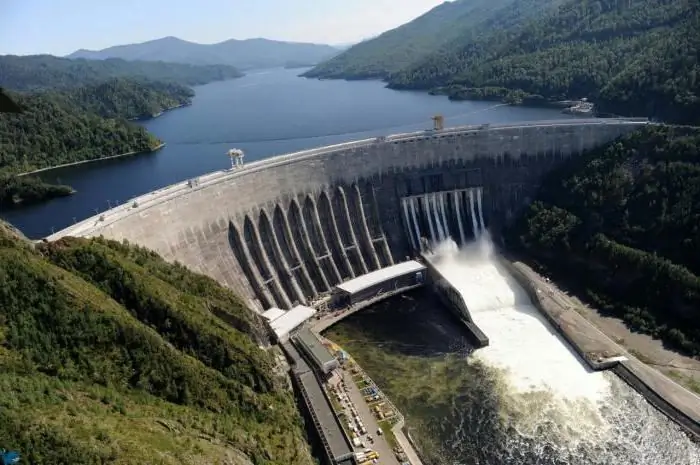

Russia's power plants are scattered in most cities. Their total capacity is enough to provide energy for the entire country
Gas piston power plant: the principle of operation. Operation and maintenance of gas piston power plants
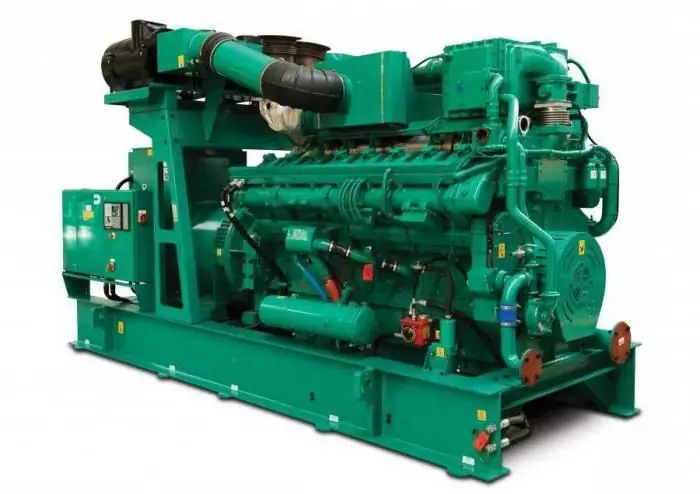

Gas piston power plant is used as a main or backup source of energy. The device requires access to any type of combustible gas to operate. Many GPES models can additionally generate heat for heating and cold for ventilation systems, warehouses, industrial facilities

