2026 Author: Howard Calhoun | calhoun@techconfronts.com. Last modified: 2025-06-01 07:12:56
One of the most common metalworking operations is cutting. It is a technological process during which a sheet or billet is divided into parts of the desired format. Modern types of metal cutting allow this operation to be performed with high accuracy and a minimum amount of scrap.
Manual Mechanical Cutting Methods
Still the most accessible and common approach to cutting metal blanks is the use of hand tools. Both in the domestic sphere and in construction, various kinds of carvers, guillotines, and sometimes grinders are used. Disc cutters on the frame effectively cope with strips of metal, and with pipes, as well as with fittings. It is enough to firmly fix the cutter platform to the floor surface and use the handle to perform work. Especially for the processing of sheet metal, a machine guillotine is used. Its principle of operation is generally similar to the cutter - the master is required to perform similar manipulations, but the mechanics of the impact on the workpiece itselfdiffers due to the design of the cutting part.
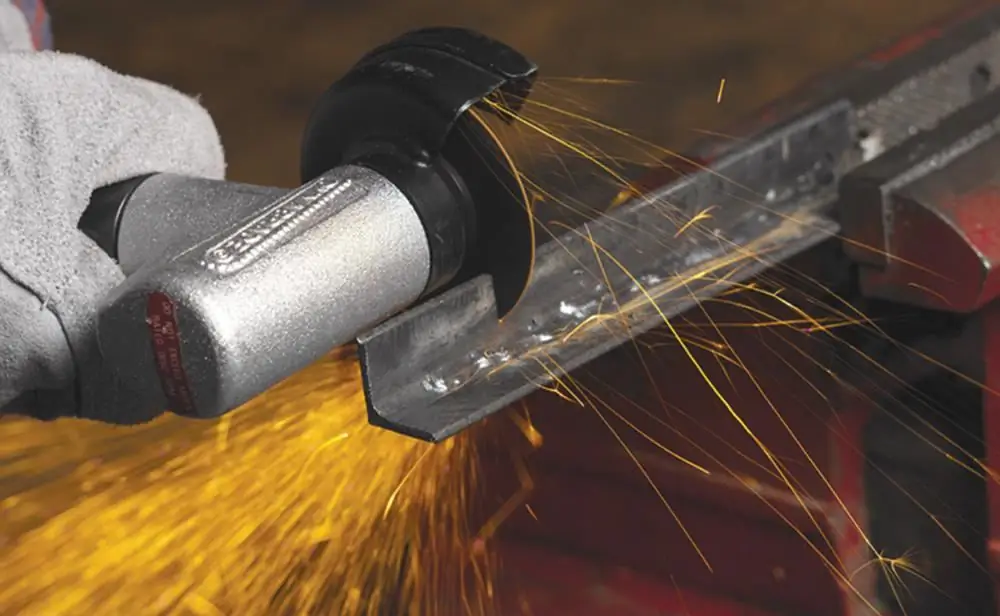

Manual types of mechanical metal cutting with the use of electrical stuffing are rarely used due to the low level of security. These methods include the already mentioned angle grinder (angle grinder) and a circular saw, which will require special discs. Both options, subject to safety rules, can be used in cases of cross-sections, when processing pipes, angles and channel bars. But to achieve high quality in both cases will not work.
Industrial mechanical cutting
At the level of professional in-line processing within production, of course, manual cutting methods are not used. Today, metalworking enterprises widely use band saw installations, consisting of a body with a supporting part, a high-power electric motor up to 1-1.5 kW and a band saw, which is mounted on pulleys. The average cutting speed on such a machine reaches 100 mm / min while maintaining high edge processing accuracy. Moreover, the latest mechanical types of metal cutting actively involve electronic means of automation and programming of operations. This provides a more detailed setting of working parameters, makes it possible to simulate cutting parameters, process the same edges and form a figured cut according to computer graphic templates.
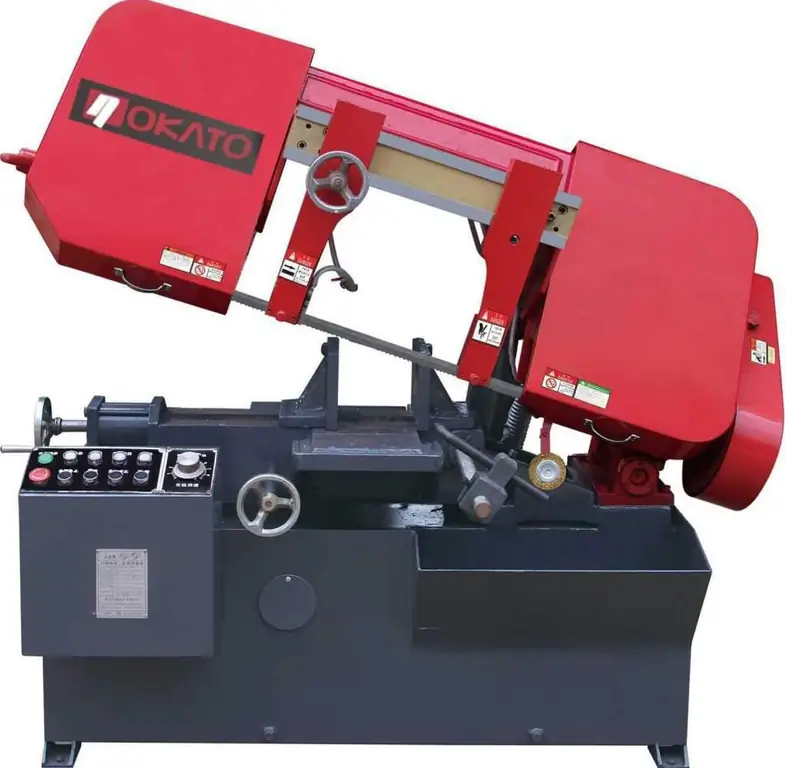

Industrial metal impact cutting
The method is implemented with guillotine type equipment, but not in the manual above mentionedversion, but with electromechanical, hydraulic and pneumatic drive systems. The operator is only required to lay the workpiece (usually sheet) on the desktop and fix it with clamping guide elements. Next, the worker presses the button through the remote control or control panel, after which a special knife hits the technological hole, cutting through the laid part. The principle of force action is determined by the drive used. The guillotine type of metal cutting with hydraulics, for example, is considered the most powerful, allowing you to accurately cope with 6 mm sheets. In electromechanical models, the emphasis is on the implementation of automatic feeding of workpieces, which has a positive effect on productivity.
Plasma Cutting Technology
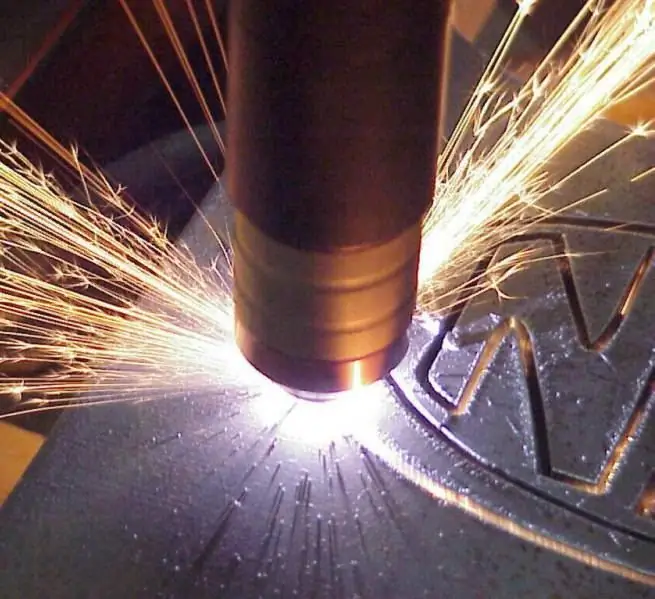
This group of metal processing methods involves the use of a high-temperature plasma jet formed by gas mixtures. The technology has been used for several decades, but only in recent years has it been possible to achieve tangible optimization in terms of the organization of the process, saving performers from the need to use gas cylinders and large equipment.
Modern types of plasma metal cutting involve the use of compact and ergonomic plasma cutters that generate a high-temperature electric arc. Under the influence of flows of ionized gas, a metal melt is formed. The method is quite effective, but requires high power to maintain temperatures of the order of 20,000-25,000 °C. Under these conditions, one can calculatefor the following cutting thicknesses:
- Alloyed and carbon steel alloys - up to 50 mm.
- Copper - up to 80 mm.
- Cast iron - up to 90 mm.
- Aluminum - up to 120 mm.
As experts note, plasma cutters justify themselves with high-precision processing of workpieces up to 100 mm thick. Thicker products are more appropriate to cut in other ways, which will be discussed below.

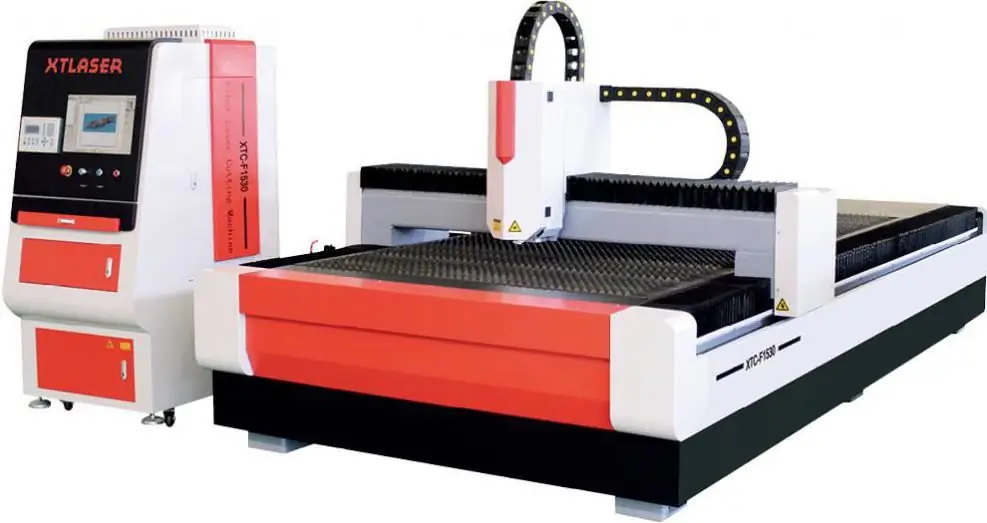
Laser Cutting Technology
One of the high precision cutting methods that also allows for engraving. To date, the following types of lasers for metal cutting are used:
- Universal. Can cut other than metal, plastic, wood and composite materials.
- Fiber. The laser is generated by a fiber optic filling that provides high cutting speed with minimal material loss. By the way, the cutting line width can be up to 0.1 mm.
- CNC models. The regulatory basis is based on numerical control.
- Industrial models. They focus not so much on the quality of cutting, but on power and productivity. Such devices can process up to 10 tons of blanks per day.
One of the few drawbacks of all types of laser cutters is the restrictions on use in relation to certain types of metals. This primarily applies to titanium and aluminium, but some of the higher alloys may be excluded depending on performance.

Thermal metal cutting
A rather extensive group of methods that are widely used in industries, in construction and in the household. The most effective types of thermal cutting of metal are based on a combination of the principles of laser and plasma processing. The emphasis is on a balanced combination of thermal power and optical accuracy. The technology is implemented by thermal cutting machines, which, depending on the functionality, can also perform cutting and engraving operations, chamfering and end processing.
Oxyfuel metal cutting
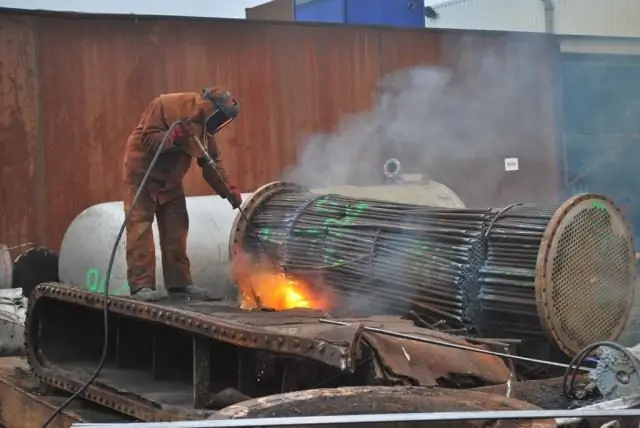

The method is based on the high-temperature effect of essentially a welding arc, which is formed during the combustion of an oxy-gas mixture. Unlike conventional gas, thermal and plasma processing methods, this method requires preheating of the part, and only then the oxy-fuel jet enters the business, accurately forming a cut line on the target surface. The quality of the work will largely depend on which tool is used. At the moment, there are several signs of the separation of torches for oxygen cutting of metal by type:
- Destination - for manual or automatic cutting.
- Fuel type - acetylene, substitute gases or liquid fuels.
- Cut type - separation, surface, flux.
- The principle of action - non-injector or injector.
- Oxygen pressure level is highor low.
- Mouthpiece type - multi-nozzle or slotted.
Waterjet metal cutting
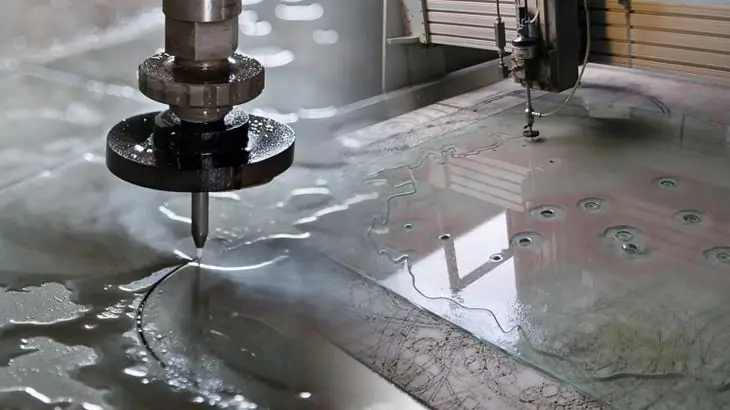

A very technological and productive method of processing various materials, thanks to which metal blanks can be cut with a thickness of about 300 mm. The main means of influence in this case is a water jet supplied under high pressure at a level of 6000 bar. For its supply, diamond, ruby and sapphire nozzles are used, with an outlet diameter of up to 0.1 mm. Almost all types of metal cutting in this way involve the admixture of sand abrasive particles (usually garnet sand). There are also techniques using fine metal sand that can be reused. As for productivity, according to average estimates, waterjet machines provide cutting of metal with a thickness of 100 mm at a speed of about 20 mm / min.
Conclusion

Cutting metal with certain parameters may be required by both construction or manufacturing enterprises, as well as an ordinary private trader. It is also possible to solve such problems in different ways, but it is far from always possible to use specialized equipment. Therefore, there is a separate type of activity - metal cutting with the possibility of additional processing. Prices for such services are on average 500-700 rubles/m with a workpiece thickness of 70 to 100 mm. You can manage on your own if we are talking about small volumes and there isgrinder or mechanical cutter. At least such equipment is quite affordable for the same home master.
Recommended:
Oxyfuel cutting of metal: technology, necessary equipment, safety precautions
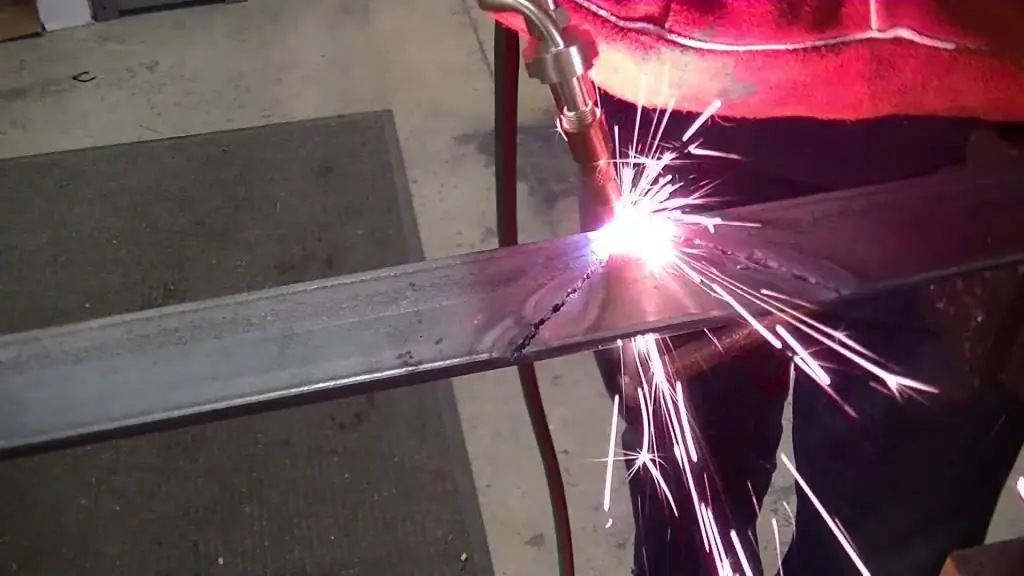

Oxy-fuel cutting of metals (in the literature you can find the term "oxy-fuel cutting") is actively used in industry for cutting sheet material from steel and other alloys into workpieces of the required length. The article contains information about the technology itself, about the necessary equipment and basic safety precautions for oxygen cutting of metals and other materials
Metal cutting: methods, equipment and tools
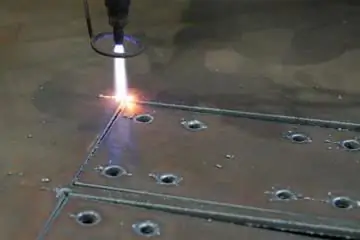
Metal cutting is performed in order for the workpiece to acquire the desired shape. To this end, it is necessary to remove the excess. Such manipulation is carried out through the use of different cutting tools on special machines. In mechanical engineering, metal cutting is very important. Indeed, without this process, neither ordinary machines nor other devices can be made
Sheet metal cutting: description, types. metal bending
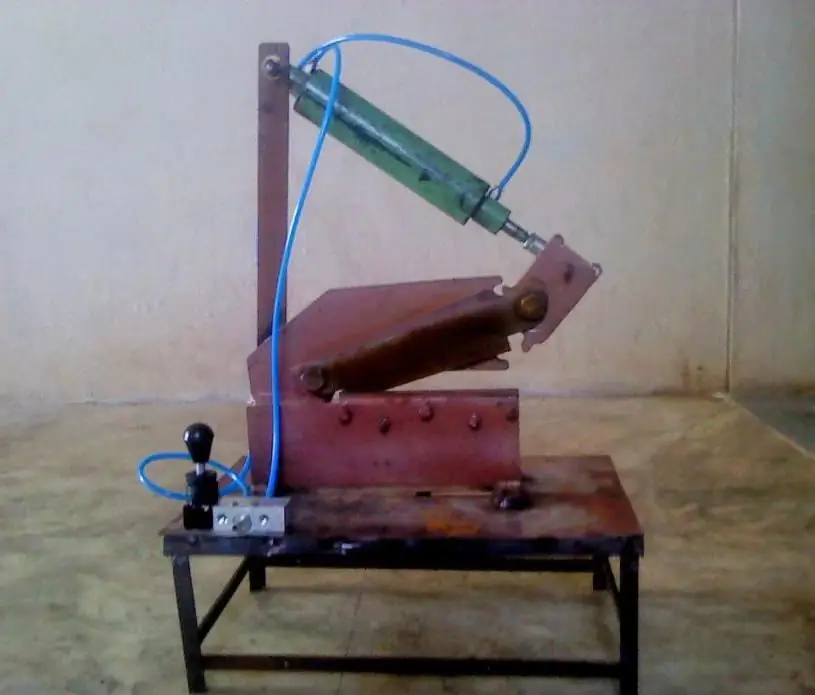

Today, sheet metal cutting is one of the fairly common technological processes that allows you to get blanks of the desired size and shape. However, there are many methods for performing this procedure and a wide variety of equipment
Cutting mode for milling. Types of cutters, calculation of cutting speed
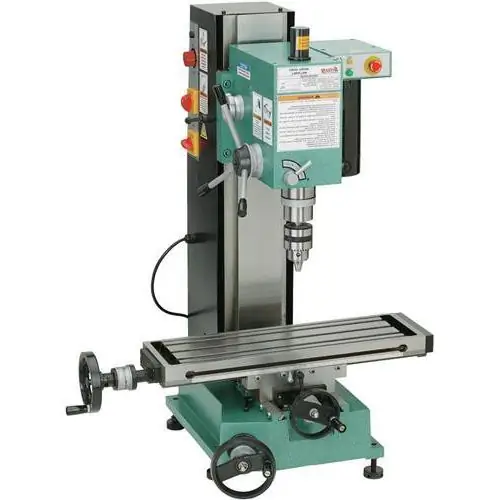

One of the ways to finish materials is milling. It is used for processing metal and non-metal workpieces. The workflow is controlled by cutting data
Metal cutting machine. Plasma metal cutting machine
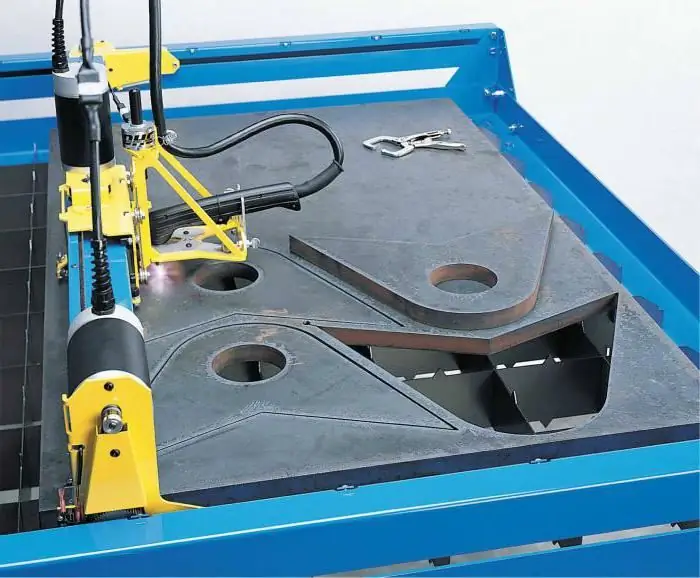
The article is devoted to the apparatus for cutting metal. The technology of plasma cutting, as well as the device and features of the equipment are considered

