2026 Author: Howard Calhoun | calhoun@techconfronts.com. Last modified: 2025-06-01 07:12:56
Oxy-fuel cutting of metals (in the literature you can find the term "oxy-fuel cutting") is actively used in industry for cutting sheet material from steel and other alloys into workpieces of the required length. Also, this technology is used when carrying out a number of repair work and dismantling of structures. Its popularity is due to the relative simplicity and low cost of equipment, as well as a high degree of security. The article contains information about the technology itself, the necessary equipment and basic safety precautions for oxygen cutting of metals and other materials.

Technology Basics
Before cutting, it is recommended to heat the metal with a torch flame. This applies only to materials with a large cross section. Said flame appears due to the reaction of oxygen with gas. If this recommendation is neglected, then the metal will inevitably lead, there will bewarping. However, if the geometric shape of the cut pieces is not important, for example, when dismantling structures made of building steel, as well as when cutting thin-walled sheets, gas welding and oxygen cutting of metal without preheating of products is allowed.
High temperatures in the cutting zone are achieved by burning highly purified oxygen from a cylinder. Very high pressure metal tanks contain 99 to 99.8% oxygen. If oxygen of ordinary purity is used for heating (roughly speaking, atmospheric air), then high-purity oxygen is needed for effective oxygen cutting of metal.

Surface preparation
If the task is to cut a large object into transportable pieces that is to be disposed of, then surface preparation can be omitted. The cutter will cope with this task in the shortest possible time. Another thing is the production of new products. In this case, it is important to obtain a high-quality cut line, clean from scale and other unwanted inclusions. Oxy-fuel cutting of metal is preceded by a thorough cleaning of the material.
There are a large number of methods for removing pollution. The most popular of them are heating the surface with a gas flame and mechanical cleaning. The first way is the simplest. It allows you to effectively eliminate scale - the worst enemy of the gas welder. Its essence lies in the heating of the metal surface to critical temperatures. The second method is more expensive and requiresspecial equipment (sandblasting machines, scrapers, brushes, etc.) and skilled workers.

Requirements for materials
Oxy-flux cutting of metals can be subjected to far from all grades of steel and alloys. One of the main conditions are the melting point and the ignition temperature. For the normal course of the process, the first indicator must be significantly higher than the second. It is clear why: otherwise, the material will melt rather than burn, which will lead to the formation of streaks. The cut line will have an inaccurate appearance, often this makes it impossible to further process the part on machining machines as a result of the displacement of the bases. In addition, such a metal layer may have poor mechanical and physical properties.
Certain elements added as impurities to the composition of steels can have a negative impact on the oxy-propane metal cutting process. So steels are considered the most processed, the carbon content of which does not exceed 0.3%. The cutting speed does not decrease with increasing carbon content, however, the steel becomes prone to overheating, hardening of the surface layer and the formation of hardening cracks, which can serve as stress concentrators and lead to brittle fracture of the entire workpiece.

Hand cut
Oxyfuel metal cutting, depending on the degree of automation and mechanization, is divided into mechanized andmanual.
Manual welding is advisable to use in small-batch and single-piece production, as well as when carrying out work on the dismantling of structures and structures. Ideal for cutting blanks from pipes, removing sprues from castings, and so on.
Oxyfuel cutting equipment for metals and alloys is highly mobile, easy to operate and reliable. Thanks to these qualities, this technology is the most common both in industrial enterprises and in repair organizations.

Mechanization of the process
Over the past decades, robotics has developed very rapidly. Today, robots are used almost everywhere. And oxygen-arc cutting of metals is no exception. Nowadays, CNC cutting equipment is no longer a surprise. These machines can be equipped with multiple oxy-fuel cutting torches, greatly enhancing their already high performance. All leading foreign machine-building holdings and companies have long been actively introducing such equipment into their production chains, and domestic companies are trying to keep up. The level of mechanization of welding works is on average about 80%.

The essence of oxy-flux metal cutting
Traditional cutting is not suitable for all materials. For example, steel alloyed with chromium and nickel is difficult to cut. A similar problem occurs whencutting non-ferrous metals and cast irons.
Then oxygen-flux technology comes to the rescue. Its essence is as follows. Flux powder is fed into the cutting zone. This substance ignites and burns during cutting, releasing a large amount of heat, which makes it possible to melt refractory carbides, borides and metal oxides.
Oxy Flux Cutting Equipment
It can be said that for this type of metal cutting, ordinary standard equipment is used, additionally equipped with a flux supply device (the so-called flux feeder and an oxygen cutting torch for cutting metal with flux supply). The most common installations of this type are devices designed by the research institute Avtogenmash URHS. This equipment is designed for cutting steels with a high content of chromium and other alloying elements.
Such equipment can also be used for mechanized cutting by equipping the machine with a flux feeder.
Oxy-flux cutting techniques
Technique does not differ from traditional methods of classical oxygen cutting. The process itself can be carried out both manually and mechanized using assistive devices, robots and devices. It can also be both dividing and surface. Recommended for cutting and cutting steels with a high content of chromium and nickel (i.e. refractory steels).
Features of oxy-flux cutting of cast iron
When burning, flux releases a lot of heat. So much so that the so-called chilling of cast iron occurs. The essence of this phenomenon lies in the fact that carbon passes from a free state to a bound one. In other words, carbon atoms in a certain area form a chemical compound with metal atoms. This is accompanied by a deterioration in the mechanical properties of cast iron (hardness increases, it becomes more brittle). As a result of accelerated heating and cooling, cracks appear on the surface, which can cause the destruction of the product.
The problem can be solved by preheating the metal and regulating its cooling rate. Only a worker with high qualifications and extensive experience in carrying out such work can cope with such tasks.
Features of oxy-flux cutting of non-ferrous metals and alloys
Like cast iron, copper must be heated before cutting. Heating is carried out to a temperature of 800-900 degrees Celsius. Copper has a high thermal conductivity, so cutting without preheating will result in significant warpage, spatial distortion, and scrap.
Copper-based alloys with other elements (brass, bronze, etc.) also need to be heated. However, the preheating temperature should not exceed 500 degrees Celsius.
Advantages and cons of oxyfuel cutting technology
Compared to other alternative methods of cutting sheet material of different steel grades, this technology is excellent for cutting along curved lines, for cutting large diameter holes. Also, this method allows you to get blind holes.
The second, and very significant, advantage is the ease of use of the equipment. The gas cutter has a small mass, so that the welder can work with it for a long time without getting tired. This has a positive effect on performance.
Gas is a relatively affordable and cheap fuel. And this is the third benefit.
A very significant drawback of the technology is the explosiveness of the substances used. Therefore, violation of technological discipline is not allowed. Ignoring safety regulations can lead to serious consequences.
Rules of operation of the oxygen reducer for metal cutting
Before connecting the reducer, the worker must ensure that there is no contamination on the threaded surfaces. If there are any, it is necessary to treat contaminated surfaces with kerosene or solvent. Only after purging the system and removing all foreign particles and elements that can get into the gearbox and disrupt its operation, you can put on and fix the nut on the gearbox.
In the same way, other gearboxes are installed.
Gases are started by smoothly opening the cylinder valve. If no deviations from operation are observed, the valve can be opened completely. If the gearbox starts to heat up, make abnormal noise, you must immediately close the flywheel of the oxygen cylinder for metal cutting.

Safety during work
Afterpreparatory work, it is necessary to make sure that there are no gas leaks. This can be very dangerous. Only then can you light the cutter and adjust the flame.
If you need to make a short pause in the work (no more than two or three minutes), then just turn off the cutter valve. In the event that work is stopped for a long time, it is necessary to close the reducer and the valve of the gas cylinder.
Only workers who have passed all the necessary instructions are allowed to work on oxygen cutting of metal.
It is forbidden to carry out any work near explosive tanks and flammable materials. If work is carried out in small enclosed spaces, then workers should take regular rest and breathe fresh air.
Welding work in production that is carried out systematically (not temporary) should be carried out in specially equipped rooms. At the same time, the area of \u200b\u200bone workplace is not less than four square meters. Passages between workplaces should be at least 0.8 meters.
The premises must be equipped with a powerful exhaust of harmful substances. Its capacity should be 2500-3000 m3 per 1 m3 of flared gas.
In the event that more than ten workplaces of welders are equipped in one room (workshop), gas should be supplied to them not from cylinders, but centrally from a gas distribution station. It is allowed to supply gases from existing gas pipelines.
Cylinders with working gas may only be transported with protective caps. They areprevent the valve from damage and contamination. It is forbidden to transport cylinders over long distances by hand. For these purposes, you need to use special devices and trolleys. Cylinders hitting the ground or each other is not allowed.
In an oxygen cylinder for cutting metal, in case of violation of technology and work order, an explosive mixture of gas and oxygen can form. Therefore, it is necessary to approach the adjustment of gearboxes with responsibility.
Recommended:
Safety precautions for a welder during work: standards, rules and instructions

Welder is not an easy profession, but very necessary and in demand. However, we all know that this type of activity is not the safest. Today we will look at the safety precautions that professionals must follow in order to avoid accidents while working
Vulcanizer presser: job description, safety precautions

What a vulcanizing presser does at an enterprise depends on his rank, qualifications, the focus of the company's work and other factors. This specialist processes rubber products using volcanic hydraulic presses. Employees with a low level are engaged in the preparation of equipment, laying and collecting forms. Masters with a higher category carry out the process itself, taking into account the regulations and indications of instrumentation
Smoking shop: preparation of necessary documents, drawing up a business plan, selection of necessary equipment, goals and stages of development

The article deals with such a business as a smoke shop. Learn how to start a business and where to start. About how to choose equipment and how it should be. About what you need to pay attention to when choosing suppliers, and about the process of producing smoked products
Busbar installation: technology, equipment, safety

The quality of laying power lines depends not only on the stability of equipment and communications, but also on the safety of personnel. Busbar trunkings help organize reliable and compliant wiring, the installation of which increases the design possibilities when laying cables, and also provides a high degree of physical protection from external threats
Metal cutting machine. Plasma metal cutting machine
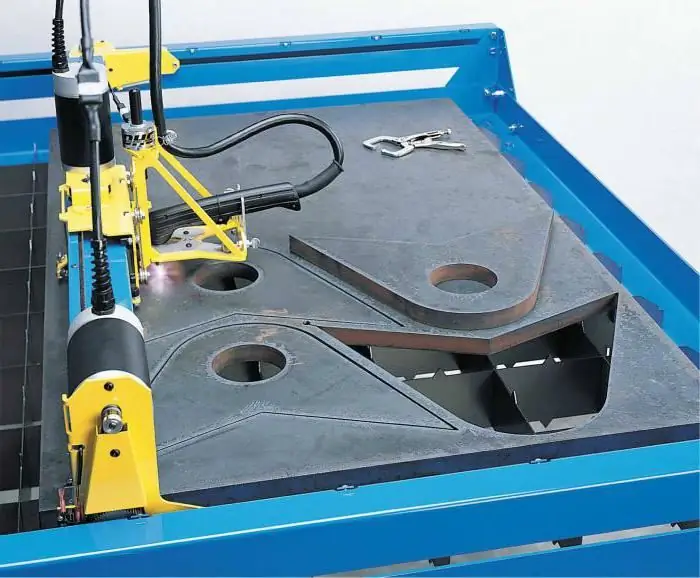
The article is devoted to the apparatus for cutting metal. The technology of plasma cutting, as well as the device and features of the equipment are considered

