2026 Author: Howard Calhoun | calhoun@techconfronts.com. Last modified: 2025-01-24 13:10:28
Situations often arise when, due to production needs, an employee is forced to use his property. Most often it is about the use of the machine. Moreover, the employer is obliged to compensate for this: pay for fuel and lubricants (POL), depreciation and other costs. How to make it as efficient as possible?
Legislative Framework
Not many people even understand what the payment of fuel and lubricants and compensation for the use of personal transport means. And employers are taking advantage of this. Although their obligation to compensate the employee for the costs is enshrined in Article 188 of the Labor Code. However, as will be seen below, its use is not the best option. Much more useful information is contained in the Civil and Tax Codes. To take advantage of all the benefits they provide, you need to approach the issue correctly.
How does it work in practice?
Often an employee is given a choice: either you go 300 km to another city in the heat on a bus,or drive your own car. It never occurs to him that the expenses for paying for fuel and lubricants and not only can and should be compensated to him. Enterprises take advantage of the legal illiteracy of employees. Most do not know what fuel at work and cost compensation are.

By the way, this applies not only to the car, but also to any other personal property that the employee uses in the performance of his official duties. Just personal transport is used most often. Accordingly, the payment of fuel and lubricants to employees at the expense of the employer is the norm. Although not all employers agree to pay.
Couple of examples
Everyone who has ever tried to work as a sales representative has experienced this. Another example where employees most often use their own transport is taxis. To receive compensation, the employee must use a car or other property only with the knowledge and permission of management. And everything must be documented.
Payment for fuel and lubricants to employees - what is it?
Often, even accounting staff do not know the answer to this question, let alone ordinary employees. Many people think that fuel and lubricants are only fuel: gasoline or diesel fuel. This is not entirely true. In fact, many more things are referred to as fuels and lubricants (fuels and lubricants):
- butter;
- antifreeze - in winter;
- other necessary consumables.
Accordingly, the payment for fuel and lubricants includes not only the cost of fuel.
How to make it official?
There are 3 waysformalize your agreements with the employer:
- additional agreement to the employment contract;
- car rental agreement;
- contract for the provision of transport services.
Each of them has its pros and cons. Let's look at them in detail below.
Additional agreement to the employment contract
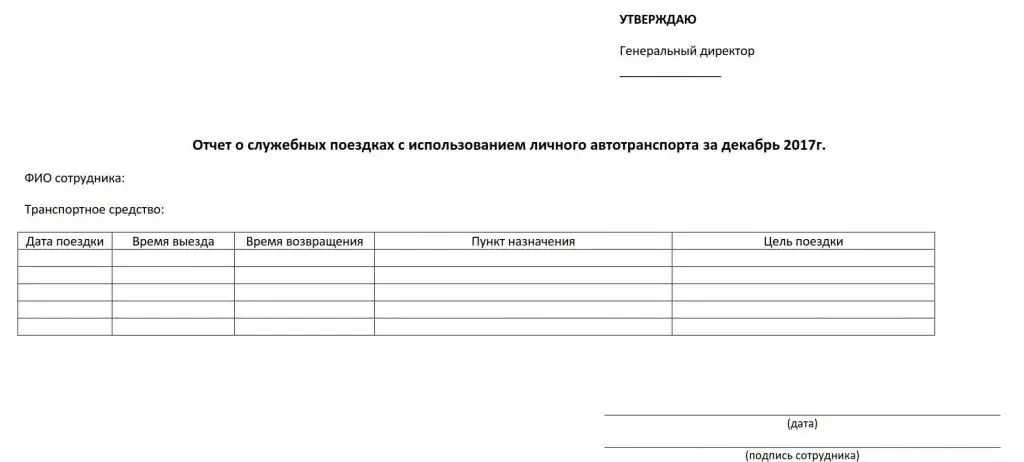
The simplest thing is to conclude an additional agreement with the employer to the employment contract. However, simpler does not mean more efficient: it will not be easy for employees to receive payment for fuel and lubricants at the expense of the employer. Below is an example of such an agreement.

It should be clearly stated:
- brand and characteristics of the vehicle;
- the amount of monthly compensation and the costs that the employer also compensates: payment for fuel and lubricants, current and major repairs, diagnostics and maintenance, insurance;
- deadline by which the actual cost report must be submitted;
- terms within which the employer compensates the employee's expenses.
The employee must often travel on instructions from the management, or the traveling nature of the work provides for the performance of his official duties. Indeed, according to the law, payment for fuel and lubricants when using personal vehicles, as well as compensation for other expenses, is possible only if there is a production need.

Every month, the employee submits a report on his trips, where he indicates:
- travel date;
- departure timeand return;
- destination;
- purpose of trip.
In addition, this document must contain the date of compilation and the signature of the employee.
Pros and cons of an additional agreement
Compensation of the employee's expenses under an employment contract is beneficial primarily to the employer. After all, you can always limit it to the size provided for by Government Decree No. 92 of February 8, 2002: 1200 rubles - for cars with an engine capacity of less than 2000 cm3 and 1500 rubles - for cars with an engine capacity of more than 2000 cm3.
However, such compensation is unlikely to suit the employee - at current gasoline prices, it is almost impossible to meet it. Accordingly, the employer has to compromise and enter into a lease agreement or a contract for the provision of transport services, or pay out of his own pocket - it will not be possible to offset compensation through tax cuts.
How to rent a car?
In this case, the relationship between the parties will be governed by the Civil Code. In practice, bareboat rentals are more commonly used. Below you can see a typical contract.

It is mandatory to specify in the lease agreement:
- car characteristics: brand, year of manufacture, color, body and engine number, state number;
- sublease conditions - it is desirable to prohibit the employer from renting the car to someone else;
- other arrangements - who and in what time frame carries out MOT, who paysconsumables and maintenance, for what purposes the car can be used - for example, only passenger transportation.

When concluding a rental agreement, you need to understand that you are thereby transferring your car to the company, albeit temporarily, but for use. Whereas under an employment contract, only you can use the car.

Therefore, the lease agreement must stipulate exactly how the employer can use your car. Otherwise, do not be surprised that you will be forced to transport various goods or some kind of garbage - after all, the company now owns the car, albeit temporarily.

Important: be sure to fix the cost of the car at the time of rental in the contract.
Often there is a problem with the fact that the parties do not know how to prescribe the payment for fuel and lubricants in the lease agreement. Even lawyers argue about this. Calculation of payment for fuel and lubricants is carried out on the basis of waybills - according to the actual mileage. For this, there are special rules, on the basis of which the write-off is carried out.
Experts still recommend concluding a car rental agreement with payment for fuel and lubricants. However, this is by agreement. If the lease does not provide for payment for fuel, a separate agreement for payment for fuel and lubricants is concluded with the supplier, and the driver is issued a fuel card with a certain limit.
It is also important to specify other nuances in advance: does the company pay you a fixed amount every monthor payment is hourly - depending on the actual hours worked, who and how pays for insurance.
Contract for the provision of transport services
Used much less often - mainly if goods are transported by personal transport. Imagine a moving company. Instead of acquiring or leasing a car, she could have entered into a contract with a loader who owns the desired car for the provision of transportation services.
Thus, the loader would perform his immediate duties (loading and unloading) under the employment contract. And he would privately provide services for the transportation of these goods from point A to point B. However, for this he would have to issue an IP, because entrepreneurial activity is prohibited in the Russian Federation without registration.
How can a car owner optimize taxes?
To rent a car or provide transport services, an employee will need to issue an IP. Strictly speaking, he can rent out his car without being an entrepreneur. However, if there are several such cars, then you still have to issue an IP. In addition, in this case, he pays less tax - 6% on simplified taxation income, instead of 13% personal income tax. However, personal income tax of 13% will still be withheld from his official salary.
There is another important nuance here. Regardless of the performance of the individual entrepreneur, he must pay insurance premiums, even if he does not have employees. The amount is fixed and in 2018 is 32,385 rubles. However, if the income of an individual entrepreneur exceeds 300,000 rubles per year, thenadditional payment of 1% of the difference "income minus 300,000 rubles".
However, the amount of insurance premiums cannot exceed a certain amount. In 2018, this is 212,360 rubles to the pension fund (this money “does not disappear”, but goes to the formation of the future pension of the entrepreneur) and 5,840 rubles in the form of contributions to he alth insurance. In aggregate, insurance premiums for individual entrepreneurs cannot exceed 218,200 rubles per year.
At first glance, insurance premiums are unnecessary extra costs. But is it really so? Not really. The fact is that individual entrepreneurs have the right to reduce the advance payment under the simplified tax system "Income" by the amount of insurance premiums paid. Thus, when renting a car, you can not pay tax at all (the amount of tax is unlikely to exceed the paid contributions), and it is completely legal. And the main part of the contributions paid goes to your future pension.
Important: the status of an individual entrepreneur and the simplified tax system does not exempt the entrepreneur from paying transport tax. It will have to be paid anyway. But property tax in this case does not need to be paid.
An example of how an individual entrepreneur increases income from renting a car
Let's imagine that Ivan rented his car to Romashka LLC, of which he is an employee, for 100,000 rubles a month. At the same time, the company takes care of the current and major repairs of the car, as well as payment for fuel and lubricants and other consumables.
Without registering an individual entrepreneur, an employee would receive only 1,044,000 rubles a year. The employer, acting as Ivan's tax agent, would independently withhold 13% of personal income tax from this amount. At the same time, having issued an IP on the simplified tax system"Income", Ivan would pay the following taxes:
- insurance contributions to the Pension Fund: 32385 + 1% × (100,000 × 12 - 300,000)=41385 rubles;
- he alth insurance contributions: 5840 rubles;
- USN 6%: 100,000 × 12 × 6% - 41385 - 5840=24775 rubles.
Accordingly, his net income was 100,000 × 12 - 41385 - 5840 - 24775=1,128,000 rubles. Moreover, 41,385 rubles would have gone to Ivan's future pension, and not to the state treasury. Thus, tax savings would amount to 125,385 rubles per year. Or a little more than 10,000 rubles a month.
Besides, in the first case, Ivan pays personal income tax immediately. In fact, he does not even see this money - the employer transfers the tax for him. In the second, Ivan receives the entire amount “in his hands”. And then he pays taxes. Moreover, he can distribute them as he pleases during the year - the main thing is to pay everything no later than December 31.
The ability to manage the timing of tax payments provides a significant advantage. Suppose Ivan decided to evenly distribute the tax burden and pay the due amount every quarter.
Thus he can additionally release the following amounts:
- January - 100,000 × 13%=13,000 rubles;
- February - 100,000 × 13% +13,000=26,000 rubles;
- March - 100,000 × 13% + 13,000 + 13,000=39,000 rubles.
Until the end of March, he can use this money as he sees fit. And only then pay the corresponding payment for insurance premiums, thereby reducing the advance payment under the simplified tax system "Income".
OnAt first glance it seems that the amounts are small. But if Ivan increases his income by 10 times - rent out several cars or choose leasing instead of renting, the savings will become impressive.
How can a business save on taxes?
If the company is on the DOS (general taxation system) or the simplified tax system "Income minus expenses" (one of the types of simplified taxation system), then the cost of renting a car, providing transport services or paying compensation under an employment contract can be taken into account to reduce the tax base. True, in the latter case, for cars, the deduction amount is limited by law.
In the case of renting a car on DOS, not only the rent is offset, but also:
- fuel and lubricants and other consumables;
- maintenance and overhaul of cars;
- Maintenance, washing, parking fees and car parking;
- insurance;
- driver wages.
Moreover, only documented expenses are recognized as deductible expenses. At the same time, they must be economically justified.
Important: the company is not the owner of the rented car, and therefore is not obliged to pay property and transport taxes.
Businesses usually make more money than car rental costs. Accordingly, by reducing income tax, it is possible to more than compensate for all actually incurred costs.
Summarize
Article 188 of the Labor Code obliges the employerCompensate the employee for the use of personal transport for official purposes. If such use is supposed to be occasional, it is enough just to conclude an appropriate supplementary agreement to the employment contract and submit the report on time.
However, if an employee without the use of personal transport cannot perform their duties and is forced to use their car for business purposes all the time, this compensation will not be able to cover most of the actual costs incurred. Is that only at the expense of the profits of the enterprise. The organization will be able to use such compensation to reduce income tax only in the amount established by law, which will not cover even a tenth of the actual costs.
Accordingly, this approach is not beneficial to either the employee or the company. And all because of the peculiarities of taxation: an employee, as an individual, pays too much personal income tax, and the company cannot optimize taxes properly. It is much more profitable for both parties to conclude a lease agreement or the provision of transport services (if other passengers or cargo are to be transported).
Only in this case, the employee will have to issue an IP - the procedure is not complicated and does not take much time. Some people think that, having become an individual entrepreneur, they will not be able to work on a labor basis as a private person. However, in fact it is possible - the law does not prohibit.
Recommended:
Calculation of average earnings upon dismissal: calculation procedure, rules and features of registration, accrual and payment

To get confidence in the correctness of all accounting calculations upon dismissal, you can easily do all the calculations yourself. The calculation of the average earnings upon dismissal is carried out according to a special formula, which, with all the features, is given and described in the article. Also in the material you can find examples of calculations for clarity
How the advance is calculated: calculation procedure, rules and features of registration, accrual and payment

The correctness and timeliness of payroll is a matter of interest not only to the accounting department, but also to the employee himself. There are different types of payments such as advance payment, vacation pay, compensation payments, and each of them has its own rules and approved benchmarks
Surcharge for traveling nature of work: calculation procedure, rules for registration, accrual and payment

At many enterprises, the work of certain categories of employees is traveling. First of all, we are talking about drivers transporting personnel, transporting products, materials and other goods. In the article we will talk about the additional payment for the traveling nature of the work, taxation and accounting of the allowance
Maternity allowance: how it is calculated, calculation procedure, rules and features of registration, accrual and payment

How is Maternity Benefit (M&B) calculated? Once every woman who plans to go on maternity leave has to face this question. In 2018, a lump sum payment to expectant mothers is provided for the period of preparation for the birth of a child and after its birth
How study leave is calculated: calculation procedure, rules and features of registration, accrual and payment

Studying leave is a type of additional leave, which is due to employees receiving their first education. It is calculated according to average earnings, according to general rules. Regulates payment and accrual of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation