2026 Author: Howard Calhoun | calhoun@techconfronts.com. Last modified: 2025-01-24 13:10:45
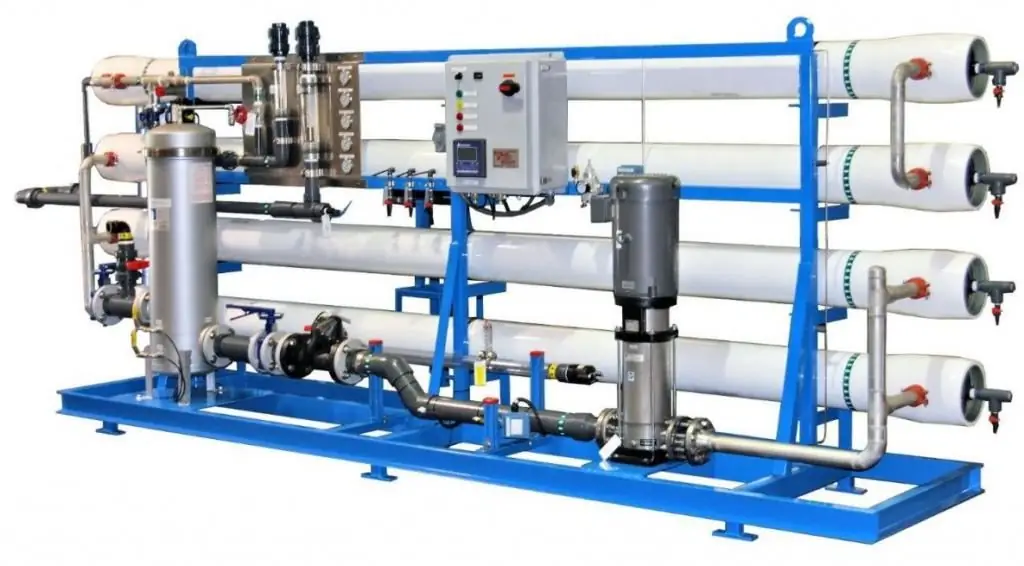
Industrial reverse osmosis plants are characterized by a high degree of water purification and low operating costs. The main element of the working module is a block of membranes through which fluid is passed. The excess pressure created contributes to the process of reverse osmosis - the flow of "solvent" (pure water) through the membrane. Unlike traditional chemical desalination, this technology is more environmentally friendly, as it does not require the use of aggressive reagents.
Destination

Industrial reverse osmosis plants are used to purify water from mineral s alts for the purpose of its further use in industrial, commercial and domestic purposes. This technology is very promising, as it allows you to remove very small particles from the liquid - up to 0.0001 microns (calcium and magnesium s alts that affect water hardness, sulfates, nitrates, dye molecules).
Water purification by this method is used inareas such as:
- reducing the amount of s alts in waters extracted from local aboveground (springs, rivers, lakes) and underground sources;
- desalination of sea (brackish) water;
- preparation of solutions for technological processes;
- water treatment of boiler houses and boiler plants;
- finishing wastewater treatment in a closed water circuit;
- disinfection of water for medical purposes;
- food industry - clarification, stabilization and concentration of juices, soft drinks and wines.
Most often, industrial reverse osmosis plants are part of two-stage purification systems. At the first stage, the liquid undergoes mechanical filtration, which removes larger particles.
Essence of technology
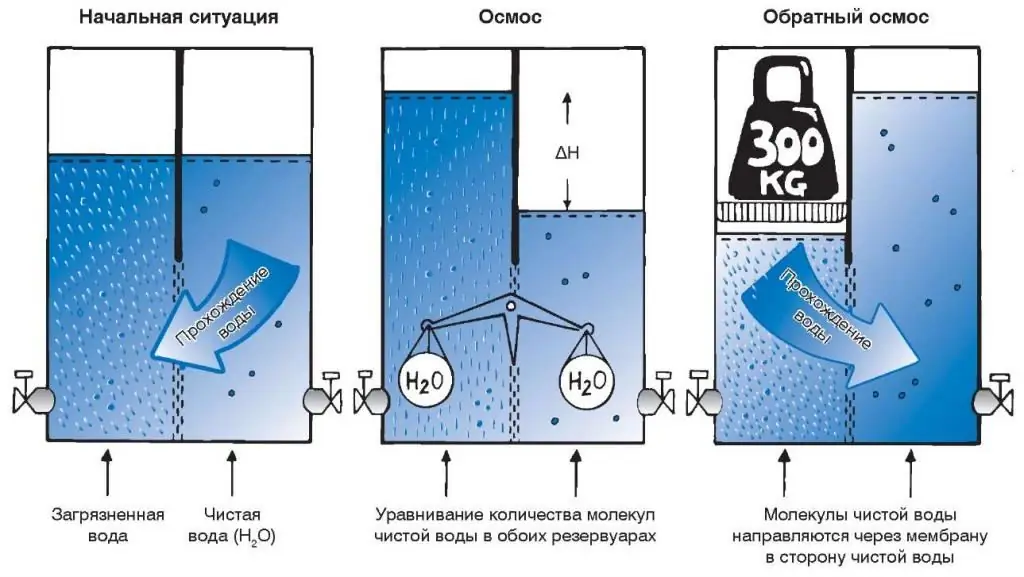
The principle of operation of the reverse osmosis plant is that the liquid to be purified is passed through semi-permeable membranes that completely or partially trap molecules. With direct osmosis, water flows towards the solution. If you apply pressure in the first composition above the equilibrium (osmotic) value, then the water will move in the opposite direction. This ensures the selectivity of cleaning.
The required pressure level in the reverse osmosis filter installation depends on the concentration of s alts (the higher it is, the higher the pressure). So, with a mineralization of 20-30 g/l, it is 5-10 MPa. Cleaning equipment can use its own pressureindustrial water supply systems or increased medium pressure (use of pumps). The type of membrane affects the degree of purity of water. When it becomes clogged, the system loses its effectiveness, so it is necessary to carry out maintenance of this unit in time.
Package
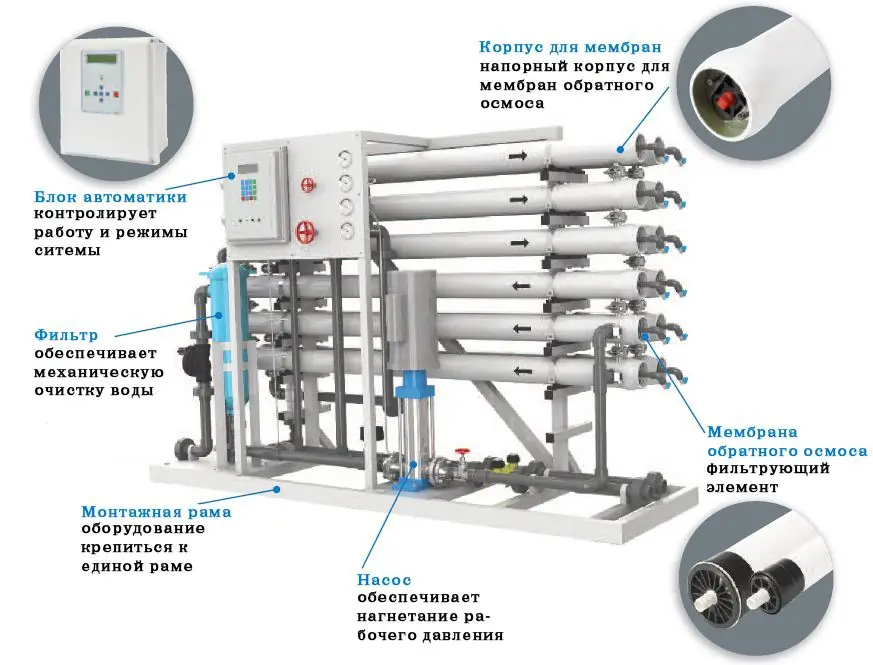
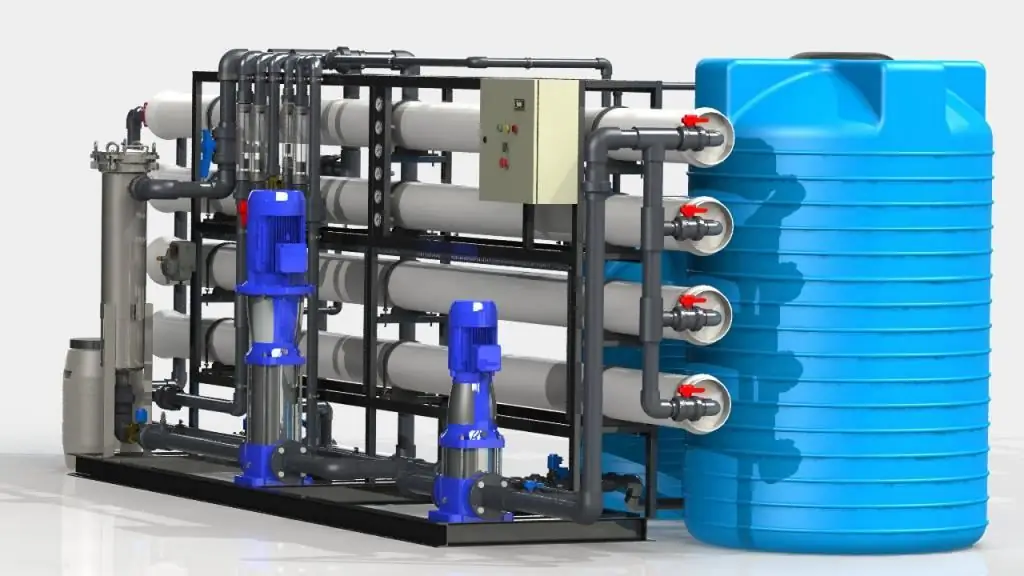
The main components of industrial reverse osmosis plants are:
- base (stand);
- prefine filter (water treatment equipment);
- membrane units (their number is determined based on the performance of one unit and the entire installation as a whole);
- high pressure pumps to provide the necessary differential pressure;
- piping with instrumentation and valves;
- flushing unit for membrane cleaning;
- electric control cabinet and controllers.
Modern units are modular in design, allowing for final assembly on site with selected specifications that can be modified if required. The main unit is pressure vessels with reverse osmosis membranes. Additionally, the installation of a reverse osmosis system can be equipped with the following types of equipment:
- water treatment system before osmotic treatment;
- capacity of pure or original liquid;
- dispatch system.
The equipment may also include a system for inhibitiondeposits of s alts (carbonates, sulfates and phosphates) on membranes, which includes a dosing pump for reagent supply, level sensors, valves and tubes. Installation of the reverse osmosis pump is carried out separately. It is mounted on the reagent tank using a bracket, after which the reagent intake line and the level sensor in the tank are mounted. This technological equipment allows you to extend the life of the membranes and reduce maintenance costs. Antiscalant (sedimentation inhibitor) is added to water at a concentration of 2-5 mg/L.

Recommended schemes
There are several layout options for industrial reverse osmosis plants, which are selected depending on the properties of the source water:
- Treatment of mineralized water coming from the well: coarse filter (CSF) - reverse osmosis unit (ROO).
- Purification of water with a high content of iron, suspensions, high color: CSF - mechanical backfill filters (through a layer of filter load) - sorption purification filters - UOO.
- High mineralization water treatment: CSF - ultrafiltration (water softening) - sorption purification filters - UOO.
Key Features
Installations vary in several key ways:
- Purity of the flow through the membrane (80-99, 8%).
- The pore size of the osmotic membrane (removal of heavy organic particles does not require the installation of ultra-fine membranes).
- Performance.
Types of membranemodules
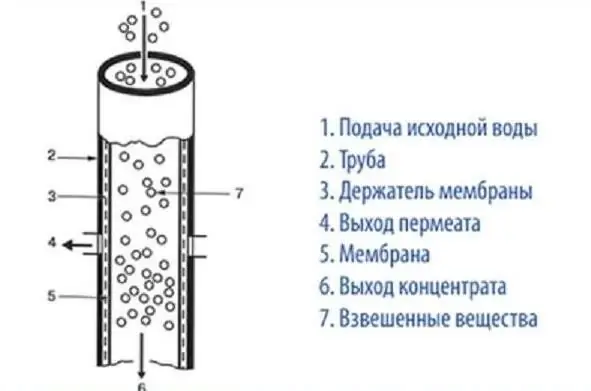
The following main types of membranes are distinguished by location and appearance:
- Tubular. The membrane is located along the inner cylindrical surface of the pipe, the flow of purified water exits through the side holes, and suspended particles settle down. The diameter of the tubes is most often in the range of 4-25 mm, they are placed in the housing in parallel or in series. The advantages of such a scheme are a high flow rate (up to 6 m/s), no need for preliminary fine filtration, and easy maintenance. Disadvantages include large dimensions and high processing costs.
- Fiber. Hollow fibers with a diameter of 0.6-2 mm are used. Water can flow both inside and outside. In some models, the fibers are fixed with a fabric mesh. These membrane modules withstand external and internal pressure and can be backflushed regularly. Fiber systems are mainly used for ultrafiltration, as the holes become clogged with large particles.
- Plate. The membranes are fixed in a holder plate, and the module itself is a cassette with a set of rectangular frames. They are easy to assemble and clean, but the tortuous and complex configuration of the block results in pressure drops and reduces the reliability of the equipment.
- Spiral. The membranes and receivers of purified water (permeate) are wrapped in several layers around the central collector tube. Such modules are the most compact in terms ofcompared to other types, but very sensitive to contamination.
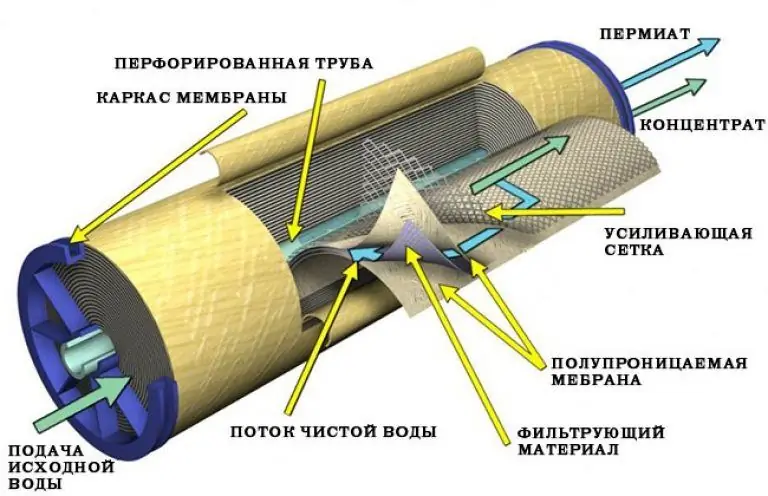
Flat membranes are most often made from cellulose acetate or polyamide films.
Operation principle
The working principle of an industrial reverse osmosis plant is as follows:
- Pre-cleaning in pre-filters.
- Water is supplied by a high-pressure pump to the membrane module, where it is divided into 2 streams - purified liquid and concentrate with a high salinity.
- Exit of purified water from the reverse osmosis unit, measuring its flow, collecting it in a container.
- Discharge of the concentrate into the sewer or directing it to the pump inlet (repeated treatment recycling).
In case of unacceptable increase in back pressure, a relay is activated, which turns off the installation. The same happens when the treated water collection tank (level switch) is filled. Membrane flush starts automatically.
Water preparation
Reverse osmosis membrane technology assumes the almost complete absence of mechanical impurities in the source liquid. Industrial water purification in this case is inefficient, since foreign particles get into it when transporting water through pipelines. Therefore, the reverse osmosis system must include pre-filters at the inlet to the membrane unit.
Such equipment is usually made in a universaldesign and consists of at least 3 types of filters: coarse and fine filters, as well as for collecting organic substances (sorption filters). Additional options are ultrafiltration, iron removal and clarification systems. Failure to use this unit causes the working membranes to quickly clog, reducing the efficiency of the reverse osmosis process.
Installation and commissioning
According to the installation instructions, reverse osmosis must be installed indoors. These units are not designed for outdoor use.
Installation work is carried out in the following order:
- reagent system installation;
- connection of pipelines for supplying raw water and receiving treated water;
- programming the controller (setting the maximum allowable value of electrical conductivity, water temperature, the duration of washing the membranes before the work cycle, the time interval between their cleaning and other parameters);
- Checking the operation in manual mode (opening the source water supply, the taps for the outlet of the purified liquid and concentrate, turning on the high pressure pump);
- transfer the unit to automatic mode.
Recommended:
Air-foam fire extinguishers. The principle of operation of the device and rules of use

Air-foam fire extinguisher device and its scope, instruction manual. Disadvantages of using a chemical foam fire extinguisher. Safety Precautions When Using a Foam Fire Extinguisher
Electric locomotive 2ES6: history of creation, description with photo, main characteristics, principle of operation, features of operation and repair

Today, communication between different cities, passenger transportation, delivery of goods is carried out in a variety of ways. One of these ways was the railroad. Electric locomotive 2ES6 is one of the types of transport that is currently actively used
Reverse osmosis water treatment plant

The article is devoted to reverse osmosis water treatment plants. The features of such models, reviews, cost, etc. are considered
Osmosis is What is reverse osmosis?

The article is devoted to osmosis - the filtration process, which results in water purification. The principles of operation and varieties of membrane filters operating on the principle of reverse osmosis are considered
Gas piston power plant: the principle of operation. Operation and maintenance of gas piston power plants

Gas piston power plant is used as a main or backup source of energy. The device requires access to any type of combustible gas to operate. Many GPES models can additionally generate heat for heating and cold for ventilation systems, warehouses, industrial facilities

