2026 Author: Howard Calhoun | calhoun@techconfronts.com. Last modified: 2025-01-24 13:10:47
The world has been dealing with a process approach to business organization for a long time and quite effectively, and the Business Process Model and Notation (BPMN, notation) standard is a thoughtful procedure with a correct description of business processes. Companies are constantly improving various specializations of this standard and thereby achieve a very significant increase in all quality indicators of their work. BPMN notation is understandable not only for experts of the subject area in which it was created, any worker can operate with its logical calculations.
Modeling and standardization
At the same time as being simple, this standardization is the most complete model of the described business process, compiled in a machine-readable form. BPMN (when viewed in the BPMN 2.0 version of the notation) builds models of the most complex processes in business in a very powerful and expressive way, and in the most understandable system. Most importantly, along with this standard,graphical models and are converted into a beautifully structured and machine-readable form that is based on XML. The BPMN notation language is absolutely executable, that is, it allows you to model processes that are subsequently performed using BPMS (automated business process management systems). Such standardization is extremely useful precisely because modelers can use some software products, and performers - others, if they support this standard.
To build a certain model, more than one version can be used (BPMN 2.0 notation (PDF) and others), sometimes a model is made up of fragments of different notations, but the way they are systematized and read is the same. An increasing number of entrepreneurs are implementing in their companies the execution of business processes based on this standard. The demand for specialists who know this modeling language is growing every day. An increasing number of people are studying the graphic elements of BPMN notation and the rules for building models. For this, there are special courses where those who wish will get acquainted with the purpose of this language, with the types of diagrams, and see the possibilities of automatically executing the constructed models. The most interesting is practical experience in BPMN 2.0 notation (also available in Russian), modeling and analysis, business process development.

Specialists
Who is capable of describing business processes? BPMN modeling notation is easily done by anyone involved in automation,development of business processes. These are business consultants, business analysts, project managers, system analysts, architects and developers of computer systems, methodologists, quality service workers. Usually these people are able to read technical documentation in English, participated in any analysis projects, described BPMN notation, optimized or automated business projects, or developed and maintained software. This methodology has an international status, and not a proprietary one, like many other standards, and not even a national one. That is why since 2005 they have been analyzing and reorganizing business using process modeling in BPMN notation.
This technique provided accessible information to almost all users - from the largest analysts who create diagrams and developers who implement technologies for executing business processes according to these diagrams, to company executives, that is, ordinary users who are busy managing and tracking execution of the constructed model. In this way, Business Process Modeling Notations (BPMN) bridge the gap between model creation and model implementation. Here are some of the best ideas from other methodologies. For example, for better flexibility and readability, business process modeling in BPMN 2.0 notation follows the flowchart tradition.
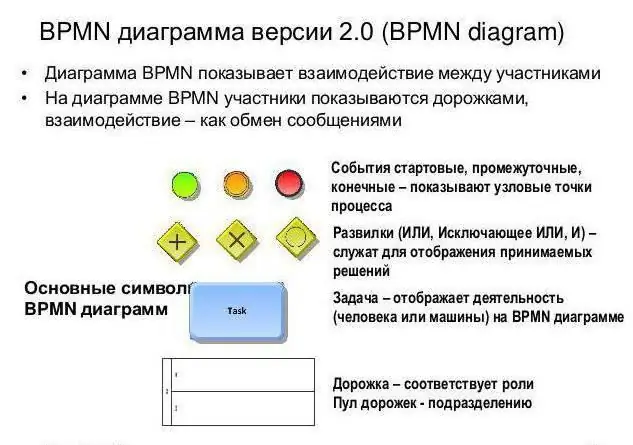
Symbols (elements) BPMN
Supports and develops BPMN organization OMG. This is not a meme of Internet regulars, meaning "oh mein goth", but a very famous firm Object ManagementGroup, which includes more than eight hundred companies that develop standards like BPMN notation. We owe all the useful changes in new versions to the OMG developers. It was this organization that chose the promotion of the UML BPMN notation, which is used to model object-oriented systems, as a key direction. Therefore, when developing diagrams, in addition to concepts and concepts (control flow, action, data object, etc.) in BPMN there are many concepts characteristic of the object-oriented approach: message, exchange and message flow.
Graphic notation symbols are parsed according to their purpose and combined into categories. These are: Flow Objects - flow objects, Data - data, Swimlanes - areas of responsibility, Connecting Objects - connecting objects, Artifacts - artifacts. The control flow, data object, and flow object symbols are additionally divided into subgroups according to semantic features in order to display the specifics of ongoing events, flow branching features, execution of actions, and so on. They indicate the specifics due to additional graphic images - markers, icons placed inside the main symbol. Also, event symbols come with a different type of outline and background color.
Events by time
During the execution of a business process, various and numerous events always occur that have their impact, despite the fact that most often they are optional elements and are not displayed in the business process diagram. This is receiving and responding to a message, changing status indocuments and much more that it makes no sense to list - a lot of events take place literally at every step. To classify them, the characteristics of each are determined. The first group - by the time of the onset. This is the start event that will show the beginning of the chart. From here, the control flow can only be outgoing, and the message flow can go both ways. The start event on the business process diagram is usually one, but you can not display it at all. Sometimes there are even several of them, if the mapping occurs with tracks, pools and deployed subprocesses. The outline of the event is shown as a thin single line.
The end event is the result of the execution of a business process. The flow of control only enters here, and the flow of messages still moves both to the input and to the output. The incoming stream is represented by an arrow. The diagram displays only one end event or several - they are outlined as a thick single line. An intermediate event is any of the others that occur during the execution of a business process. One stream enters here and one exits too. Only Boundary (boundary event) occurs and is processed immediately - either at the very beginning or at the end of the action. It is displayed on the contour (border) of the action, and contains only one stream - either incoming or outgoing. And such an event is indicated by a thin double line.
Events: subprocess interruption and result type
Since the events during the modeling of a business process are very different, the next block was classified those thatcapable of interrupting the action. The first to be marked are non-interrupting events - these are intermediate or start events that occur during execution, however, initiate the outgoing thread associated with it only when the activity is completed. The contour of such an event is depicted by a dashed line. Next is a interrupting event that occurs before or after the standard action. In exceptional situations, this event requires a stop or termination of the action if the necessary information is missing or an error is shown during processing, if additional actions are needed, and the like. Here the contour is shown as a solid line.
The third kind of events are classified according to the type of result. First of all, here we need to talk about the processing initiator. This is an intermediate or start event that occurs as a result of the execution of actions and is the result of the execution of a process - standard or not. The triggering event is represented by an unfilled icon. It is necessary to add one more event to this section, which also speaks of performance, only here it is the result of processing. This is an intermediate or final event that occurs during the execution of actions and is one of the final results of the execution of the process - standard or not, it is displayed as a filled icon.
Actions
Diagrammatically, a process looks like an ordered set of actions that are performed to obtain a certain result. On a BPMN notation vertical diagram, from top to bottom, a sequence is given showing the executionprocess over time. You can also trace it in the direction of the arrows of the connecting elements from left to right. The displayed actions have three main views and many varieties, each with its own icon or icon.
Task - a task. Elementary action, that is, indivisible. The type or specificity of the task is indicated by a marker or icon in the upper left corner of the action symbol. The task can be Service (service), for the provision of a service, which is an automated application or web service. Send - send a message. If the message is sent at least once, the task can be considered completed. Receive - receiving a message (the same principle: if a message is received once, the task is completed). The User's task is considered to be characteristic and is performed by the executor with the help of software and with the assistance of other employees. A task that requires manual execution is Manual, which is performed without the help of automation. Business-Rule - a business rule, according to the technology, the fulfillment of this task depends on the circumstances, the choice of a method helps to set a business rule. Script - a script where the execution of operations is strictly in the order described in a language recognized by the performer. Usually this kind of task is performed by automated means.
Subprocesses
Sub-Process - sub-process. It includes gateways in BPMN notation, workflows, events, and many other activities. Thus, a sub-process is a composite action, parts of which are directly displayed inside the symbol on the diagram or are placed onseparate decomposition diagram. In the latter case, the main diagram should show a + sign in the center of the sub-process (bottom edge of the activity). There are standard subprocesses, but they are not enough, so two specific varieties of it appeared. This is an Event Sub-Process - an event subprocess that always starts when a start event occurs. The diagram shows it in no way related to the rest of the activities and workflows. The outline of such a sub-process is depicted by dots.
The second type - Transaction (transaction), this is an action consisting of different operations with a successful completion, that is, obtaining a positive result. You can get a specific result only if all the components are successfully completed. If problems occur during the execution of the subprocess, the results of all previous operations will be canceled (cancel event). Such interference may be the impossibility of performing a particular operation or its incorrect performance. To avoid canceling previous events, you can try a failed operation to compensate (event compensation). The outline of such a sub-process is shown as a double solid line. To include in the diagram all tasks or sub-processes that are reused, there is a Call - a call, which is indicated in the diagram by a bold outline.
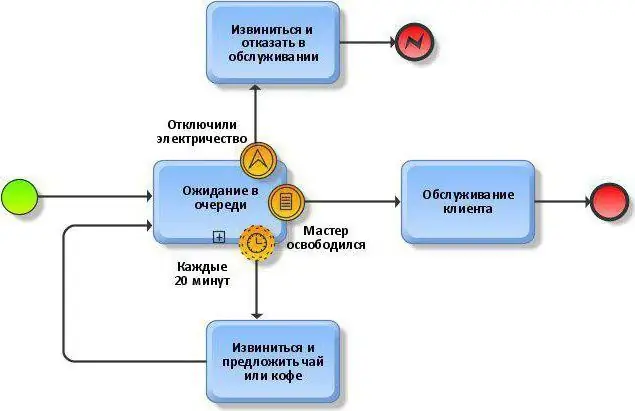
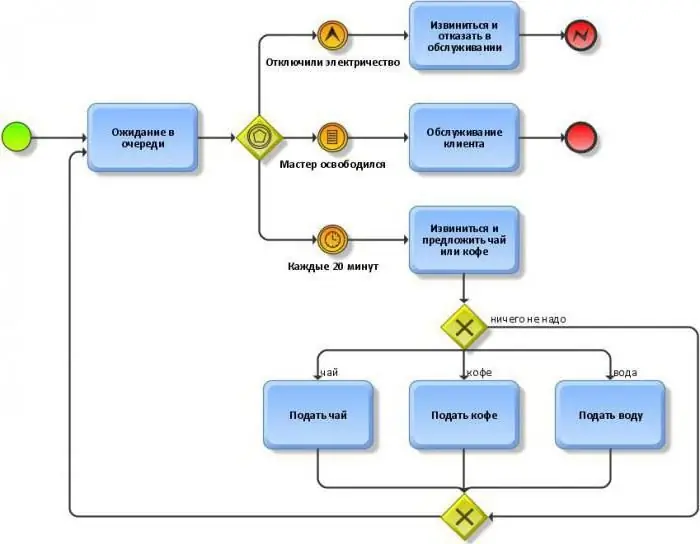
Gateways
Gateways in BPMN notation are intended to indicate the specifics of the flow of operations and their passage through parallel or alternative branches. The gateway can do without outgoing or incomingstreams, but always has at least two of its own, either incoming or outgoing. The marker inside its symbol specifies the gateway type. It can be Exclusive, XOR - exclusive with an exclusive "or", designed to split the flow into alternative routes. During the execution of the process, only one of the proposed routes can be activated. Skip conditions are contained next to the designator line. Inclusive, OR - non-exclusive with logical "or" gate designed to divide the flow into routes, where each is activated if the condition of the boolean expression associated with it is met. Several paths can be taken in this process, but if any one of them is not true, then the choice is impossible.
Analog of a non-exclusive gateway - Complex. The difference is that there is only one expression that determines the activation of a particular workflow. Parallel, AND - a parallel with logical "and" gateway is needed for branching or merging parallel operations. Exclusive Event-Based - An exclusive but event-based gateway that separates the workflow into alternative routes. Exclusive Event-Based Gateway to start a Process is also an exclusive gateway, the events on which it is based start the entire process. This is the start character of a process or subprocess that has no input streams. The Parallel Event-Based Gateway to start a Process works in the same way - a parallel gateway, also based on events that start the process. However, with its help, you can activate several processes at the same time,if the events associated with them fire. Naturally, it has no incoming streams. The pictures clearly show the BPMN notation in the examples of diagramming with two kinds of gateways.
Data and flows
The data object is contained and used in charts specifically, which demonstrates the use of additional markers. Data Inputs - input data, that is, the initial information in order to start the execution of actions. Appears on the top edge of the symbol. Data Collection - a set of data, that is, an entire array or collection of data of the same type. Displayed below the symbol. The data object and the action are linked together using an association.
Standard picture of the workflow can be supplemented in the diagram with the indication of specific flows. Conditional Sequence Flow - designation of a conditional flow of operations when branching it. Shown as coming from an action (if you don't want to use a gateway in the diagram). Default Sequence Flow - the default sequence flow, most often comes from a gateway or action, not associated with logical expressions.
Examples and conclusions
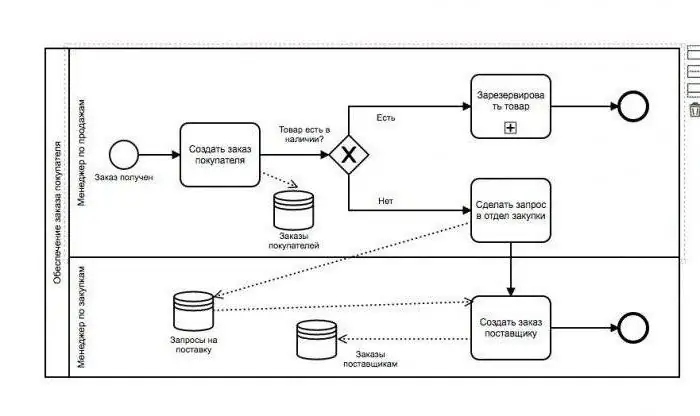
Start event, as the name implies, indicates the start point of a process. This is the starting point, which means the absence of any kind of incoming flow. The start event in BPMN notation examples is denoted by a circle in which the center is free. Such an event can be a letter or a call from a client, for example, sent to an online store or to the website of a company thatmodels this business process. Further, the flow of operations goes along the lines and indicates the execution of the process up to the red circle, which indicates completion, the end event. By the way, there may be several of them, and it is easy to trace where exactly the flow of operations came to an end, completing the process. No outgoing stream is possible from the red circle.
If the diagram is not in color, then the end event is highlighted with a thick circle-shaped line. For example, in practice this event may be the issuance of an ordered product that has gone all the way from clearance through processing to issuance. In the course of all this work, the diagram shows the actions that were performed on the way from the start to the end event. The action is indicated by a rectangle with rounded edges. Gateways - rhombuses. This language is understandable to users, it is only necessary to familiarize yourself slightly with the display system that is present here in the illustrations.
Recommended:
How sheep are sheared: methods, timing, preparation of the animal, description of the process

Sheep wool is a quality natural material. Its properties are unique, it has no analogues. The history of the development of mankind shows that since ancient times people have used sheep wool for various needs. It was and is received by shearing sheep's hair
Management process - description, objectives, functions and definition

All enterprise systems have their own organizational structure, thanks to which there is a management process. Every person who has chosen a career as a manager and wants to achieve high performance in it needs to know about management processes
Mobile feed mills: description, technological process

Today you can hear a lot of discussion about progressive installations used in agriculture, which are mobile feed mills. The principles of the device, the benefits of implementation and customer reviews of this equipment can be found in the article
Polishing - what is it? The essence of the process, description, types

Currently, when metal products occupy a significant place in people's lives, the process of their cleaning has become quite common. An effective method of cleaning metal from contamination and removing irregularities is polishing
Process engineer: job description. Process Engineer: Job Responsibilities

The job description of a process engineer is an addition to the employment agreement and defines the duties, rights and degree of responsibility of the person applying for the specified vacancy. This administrative document is intended to specify the powers of the administrative apparatus in relation to the specialist technologist, as well as to designate the functions of an employee

