2026 Author: Howard Calhoun | calhoun@techconfronts.com. Last modified: 2025-01-24 13:10:32
Flanged connections are often used in industry. They must ensure the tightness and strength of the assembled structures. The role of a high-quality connection is important, because an unstable bond can lead to large losses and threaten the danger to the maintenance personnel. The main connection element is the flange. This part is a metal disc and provides a strong and tight detachable connection. The flange has found its application in the industry of pipeline transport, public utilities. Thanks to the use of various materials for its manufacture, it becomes an almost universal element of pipeline structures.

Types of flanges
For technological pipelines, a large number of designs of this part have been developed. All flange connections consist of the following elements - flanges, gaskets, fasteners. The main task assigned to this node is to combine parts of the pipeline or to connect to pipesadditional equipment. Flanges are divided into types depending on various parameters. By design, they are divided into:
- whole;
- free.

The difference lies in the fact that the one-piece flanges together with the body undergo respectively the same loads. They are made together with fittings in the process of casting or stamping, and alignment can also be done by welding. As for the free ones, they are a disk that is attached to a welded flange or flanged edge of the pipe. Both types have both disadvantages and advantages. Loose flanges are easy to assemble, their design makes it easy to align the holes for the studs. The disadvantage is less strength and stiffness than solid flanges.
Separation of flanges by purpose:
- For fittings and pipelines. Flanged connections of pipelines of this type are used for all types and branches of pipe, transport and housing and communal services.
- For vessels and apparatuses, such connections are used for distillation of oil, equipment for heat supply systems, as well as tanks for reservation.
Standards
All flanges are divided into several types depending on GOST and execution:
- Casted flanges are made as a single unit with the body. They can be cast from steel or cast iron.
- Steel flanges that are threaded on the neck. This type has a rather limited application and is mainly usedfor low pressure pipelines.
- Collar flanges. They are a product made of steel, which is obtained by butt welding. The purpose of collar flanges is to connect pipelines with high and medium pressure. This type has the advantage of being easy to install and economical. Compared to flat welded flanges, which we will consider in the next paragraph, they reduce the manufacturing labor intensity by an average of 20% and the amount of welding work by half.
- Flat welded flanges. They are made of steel and used such flange connections for process pipelines.
- Loose flanges. This species has its own characteristics and is divided into three subspecies:
- with collar, they are used for pipelines with aggressive environments, from which the collar protects the flange itself;
- on a flanged pipe;
- on a welded ring, they are used for pipelines made of non-ferrous metals - copper and its alloys, aluminum, and stainless steel;

Connection selection options
- Shape of flange connection. Flanges can be: round, oval or rectangular.
- Conditional pass. Its size corresponds to the inner section of the flange through which the medium will flow.
- Design. This parameter regulates flange connections, GOST 12815-80 includes 9 different performance categories.
- Pressure. Connections can withstand the maximum nominal pressure, it dependson the design and geometric dimensions of the flange. This parameter is also provided for by the main regulatory document.
- Material. For the manufacture of cast iron, carbon, alloy, stainless steel. The material is selected according to the application medium used. High value metals can also be used.
Electrically insulating joint

The insulating flange connection has a number of differences from other types and has the task of preventing the passage of electric current, as well as protecting against electrochemical corrosion. Most pipelines are laid underground, where stray currents are likely to occur. In general, they do not pose a danger to the entire pipeline at the inlet, but are very dangerous at the exit point. Such an impact can lead to the destruction of the metal, the formation of cracks and leakage of the transported liquid or gas, the insulating flange connection provides the necessary safety. It consists of flanges, special insulated gaskets, bushings and fasteners. Such a connection is used in the following cases:
- at the border of the pipeline and its transition from the supplier to the consumer;
- when pipes are flanged to match the different materials they are made from;
- on pipelines that are laid in the area of sources of stray currents;
- at the outlet of an insulated pipeline network that connects to a non-insulated pipeline;
- on the ground sections of gas distributionstations.
Other types of flange connections
- Measuring flange connections. They provide connection of pipeline networks with additional equipment and measuring devices.
- High pressure connections. Such nodes are subjected to variable loads from operating mechanisms. Therefore, in order to ensure density and strength, as well as durability, a number of technological nuances should be observed during installation. The twisting of the studs is done gradually in a circle and in a certain sequence. Flange connections can be made stronger by using a lens type gasket. To use this type of gasket, it is first necessary to grind the surface of both gaskets and pipes directly. The best option for this type are threaded flange connections. Can also be used along with a lens gasket, flat metal. Maximum flange tightness is ensured by using flat gasket materials such as copper or aluminum.
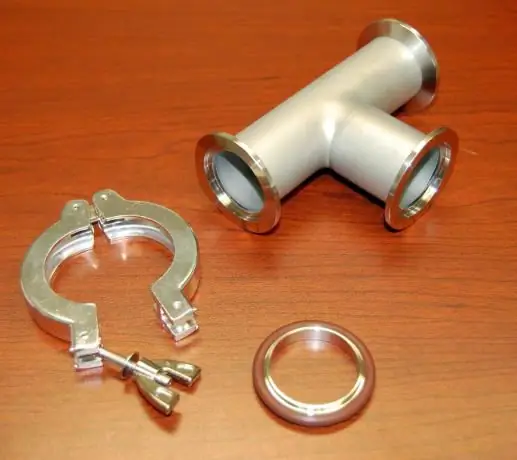

Flanged lock. This connection by design is fully consistent with the flange, the difference lies in the fact that instead of the usual fasteners - bolts and studs, a special design is used in the form of a strip that compresses the flanges and tightens with bolts. In such connections, there are no holes along the diameter of the flanges. This type has proven itself in nodes that require quick and periodic disconnection-connection. In this case, you can use flat welded flanges or butt welded
Flange fasteners
For the installation of flange connections, fasteners are required. For fastening pipelines, the following fasteners are used: bolt, nut, stud and washer. Since flange connections of pipelines are a rather responsible design, requirements are imposed on fasteners in accordance with the following parameters:
- Wednesday. She may or may not be aggressive. Based on this environment setting, the fastener is selected. For aggressive environments, preference is given to steel with anti-corrosion properties. It is also possible to use special coatings that prevent corrosion.
- Temperature. The temperature of the liquid or gas that will be transported through this pipeline, as well as the temperature regime of the environment, plays a role here. Each material has a working temperature range, according to which the product is selected. If the environment does not exceed -30 ºС, ordinary steel grades can be used, for lower temperatures cold-resistant grades are used.
- Pressure. The higher the working pressure, the higher the parameters must have the material used, from which the studs for flange connections are made.
- Indicators of fasteners: thread type, pitch, length.
- Material. The steel used in the manufacture of fasteners for flanged joints can be classified into four categories:

- general purpose carbon steel, working temperature should not exceed 200ºC, and the maximum diameter is 48mm;
- carbon steel, used for high precision products, the operating temperature cannot be higher than 300 ºС;
- carbon steel with high quality, fasteners made of this material can be operated at temperatures above 450 ºС;
- alloy steels that have heat-resistant and anti-corrosion properties.
Limited use of fasteners
The choice of fasteners is determined by the above parameters, but there are some limitations:
- Fasteners operated at working pressure up to 25 kgf/cm are not limited by the choice of product type. As for the pressure that exceeds this figure, only studs for flange connections can be used, the use of bolts is prohibited.
- The steel grade for the “stud-nut” pair can be chosen either the same or different. If one material is used, the strength of the nut must be less than the strength of the stud by 20 units.
There is a special GOST stud for flange connections, according to which the nominal dimensions of the fastener are selected. The choice of sizes depends on the working pressure to which the stud will be subjected.
Pads
This part is included in an insulated flange connection to provide the necessary tightness between the flanges. Gaskets are divided into different types according to certain parameters. Depending on thethe material from which they are made, there are categories:
- metal;
- non-metallic;
- combined.
Distribution of gaskets by elasticity:
- elastic;
- hard.
This property predetermines the material from which gaskets for flange connections are made. Elastic are obtained from combined and non-metallic species. Rigid gaskets are mainly metallic, but also non-metallic, obtained from materials such as fiber, hard rubber, paronite, etc.
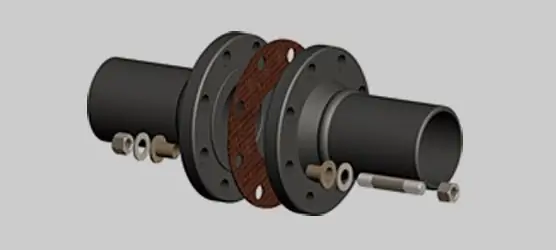
Design features of gaskets
On this basis, gaskets for flange connections are divided into:
- Flat (can be both metallic, non-metallic and combined), they are used in connections with flat surfaces. The inner diameter of the flat gaskets should be 1-3 mm larger than the pipe diameter.
- Lens gaskets are made from carbon and alloy steels and can be either rigid or flexible.
- Oval provide a good seal with moderate bolt loading. The contact of the gasket product occurs along the outer and inner circumference with the flange. The material for these gaskets is either carbon steel or stainless steel.
- Corrugated gaskets can be either metal or non-metal. They are made of a thin sheet of copper, mild steel, asbestos cardboard is used as a non-metallic material orpaper. The inner diameter corresponds to the flange diameter, and the outer diameter is adjusted by the location of the bolts.
- Spiral refers to elastic gaskets. Such a gasket consists of three elements - a spiral part and two restrictive rings.
- Toothed gaskets, the material for these gaskets is mild steel or alloy steel. An insulated flange connection with this type of gasket can be operated at temperatures not exceeding 480 ºС.
Calculation of flange connections
After determining the type of flange, depending on its purpose, the type of gasket product, as well as the materials from which the product will be made, the designers select the required dimensions of the part according to special tables. They are presented in the relevant GOSTs. Even though flanges are standard parts, it is very often necessary to design a custom product. The calculation system includes the following items:
- Calculation of plastic deformations at the base of the bushings, this applies to joints operating at low temperatures and pressures.
- Accounting for external bending moment arising from the load on the bolts. This parameter determines the strength characteristics of the flange.
- Calculation of emerging stresses, especially for products that are obtained by welding.
- Selection of bolt pitch, incorrectly defined this parameter can cause deflection of the flange rings between the bolts.
Calculation of flange connections must take into account the type of load. There are two options -in the first case, the load from the bolts is transferred to the gasket, in the second case, the loads are evenly distributed between the gasket and the support ring.
Recommended:
Business connections: defining the concept, reputation, connections, establishing relationships

Success in business is impossible without establishing relationships with other people. Therefore, every business person tries to expand his circle of contacts, because any business or friendly relationship can become a necessary resource in business development. Let's talk about what connections and relationships are in the business world, how to develop connections, and why they are needed
Detachable connections: photo, drawing, examples, installation. Types of detachable and permanent connections

In mechanical engineering and instrumentation, not only the parts that are used in production, but also their connections play a very important role. It would seem that everything should be extremely simple, but in fact, if you delve into this topic, you will find that there are a huge number of different compounds, each of which has its own advantages and disadvantages
Clothing industry as a branch of light industry. Technologies, equipment and raw materials for the clothing industry

The article is devoted to the clothing industry. The technologies used in this industry, equipment, raw materials, etc. are considered
Dairy industry in Russia. Dairy industry enterprises: development and problems. Dairy and meat industry

In the economy of any state, the role of the food industry is huge. Currently, there are about 25 thousand enterprises in this industry in our country. The share of the food industry in the volume of Russian production is more than 10%. The dairy industry is one of its branches
Connections: purpose, types of connections. Examples, advantages, disadvantages of types of compounds

Machines and machine tools, equipment and household appliances - all these mechanisms have many details in their design. Their high-quality connection is a guarantee of reliability and safety during work. What types of connections are there? Let's take a closer look at their characteristics, advantages and disadvantages

