2026 Author: Howard Calhoun | calhoun@techconfronts.com. Last modified: 2025-01-24 13:10:32
Machines and machine tools, equipment and household appliances - all these mechanisms have many details in their design. Their high-quality connection is a guarantee of reliability and safety during work. What types of connections are there? Let's take a closer look at their characteristics, advantages and disadvantages.
Classification
Different types of connections can be divided into two main groups. The first of which, according to the principle of action:
- Moving. Parts can move relative to each other.
- Stationary. Both parts of the part are rigidly fixed to each other.
In turn, each type of the previous classification can be carried out in two ways of connection:
- Detachable. It is used when periodic replacement of parts, assembly and disassembly of the mechanism as a whole is required. These are the following types of connections: threaded (with the help of running bolts), toothed, keyed, etc.
- One-piece. Such connections can only be dismantled using mechanical action, which destroys the mating parts. What are these types of connections? Among them are welding, gluing, riveting, flaring, crimping, interference fit, stitching, punching, etc.
So, let's take a closer look at the main types of connections of parts.
Thread method
An old and long-tested mounting option. The following elements are used for it: bolts, screws, studs, screw ties and others. Fastening is carried out due to the thread on the fastener and in the hole of the part.

Spiral protrusions on the rod and in the technological hole of the parts are called threads. Consider the main fasteners:
- A bolt is a threaded rod with a fixing head at one end. Its shape is hexagonal, square, round, etc.
- The screw differs from the previous product in that there is a slot (slot) for a screwdriver on the head. It can be hexagonal, straight, cross, etc. According to the type of head, products are countersunk, cylindrical, semicircular, semi-secret.
- Stud is a threaded rod at both ends. Unlike previous options, it does not have a head.
- The locating pin is slotted at one end.
- Nut - a prism with a through hole or plugged on one side.
Washers are produced for these hardware: flat, spring, deformable. This fixation is applied everywhere.
Keyed
Keys fix the shaft with parts that transmit rotation and vibration. The design of such elements can be prismatic,wedge, segment, tangential. Such fasteners form the following types of connections:
- Non-stressed ones are made with the help of prismatic segment keys. No prestressing during assembly.
- Stressed are produced by tangential and segment keys. Mounting stress appears during assembly. Used for complex mechanisms.
Toothed (splined) connections
Mounting occurs due to the protruding teeth on the shaft and the recess under them in the hub.

The sizes are fixed by the standards. This method is used for movable and fixed mounts.
Here, there are three options for fixing in terms of stiffness: light, medium, high. The difference is in the number and height of the teeth. It lies in the range of 6-20 pieces. Tooth shape:
- Triangular are of little demand. Used for small fixed shafts and low torque.
- Squamous. Centered on the side faces, on the inner and outer diameters.
- Involute. Suitable for large shafts.
Where are these species used? The purpose of the connections of such a plan is the transmission of torque. The most famous application is power tools.
We looked at detachable mounts. Next, we will study the main types of permanent connections.
Welding
What makes them special? These types of joints are formed by heating and fusing the material at the attachment point to form a weld. This clutch is considered one of the mostcommon.

There are several options for welding. The most popular ones:
- Arc welding. Three main subtypes can be distinguished: automatic submerged arc (distinguished by high productivity and quality, used in mass production), semi-automatic submerged arc (used for short intermittent welds), manual (reduced productivity speed, quality depends directly on the experience of the welder).
- Contact welding. Used in mass production for thin sheet metal. The seam is overlapped.
One of the popular mounting options is shown in the photo.

Often used in suburban construction.
Soldering
Unlike welding, at the moment of soldering, the metal surface does not heat up to the melting temperature. The role of the binder is performed by molten solder, which has a lower melting point.
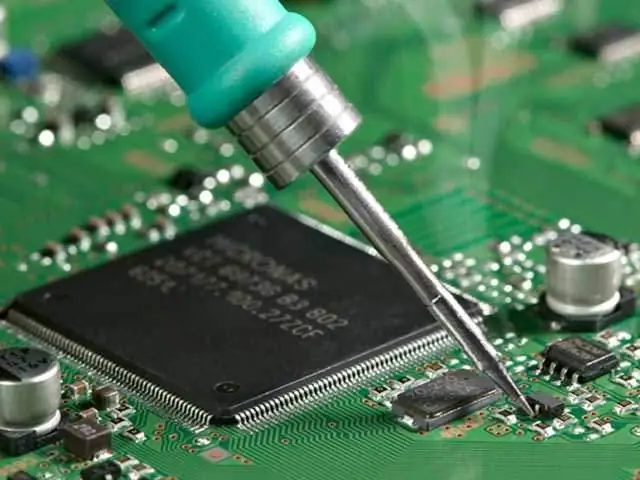

This clutch method is used for small parts. This is due to the limitation of the gap between the surfaces of the parts.
Adhesive joints
This fastening does not require heating of surfaces.
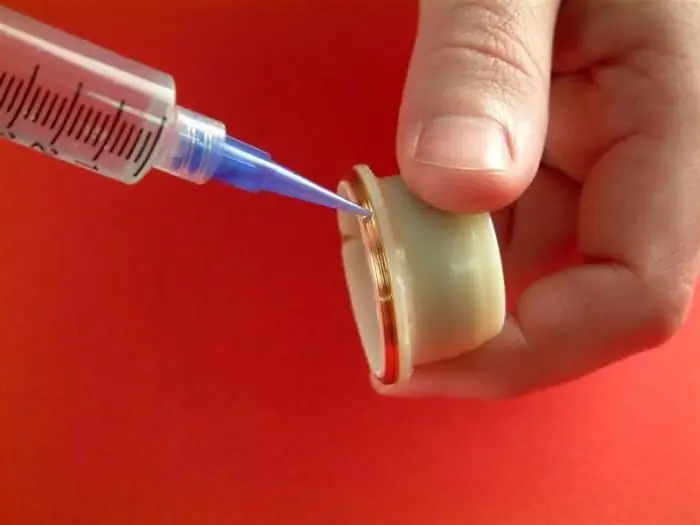
For each type of metal, its own glue is selected, which will provide a tight grip. Parts are prepared for such operations. The surface is polished, degreased, a special primer is applied, after which the gluing operation is performed. The compositions used are distinguished by additional properties and adhesion to various surfaces.
Riveted fixation
This bonding method is mainly used for connecting sheet metal and shaped profiles. The technological hole in the surfaces is carried out by drilling, then the riveting is inserted.
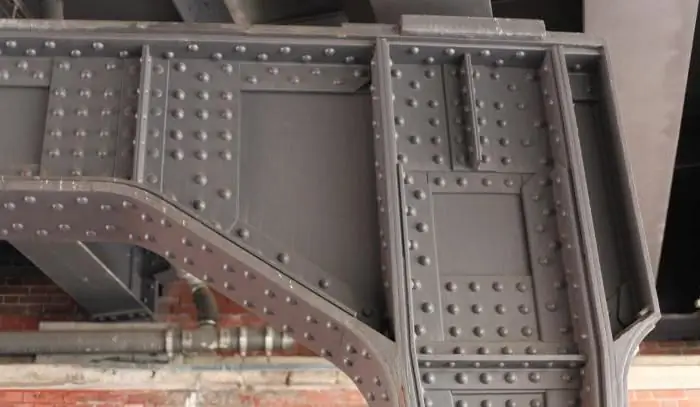

Due to mechanical action, the rod and head are deformed, fill and fix the hole. This operation is carried out manually and mechanically. Rivets fix material that is not amenable to welding, soldering, gluing, and to parts where it is necessary to delay the destructive process.
Interference connections
Produced by fitting the seats of the parts. The coupling occurs due to the force of friction. Basically, this species is considered one-piece. But this is conditional. In practice, they still dismantle and replace parts.
Advantages, disadvantages of types of connections
Each fastener has its own characteristics. Consider all options in terms of advantages and disadvantages:
- Threaded. Withstands heavy loads, reliable grip, a wide range of products, ease of installation and dismantling, the ability to use mechanization, low cost. Disadvantages: increased amount of stress concentrates, reduces resistance.
- Keyed. Simple design, easy installation and dismantling. Disadvantages: the groove for the veneer weakens them by reducing the cross section of the shaft and hub. It also occurs due to the concentration of torsional stresses andbending. Labor-intensive fastener manufacturing process.
- Toothed. Forms a good grip and accurate direction of axial movement, transmits more torque, fewer parts, reliability under reversible and dynamic loads, less shaft weakening, reducing the length of the hub. Disadvantages: increased price, complex production technology.
- Welding. Low cost of work, the connection is sealed and tight, the use of automated processes, the ability to work with a thick profile. Disadvantages: in manual welding, the quality depends directly on the qualifications of the worker, deformation of the surface of parts when heated, low reliability during vibration and shock.
- Soldering. No deformation of the surfaces of parts, high accuracy, the possibility of desoldering. Disadvantages: Complicated base preparation process, minimum clearance must be maintained.
- Glue. Low cost, there is no weakening of the working section, the possibility of combined use with other types of fasteners, the tightness of the joint, increases the anti-corrosion properties of the seam, resistance to water, chemicals, temperature changes, the simplicity of the application technology. Disadvantages: careful preparation of the base, if the composition is incorrectly selected, strength characteristics may decrease.
- Riveting. Can be applied to materials that are not weldable, reliable, prevents fatigue cracks. Disadvantages: laboriousness, material consumption, during the process deformation of the surfaces of parts appears due tomechanical impact.
- Interference connections. The design is quite simple, good arrangement of parts relative to each other, withstands heavy loads. Disadvantages: difficult to assemble, strength dissipates under the influence of vibrations and vibrations.
As you can see, each type has its own advantages and disadvantages. Given these factors, select the optimal types of fasteners in each case. Consider where the various compounds are used.
Types of connections. Application examples
Threaded, glued, welded connections are found everywhere in any industry. For example, construction, furniture, heavy industry and so on. Keyed and slotted fixings are widely used in power tools, equipment, mechanical engineering. Interference connections are installed on the shafts of gear rings, worm wheels. Soldering is often used in electronic systems where maximum precision is required. Riveting is used for stitching sheets of thin metal. However, as shown in the last photo, fairly large channels can be fastened with rivets. This is just a small list of applications for individual mounting options.
It can be said that with technological progress, clutch technology is rapidly developing, which means that new types of parts connections will appear. The modern world is filled with aggregates, machines and mechanisms. The quality and service life of the components depend on how firmly the parts are fixed. It is also important that the connection does not distort the shape of the product and does not introduce additional changes inconstruction. Therefore, it must comply with technological standards. If they are observed, the number of emergencies at enterprises will be reduced significantly, and the units themselves will last a very long time.
So, we found out what types of connection parts exist.
Recommended:
Detachable connections: photo, drawing, examples, installation. Types of detachable and permanent connections

In mechanical engineering and instrumentation, not only the parts that are used in production, but also their connections play a very important role. It would seem that everything should be extremely simple, but in fact, if you delve into this topic, you will find that there are a huge number of different compounds, each of which has its own advantages and disadvantages
What are flange connections? Types of flange connections. Flanged connections in industry

Flanged connections are often used in industry. They must ensure the tightness and strength of the assembled structures. The role of a high-quality connection is important, because a weak bond can lead to large losses and threaten the danger to the operating personnel
Riveted connections: advantages and disadvantages
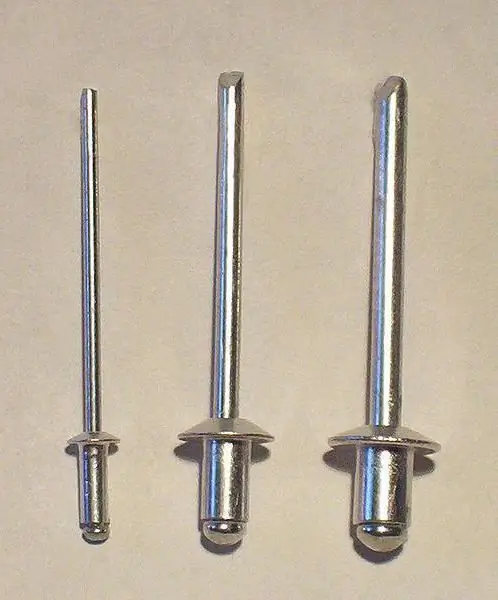

Riveted joints are made from special parts. Such a fixed bond is difficult to separate. Rivets themselves are made of plastic material. Rivet joints consist of three elements - two parts of the parts to be joined and a rivet. The last element is placed in special holes, which are located at the edges of the parts to be joined. The rivet holds the part in the required position
Mineral wool density: classification, advantages and disadvantages, purpose of mineral wool and application

Mineral wool is the most popular type of insulation for an apartment or house. Today it is used by everyone, from builders to the owner of the apartment, who wanted to insulate the room. The simplicity of its installation allows you to immediately insulate the entire house (ceiling, walls, floor). We will study the features and characteristics of the named material further in the article
Plain bearings: designs, types, production, purpose, advantages and disadvantages

Sliding bearings are used in generators and internal combustion engines. These are parts that are capable of transmitting torque, ensuring the normal operation of mechanisms. Bearings have a specific design. This provides a certain set of technical and operational characteristics of the part. The design features of plain bearings, their varieties, advantages and disadvantages will be discussed in the article

