2026 Author: Howard Calhoun | calhoun@techconfronts.com. Last modified: 2025-01-24 13:10:41
Hot welding is one of the most common assembly processes used in construction and industry. It is used both in high-tech operations for the assembly of equipment, and in the simplest typical work when connecting load-bearing structures. In each case, its own welding technique is used, which is optimally suited for operational parameters, working conditions and requirements for the result.
What is welding?

In the classical view, welding is the technology of forming permanent joints by creating interatomic structural bonds against the background of thermal exposure. In other words, under high temperature, plastic deformation of the workpieces is ensured and the subsequent exchange of particles between them, which leads to the formation of a joint after the materials cool. The welding technique itself only provides the necessary conditions for bringing metals intorequired state. In normal temperature conditions, the metal is a structure of solid crystalline particles, but upon reaching a certain heating index, the material softens. At the same time, it should be emphasized that the effect of temperature brings not only positive effects from the point of view of mounting possibilities. Oxidation of metals also occurs, the formation of cracks in inappropriate places due to internal stress, general warping and deformation occur. It is possible to exclude and minimize such phenomena only through the correct selection of equipment and organization of the welding process.
Welds and joints
To understand the goals of metal plastic deformation, it is necessary to determine for which structural tasks the welding operation is performed. In most cases, it is necessary to obtain a connection of two workpieces or structures with parts. Connection configurations are different - angular, butt, tee, etc. From the point of view of the formation of edges, the seam welding technique allows the formation of joints without bevels, with flanges, as well as with bevels in various shapes. One of the most difficult bevels is considered to be X-shaped, in which two straight or curved edges are mated. Although one of the main requirements for a welded joint is tightness, in some cases there are quite clear tasks for the formation of holes in the joint. For example, when connecting elements by overlapping and without an edge bevel, an elongated hole can be formed, which is later used for other structural tasks.
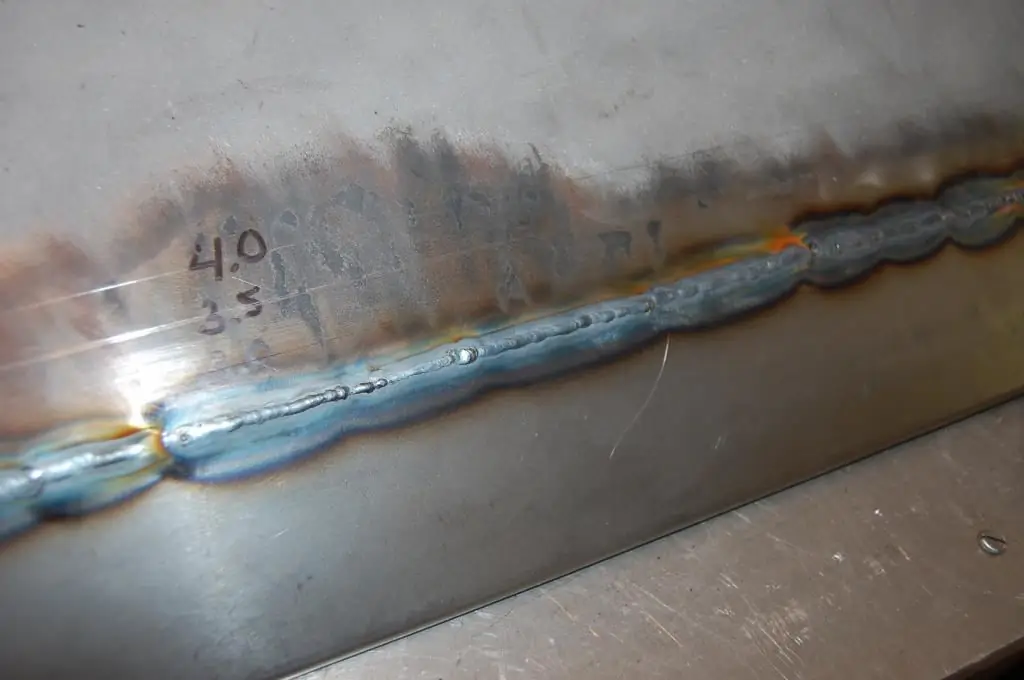

Varieties of the welding process
The very approach to the technical organization of welding can differ both in the parameters of the working environment and in the mechanics of the impact on the target material. The most popular welding technologies include the following:
- Arc welding. An electric arc is formed between the surface of the structure or part to be welded, the thermal effect of which leads to the melting of the material. This method can be manual, mechanized or automatic. For example, the automatic arc welding technique involves feeding the electrode wire with special equipment, freeing the operator's hands.
- Gas welding. If in the previous case the heat source is electrical energy, then gas welding uses an oxy-fuel flame with a temperature of 3,200 ° C. At the same time, combined methods should not be confused with this method, in which gas mixtures are also used, but not as a source of high temperature, but to isolate the weld pool.
- Electroslag welding. The impact on the material is provided by electric current, and molten slag acts as a conductor and energy modifier.
- Plasma welding. A high-temperature welding method that uses a plasma-arc jet with thermal energy up to 10,000 °C.
- Laser welding. The method is based on the use of photoelectronic energy. The melting of parts occurs under the increased influence of the light beam emitted by the laser.
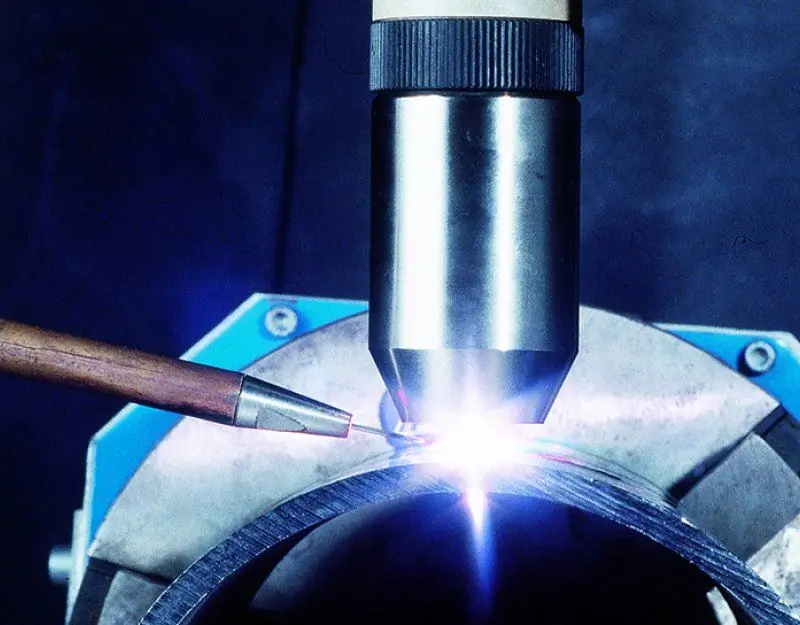
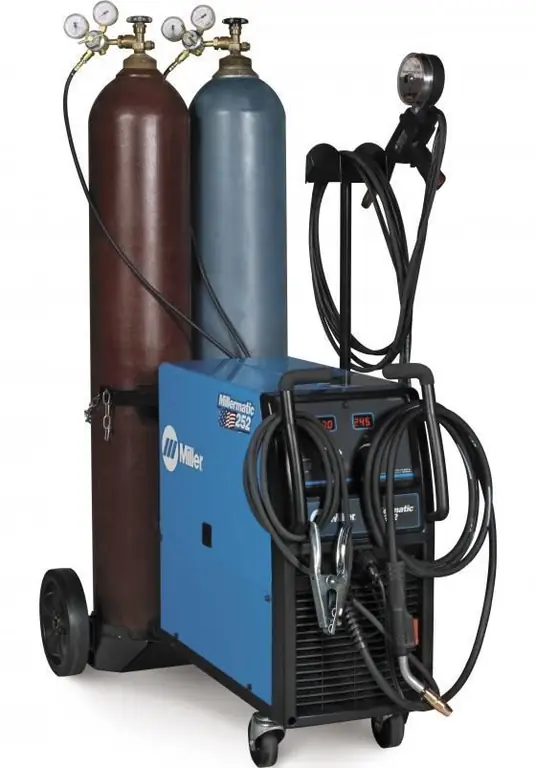
Welding machines
To perform welding operations, several technical means are usually used, including an inverter, a rectifier and a transformer. In each case, the main task of the main welding apparatus is to provide direct current. High-quality equipment supplies the work area with a smooth and stable electric arc. Of course, this applies to electrical welding technologies. The technique of welding in gaseous media is implemented by means of burners and gearboxes that regulate the supply of a gas mixture from a cylinder. Also in the case of plasma welding, special plasma torches are used that can work with workpieces up to 30 mm thick. Moreover, it should be emphasized that gas and plasma equipment is mainly focused not on the traditional tasks of connecting metal parts, but on cutting material under thermal influence.

Sew technique
Despite the huge role of equipment, much in welding work depends on the skills and abilities of the operator who controls the entire process. The task of the user of the equipment is to control the electrode and the supply of consumables present in the weld pool where the seam is formed. The key factor is the position of the operator and the direction of the seam. Experts recommend performing work, if possible, in the lower position, ensuring that the weld is welded with a bead with broadening. It is desirable to achieve deep penetration, which will make the structure of the joint more uniform and durable. In engineeringmanual welding, the stage of cleaning the seam from slag and smudges is especially important. If such flaws could not be eliminated during the main part of the work, then a second layer of surfacing will have to be performed. Usually the main first layer reaches 3-4 mm in thickness, and the subsequent ones - up to 5 mm.
Features of submerged arc and gas welding
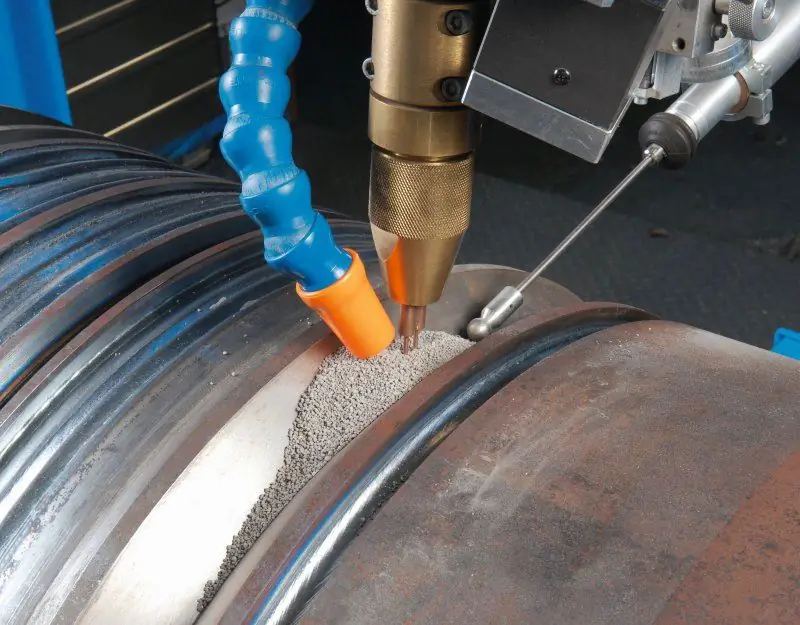

In order not to have to adjust the welding technique in the process of work, it is recommended to initially calculate the technological nuances that can improve the quality of the result. Submerged arc and gas welding is distinguished by its focus on the protection of the seam from the negative influence of the external environment and the melt. For example, when performing the gas welding technique with the supply of argon mixtures, the negative effect of oxygen, which worsens the quality of the weld structure, is reduced. As for the flux, its inclusion in the first place minimizes the splashing of the melt, and secondly, it modifies the composition of the weld by including special additives that are activated at high temperatures.
Parameters for the organization of welding production
In the production mode of organizing welding work, several factors of labor activity are taken into account at once, including the following:
- The ratio of the complexity of the operation and the time norm for its implementation.
- The amount of work is the rate of output that an employee or team performs in 1 hour. For example, in the manual arc welding technique, meters of the completed seam or the number of mounted parts may be taken into account.
- Unitservice. In this case, we mean a workplace, a piece of equipment or a site for welding, within which the activities of one employee or team are also organized.
Safety in the organization and production of welding
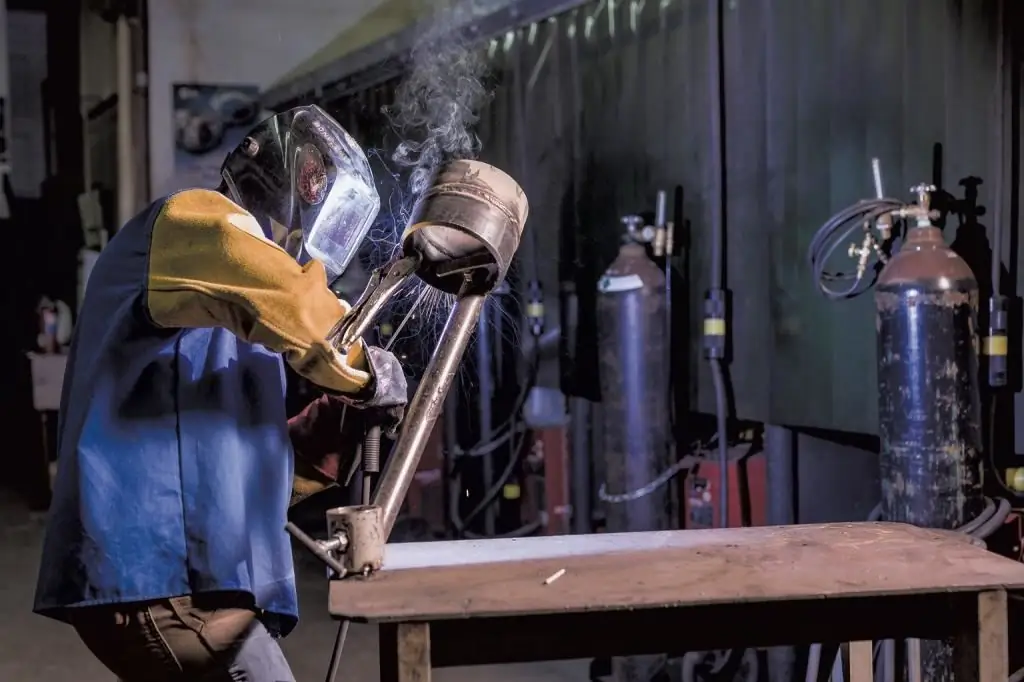

The welding process involves many risks and hazards in terms of threats to human he alth. Welding safety standards focus on several hazards at once:
- Welding radiation. Infra-red radiation with a bright glow negatively affects the eyes of the welder, therefore, in his equipment, the presence of a mask with special darkening glasses and filters is mandatory.
- Thermomechanical effect. Especially when working according to the arc method, splashes of the melt are dangerous. In fact, it is a liquid hot metal that can cause severe burns on contact with the skin. To protect against sparks and hot metal, special thermal protective clothing is used.
- Risk of fire. High temperatures and splashes of hot material increase the fire hazard. It is worth thinking about this even at the stage of organizing the process, removing flammable objects from the working area.
- Respiratory protection. Toxic gases and the release of other hazardous substances during the thermal destruction of the metal structure are also a factor in the hazardous effect. In this case, it is not enough to use masks and respirators. An active system is a prerequisite for long work processesventilation in confined spaces and regular 5-10 minute work breaks.
Welding errors
Due to the complexity of the welding process, the assumption of technological errors is not something exceptional. The most common of them include the following:
- Arc break. The electrical thermal action has not been completed to the end of the planned seam, which may result in a cracked depression at the edge of the connecting line.
- Poorly reinforced seam with thinning of the metal at the joint boundary (cut). A common occurrence in high voltage welding techniques. Ideally, cuts should not be more than 1mm deep or additional welding will be required.
- Point absence of a direct connection in the structure of the seam between the workpieces. In other words, the remaining lack of penetration, which occurs due to the inaccurate direction of the electrode during the formation of the arc, without regard to the depth of the thermal effect.
Conclusion

With all the technological complexity of welding, the methods of their implementation are becoming more accessible to an ordinary home master. This is largely due to the fact that welding techniques are becoming more ergonomic and safer. For example, modern inverters make it possible to conveniently control the main operating parameters of the process, taking into account the characteristics of the metal and environmental conditions. The user only needs to properly organize the work area and properly control the electric arc when forming the seam.
Recommended:
How to negotiate correctly: rules and common mistakes

How to conduct business negotiations? If the meeting is informal, try to use open postures and maintain eye contact with your interlocutor. Sitting with legs crossed and arms crossed is not worth it
Quality as an object of management: basic concepts, levels, planning methods, objects and subjects

Analysis of product quality as an object of management is especially relevant if we recall the fact that a market economy reigns in our world. This system pays special attention to quality issues. The reason for this is strong competition
Identification and authentication: basic concepts

Identification and authentication are basic concepts of modern programming, but few understand them
Welding in a shielding gas environment: work technology, process description, execution technique, necessary materials and tools, step-by-step work instructions and expert advice
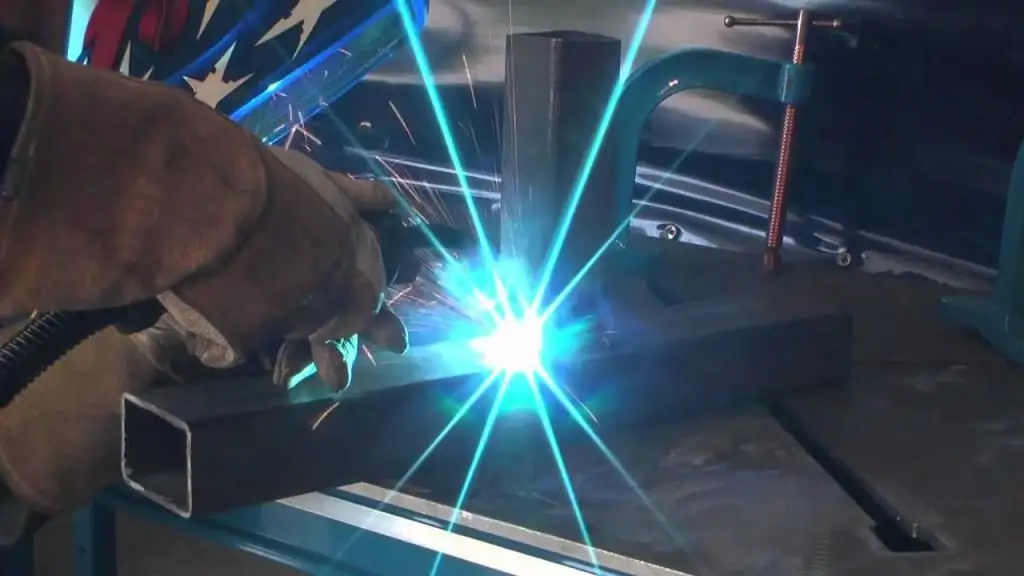

Welding technologies are used in various branches of human activity. Versatility has made welding in a protective gas environment an integral element of any production. This variety makes it easy to connect metals with a thickness of 1 mm to several centimeters in any position in space. Welding in a protective environment is gradually replacing traditional electrode welding
Flux for welding: purpose, types of welding, flux composition, rules of use, GOST requirements, pros and cons of application

The quality of the weld is determined not only by the ability of the master to organize the arc correctly, but also by the special protection of the working area from external influences. The main enemy on the way to creating a strong and durable metal connection is the natural air environment. The weld is isolated from oxygen by a flux for welding, but this is not only its task

