2026 Author: Howard Calhoun | calhoun@techconfronts.com. Last modified: 2025-01-24 13:10:27
The first organizations began to emerge in antiquity with the appearance of the first communities and tribes. They consisted of small groups, were very simple in structure and did not have complex goals. Now they have fully entered our lives, and without them there would be chaos and disorder everywhere. In the article, we will consider in detail the concept of organizations, the characteristics and types of organizations of different forms of ownership.
Definition

If we talk about the very concept and types of organizations, then we can find a lot of different interpretations. And the simplest of them considers organizations as a collection of people pursuing one common goal. To achieve it, the group must be coordinated by a leader, so in any organization there must be a managing person or a group of leaders.
The concept and types of social organizations
First of all, it is worth considering that organizations can be classified according to many criteria. Consideringorganizations - the concepts, types and functions of these associations - can be divided primarily into formal and informal.
The latter include those that arise spontaneously, do not have the rights of a legal entity and do not fit the regulations. It is simply a group of people who interact with each other and are connected by one goal. These include interest clubs, sports communities, etc.
Formal organizations are a legal entity with their own legal acts and provisions enshrined in legislation. These can be various firms and companies, as well as foundations, unions, etc. By the way, the mentioned sign is one of the important concepts in the types of organization.
Formal organizations, in turn, are divided into commercial and non-commercial. Based on the name of the categories, the first ones are aimed at making a profit, most often through doing business. And for the latter, profit is not the main goal (as a rule, we are talking about sports clubs and various charitable foundations and unions).
Classification of enterprises

In economic theory, there are many different classifications. Almost every company is unique and you will not be able to find exactly the same organizations. All companies differ in size, activities, form of organization and many other features. But there are basic forms of signs of organizations, which we will list below.
Property form
One of the biggest differences isbelonging of the organization to the state or private individuals. A mixed form is also possible, dividing property rights between private owners and the state or municipal budget. Since the 90s, more and more enterprises have passed into private hands, so the most common forms of ownership are private and mixed. Enterprises of strategic importance remain state-owned, in the defense industry, transport, education, medical, etc.
Purpose of the enterprise

Regardless of affiliation, organizations perform certain functions. This may be the provision of various services, as in educational or medical institutions, or the production of various products. It is important to note that all the functions of organizations are not limited to these two categories, there are a lot of them and they are very diverse.
Institution funding
An important concept in the types of commercial organizations is funding. The fixed capital in them can be formed by foreign, domestic participants or a mixed type. Now it is impossible to single out the advantage of any category, because in the Russian Federation all three types of organizations have become widespread.
After our economy switched to a market type, foreign investors entered the domestic market. At first, our enterprises were highly valued, and the market itself was not very specific, but at the same time, demand was high, which ensured the influx of foreign capital into our organizations. At present, the country hasmany multinational organizations, the leadership of which is represented by two or more representatives of different states.
Legal form
The organizational and legal form of management occupies an important place in the division into types of commercial organizations. The concept of the form of an economic entity and its legal status arising from this divide them into the following types:
- Business partnerships. These are commercial organizations whose capital is formed by combining parts of the contribution of participants. There are full and partnerships in faith. Responsibility, profits and losses are divided according to the share of the contribution of a particular person to the total capital. The difference between them is that in a limited partnership a manager is chosen who is trusted by the rest of the organization.
- Business companies. The most common type of commercial organizations. They are created by legal entities or individuals in order to obtain maximum benefits. Among the main features, one can single out the preservation of the initial status of participants, the pooling of capital, equal rights to participate in solving various issues. The most common are open and closed joint-stock companies, concerns, consortiums, limited and additional liability companies and various associations.
- Production cooperatives. As with previous types of commercial organizations, the concept of a cooperative also implies an association of persons to carry out activities. The main difference is the purpose for which this association exists. It may be labor or otheractivity. There is no authorized capital in such an organization. All property is formed at the expense of shares of participants.
- State and municipal institutions. Including this category in the classification of organizational and legal forms is not entirely appropriate due to the fact that theoretically state-owned enterprises can have absolutely any form. The main difference is that the property or part of it belongs to the state or local municipalities. Most often, making a profit is not the primary goal of such organizations, but more attention is paid to creating jobs and maintaining domestic production in the regions, as well as controlling production and prices in certain areas of life.

Goals and resources of organizations
Most often, the goals of the organization, concepts and types depend on the very structure and form of the organization. The key goal of any of them, regardless of function, is survival and self-reproduction. If it does not stand out as fundamental, then the organization will soon simply cease to exist.
To achieve a goal, many organizations expect the transformation of resources into the end result of achieving these goals. The composition of resources can be diverse: this can include capital, various information knowledge and experience, people and technologies.
Division of labor
In a group of people, everyone will do their part of the work, while coordinating their actions with others. This distribution is called horizontal distribution.labor. It allows you to perform large amounts of work by dividing tasks into certain groups that are interconnected. This allows you to work much more efficiently if everyone worked autonomously.
In order for the organization to achieve common goals, in addition to the division of labor, coordination is used. These two opposing concepts never go separately, because it is always necessary to maintain the interaction of separate units. Most often, during the division of labor, the latter are derived in the production, marketing and financial spheres.
The units themselves are also groups of people who are focused on achieving the same goal. That is, we can say that all complex organizations consist of other organizations, but smaller ones.

Management and vertical division of labor
Very important should be given to the concept of management of the organization and types of management. Since with a horizontal division of labor each worker performs part of the process, coordination and, accordingly, management are necessary. And when a large number of divisions are created, a large number of managers arise, among which there is also a division of labor.
In any organization, horizontal and vertical division of labor can be distinguished, these two schemes apply regardless of the purpose of the organization itself and its functions.
Signs of organization
Any organization implies the following:
- A definite purpose. It is on the basis of it that the numerical composition is formedorganizations, initial capital, development strategy and composition of units, each of which is aimed at solving its own goals, in order to achieve a common one.
- Legal status. Any formal company independently determines for itself the concept of organization, the type and principles of its activities. She must also have her own status in order to achieve her goals.
- Isolation. Each organization independently determines its own type, and in order to achieve its goals, it must have its own status.
International Organizations
Separately, it is worth highlighting the concept and types of international organizations. These are special associations of governments for the solution of common international goals. Most often they are advisory in nature, have their own constituent documents, and the decision is made by voting.
Such organizations can be created due to any events or operate on an ongoing basis. They are divided into organizations with or without government participation, regional and worldwide. Among the world-famous are the UN, NATO, ASEAN, the CIS and so on.

The life cycle of an organization
This concept means the time period from the beginning of the organization's existence to its termination, with all the changes and processes taking place in this period of time. All organizations go through this cycle, it's just that some take longer, some take less.
There are five main stages in any life cycle:
- Rise. At this stage, the formationthe concept of the purpose of the organization, the type, as well as its future functionality, authorized capital and the number of participants. At this stage, the personal qualities of the founders are manifested, since the very image of the future organization is rather vague, therefore, motivation for building the future is important during this period. Control and management is carried out by the founder of the organization, due to the small administrative apparatus.
- Development stage. It follows after the enterprise has acquired its appearance, and its basic structure and legal basis have been formed. At this stage, there is an active development and expansion of production and the occupation of large volumes in the market. It is characterized by an increase in the number of employees, the introduction of a system of material incentives and the introduction of a system of horizontal and vertical division of labor. The term of this stage depends only on the ambitions of the management and the availability of capital for development.
- Stage of stagnation. The organization is already approaching this stage with accumulated experience, knowledge and a formed structure, documents and its mission. It is worth considering that the development of the organization is going on at this stage, just not as intensively as at the previous one. It is considered the longest. It is expanding the range of the organization, as well as its territorial development. It is during this period that the maximum development of the enterprise and the most stable position in society are achieved.
- Declining stage. Sooner or later, any organization enters a stage of decline, in which it loses its position due to new players in the market and does not keep up with technical progress and fashion. This happens when management sticks to a policy that has worked in the past and doesn't want to introduce anything new. At this stage, there may be a change of leadership and restructuring of the enterprise, only in this case it can go back to the second or third stage. If this does not happen, then the organization enters the stage of old age, starting to fade away and lose its positions.
- Liquidation. If at the previous stage managers failed to correctly understand the problems and the current stage at which the enterprise is located, then after a certain stage of decline, the process of liquidation begins. Some organizations resort to a reorganization process where management is transferred to a government agency and financial support is requested for the remediation process. Sanitation facilitates transactions between creditors or debtors, and also acts as a guarantor of the fulfillment of obligations.

Conclusion
The concept of types of organization is very important, because they surround us wherever we go. Shop, school, hospital, bank and any other places we visit are different organizations. That is why a lot of attention is paid to the study of the concept of organization, essence and types.
Recommended:
Overhead costs are Definition, concept, classification, types, expense item and accounting rules

An estimate is a calculation of the costs of production and sale of goods. It includes, in addition to direct costs for the purchase of materials, wages, as well as indirect (overhead) costs. These are expenses that are directed to the creation of working conditions. They cannot be attributed to the costs of the main production, as they are the key to the proper operation of the organization
Business organizations: concept, types, structure, features

Business organizations are the basis of the modern economic system. Without them, it is difficult to imagine the complex cycles of creating science and technology-intensive products. If they are dispensed with, then only at a primitive level of production (for example, a subsidiary farm)
Thermal imaging control of electrical equipment: concept, principle of operation, types and classification of thermal imagers, features of application and verification
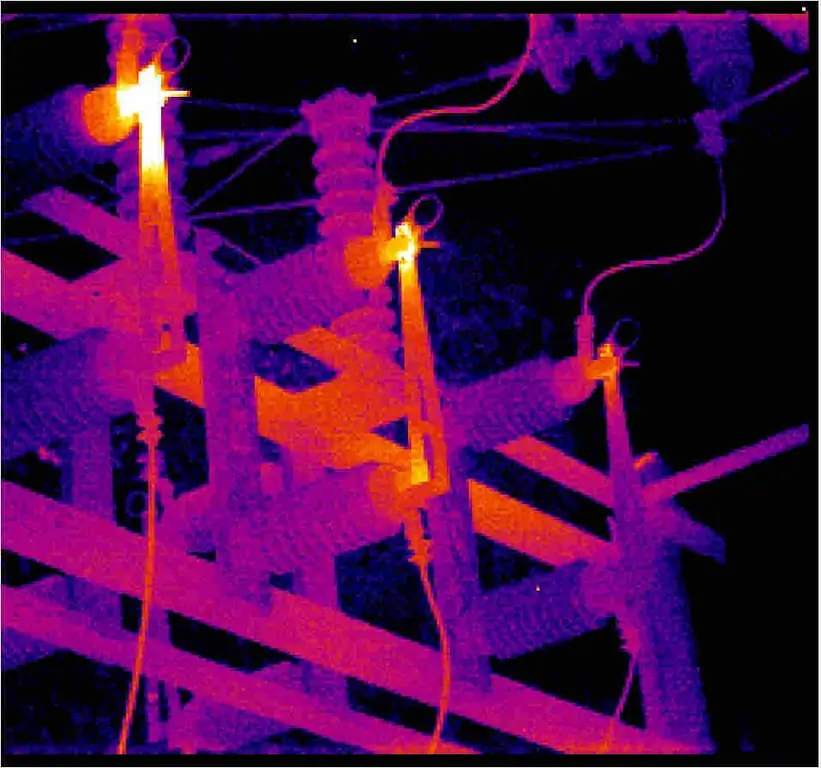
Thermal imaging control of electrical equipment is an effective way to identify defects in power equipment that are detected without shutting down the electrical installation. In places of poor contact, the temperature rises, which is the basis of the methodology
Tax and tax payments - what is it? Classification, types, concept and types

Currently, the tax system is a set of taxes and fees established by the current legislation of the Russian Federation, which are levied in the budgets of different levels. This system is based on the principles provided by law. Let us consider in more detail the issues of essence, classification, functions and calculation of tax payments
Fractal indicator: concept, definition, classification, operation algorithm and application features

The fractal technical indicator is a universal and classic trading tool. Strategies created on its basis, when properly applied, bring good profits for traders and investors. In order to always make money in the financial market, it is necessary to use confirmatory tools in trading that allow you to filter and filter out false signals

