2026 Author: Howard Calhoun | calhoun@techconfronts.com. Last modified: 2025-01-24 13:10:27
The organizational structure of an organization is… What? Scheme of boxes with the names of departments of the organization, lined up in a certain order?
It is commonly believed by the layman that the organizational structure is a kind of theoretical concept that has a very mediocre relationship to a real organization. Moreover, within some existing enterprises, too little importance is attached to the organizational structure in the implementation of their economic activities. As a result, there are blurred functions and responsibilities among the heads of departments, a chaotic system of subordination, a lack of coherence in work and accomplishment of tasks to achieve the common goal of any business - making a profit.
Analysis of the financial condition of the organization begins with the study of its organizational structure. Who needs it? Representatives of the external environment of the company - creditors, investors, suppliers, buyers and customers, they all need to clearly understand the logic of the activitypartner firm. Representatives of the internal environment - directly to the employees of the enterprise, who also need to know how they interact with colleagues, to whom they report, and to whom they can delegate part of the responsibilities. The set of groups of all employees constitutes the organizational structure of the organization's personnel.
What is the organizational structure

So what is this concept? The organizational structure of an organization is the totality of all its divisions, between which functions and tasks are distributed, as well as the relationship between them.
Organizational structure of enterprise management
The organizational management structure is the configuration of the management system that defines the authority and responsibility, accountability and relationship between the heads of departments, as well as establishing the list of staff duties.
Among the main types of organizational structures are linear, functional, linear-functional, divisional, matrix and combined.
Linear structure
The linear type of organizational structure is characterized by the fact that each division of the organization is controlled by one leader who reports to a higher manager, etc. This type has become obsolete, because it is not flexible, does not contribute to adaptability to economic changes and the growth of the company in modern conditions. The leader must be able to navigate in different areas, be a truly broad-based specialist,to give orders to each service of the organization. Although the main advantages of the linear type can be distinguished by its simplicity, the clarity of the relationship between enterprise units and their functions.
Linear structure of the organization on the example of the army
The most striking example for characterizing the linear form of the organizational structure is the army, where, as you know, a clear scheme of organization of subordination of the junior in rank to the senior leads.

The organizational chart of the army officers is shown above.
Functional structure
Functional organizational structure implies the presence in the organization of separate services (for example, sales department, human resources department, accounting department, production and technical department, etc.), the personnel of each of which can interact with each other, and not only with main leader. This removes most of the burden from the chief manager, removes the task of finding broad specialists, which are the advantages of this structure. The presence in the departments of specialists in their field helps to improve the quality of products. Nevertheless, the use of a functional organizational structure complicates intra-company communications and contributes to the development of a tendency to shift the responsibility of employees of some services to employees of others.
Functional form of the organizational structure of management on the example of an organization for the production of dairy products
Let's consider this type of organizational structure on the example of a food enterpriseindustry.

The diagram of the functional type of the organizational structure shows the relationship between the divisions of the enterprise. So, for example, the transport department interacts in the process of fulfilling its duties with the divisions of the financial service: with the accounting department for consumption rates of fuel and lubricants and write-off of spare parts, with the sales department for issuing shipping documentation and coordinating the route, with the warehouse of raw materials and the main production for transportation between them materials for workshop needs, etc. That is, the divisions are functionally interconnected, but not subordinate to each other.
Linear-functional structure
Linear and functional forms of organizational management structures are extremely rarely used in their pure form. A linear-functional management structure is capable of solving the shortcomings of these types of organizational structures. From the linear it is generalized by the presence of line managers, from the functional it borrowed the presence of functional services that help the first, but are not administratively accountable to them.
Among the advantages of this structure, one should note a reasonable balance between unity of command and narrow-profile specialization of heads of functional services; the possibility of delegating authority to lower levels of linear links of functional services. But the disadvantages include the low degree of interaction between the personnel of functional units, since the relationship is often debugged only among their leaders. Principleunity of command, if strengthened, can adversely affect the quality of manufactured and sold products.
Linear-functional structure on the example of a household appliances and digital electronics store
To illustrate clearly what this type is, let's imagine in the form of a diagram the organizational structure of a home appliances and digital electronics store.

In the diagram, solid lines show linear connections, and dotted lines show functional ones. So, for example, the cash desk is directly (linearly) accountable to the accounting department, but in the process of performing its functions, it interacts with the sales department for collecting funds, with the sales department of the store, with the personnel department for issuing funds, and with the purchasing department for organizing payments to suppliers and contractors in cash.. The sales departments of the store are directly subordinate to the sales department, but in the course of their activities they are functionally interconnected with the purchasing department, and with the accounting department, and with the personnel service.
Divisional structure
Divisional structure differs in that divisions are grouped according to some criterion: by types of products, by regions, by groups of consumers. The positive aspects of using this model are a high level of responsiveness and adaptability to changes in the external environment of the existence of the company, the release of a product of higher quality and competitiveness due to the orientation of all participants in the production process to one division. Among the disadvantages of the structure, you neednote such negative phenomena as the duplication of functions of divisions and management, the growth of conflicts due to the duality of subordination, the complexity of managing divisions in general.
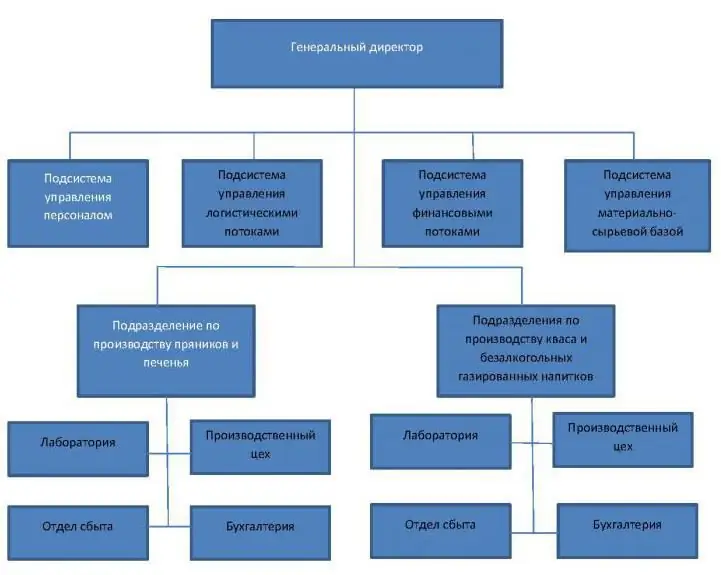
Divisional structure in the example of a food manufacturing plant
The organizational structure of a food production plant is shown as an example. The company is engaged in the manufacture of several types of products. One of the directions is the production of non-alcoholic carbonated drinks and kvass, and the other is the production of gingerbread and cookies.

As can be seen from the diagram of the divisional organizational structure of the enterprise, it took the types of products produced as the basis for the divisional division. Each includes a team of workers, a service of laboratory assistants, a group of sales managers and the composition of the accounting department for calculating payroll, product costing, etc.
Matrix type of organizational structure
The matrix structure is a type of structure with dual accountability. This type of organizational structure realizes itself in design work. For example, an organization receives an order to perform some type of work. To do this, a project manager is appointed and a number of performers from different functional services are allocated to him. However, they do not leave the subordination of their immediate supervisors, and upon completion of the work they return back to their unit. Among the advantages of this type of organizational structure:high speed of response and susceptibility of the enterprise to changes in the external environment, a high level of adaptability, optimal distribution of powers, responsibilities, accountability between functional and linear divisions. The disadvantages include confusion in prioritizing tasks between work on a temporary project and in a permanent unit, which also implies the threat of conflicts between project managers and the management of functional units. The very principle of dual accountability greatly complicates the entire management system.
To visualize this form of organizational structure more clearly, let's look at the diagram of the enterprise that took it as a basis.

The enterprise has 5 types of activities: emergency dispatch service, which provides emergency response services to several companies; provision of services for the current sanitary and technical repair of residential buildings; intercom installation services; wholesale and retail trade in electrical equipment. But the company also takes part in electronic auctions and undertakes the implementation of temporary projects. For each individual project, its manager is appointed, and a number of employees from each functional unit are released into his submission: an accountant, personnel officer, supplier and work team. After the completion of work on the project, the production staff is disbanded to the places where their direct duties are performed.
Combination structure
The main characteristic of the combinedThe organizational structure of an organization is the combination of several of the above types in it. It contains features of line management, functional relationships, division of services according to selected criteria, as well as the principle of dual subordination. The combined organizational structure makes it possible to increase the flexibility of the enterprise and its susceptibility to changes in the internal and external environment. The advantages and disadvantages of the combined structure are the same as the structures underlying it.
Combined management structure on the example of an enterprise for the extraction and processing of apatite-nepheline ore
Let's consider this form of organizational structure on the example of an organization with branches in different regions of the country, as well as engaged in several activities. Below is a diagram of the combined organizational structure.

Management is carried out by the general meeting of shareholders, which stands above the board of directors. The Board of Directors appoints the General Director and the composition of the collegial body of the Management Board, whose duties include managing the strategic development of the enterprise. The Management Board and the General Director are linearly subordinated to the Departments of Finance, Human Resources, Main Production, Logistics and Material Flows. The functional subdivisions of the Complex are enterprises engaged in the extraction, enrichment, processing, transportation of ore, as well as a research group. The organizational structure of the departments of the organization that carry out their activitiesin different regions, also constitute linear and functional services.
Regardless of the form, the organizational structure must perform the functions of dividing tasks between the departments of the organization, determining the competence of each of them in achieving the final result of the activity, and also control the inviolability of the relationship between departments.
Recommended:
Essence and concept of organization. Form of ownership of the organization. Organization life cycle

Human society consists of many organizations that can be called associations of people pursuing certain goals. They have a number of differences. However, they all have a number of common characteristics. The essence and concept of organization will be discussed in the article
Organizational structures of an enterprise - an example. Characteristics of the organizational structure of the enterprise
The implementation of plans and programs is achieved by building an organizational structure that allows you to effectively organize the joint activities of staff through the appropriate distribution of duties, rights and responsibilities. The article highlights the elements of the organizational structure, gives examples of its various types, highlights their advantages and disadvantages
Contract internal combustion engines: characteristics, advantages and disadvantages

The engine is the most expensive part of a car after the body. And after a serious breakdown, the owner faces a difficult question - to engage in costly repairs, or to change the unit. The idea to replace the engine is a good one - not to make a “capital”, but to immediately put in a contract ICE, especially since it will cost much less than repairing the old one. Today, replacing an internal combustion engine is not a problem, and the law allows you to change power units. And then another question arises - what is a contract engine, and where do they come from
What is the project structure? Organizational structure of the project. Organizational structures of project management

The project structure is an important tool that allows you to divide the entire course of work into separate elements, which will greatly simplify it
Organizational structure of Russian Railways. Scheme of the management structure of Russian Railways. Structure of Russian Railways and its divisions

The structure of Russian Railways, in addition to the management apparatus, includes various dependent divisions, representative offices in other countries, as well as branches and subsidiaries. The head office of the company is located at: Moscow, st. New Basmannaya d 2