2026 Author: Howard Calhoun | calhoun@techconfronts.com. Last modified: 2025-01-24 13:10:32
The project structure is used to define the end result to be achieved and to associate it with the required resources, activities, labor and equipment. The structure also allows you to connect the elements not only with the product or product that will arise in the end, but also with each other. The formation of the project should begin with what happens in the end. Next comes the main breakdown into blocks, which continue to be crushed and increase in number until the smallest detail required in production is taken into account. This process also includes establishing not only vertical, but also horizontal links between elements, if such actions are necessary.
What is the project structure?
The activity of any company in the world begins with the development of a common plan of action. For example, a company has an order for the supply of pasta. Now the management, specialized departments, analysts and other stakeholders draw up a plan, which is the project development structure. In this case, you need to determine where to get the raw materials from and where to process it to the desiredstates. That's two blocks. Each of them can develop further. The question of raw materials can be divided into the search for a supplier, transport for transportation and quality control. The processing of raw materials, in turn, is also divided. It is necessary to decide which room to use, where to find equipment, specialists, installers and how to start the production cycle. This is just the simplest example, because the blocks will continue to be divided until there are no questions left. This is how the main structures of the project help to achieve the desired result in a given time frame. When each performer accurately understands his functions and actions, realizes why each specific element is performed and what should be the final result, only then will the maximum efficiency of the enterprise be achieved.

Highlighted structure
The simplest organizational structure of a project is described above. But this is only the beginning. There is such a thing as a dedicated structure, which refers both to the process of organizing a company as a whole, and directly to a specific project. There is a certain company in which there is a clear division into functions, features, production cycles and the search for employees. But in order for the whole mechanism to work, management must first find a suitable project that will bring profit. This is done by a completely different company, which has its own structure. This is the specific type of organization. For example, a company is engaged in the production of metal products. The system has been worked out, but it is not clear what will happenprofitable to sell, and what products will lead to losses. To do this, another analytical firm is hired, which studies the market and issues its recommendations. Based on them, the entire working mechanism of the first company comes into action.
Dual type
This is the second type that the project management framework can accept. It implies the presence of two companies, each of which performs its part of the work. Subsequently, these elements are combined, and the final product is obtained. The same applies directly to projects within the same company. Take, for example, a company that develops computer games. One of its departments is responsible for the creation of graphics, and the second - for the storyline. Only when both components are ready and connected together, the finished product will appear. Usually this is done by another department (or company), which provides interaction between different structures and regulates their activities.

Complex design
This project structure is characterized by the presence of many departments (or enterprises) at once, each of which has its own area of responsibility. On the example of the same computer game, the whole system may look something like this: there is a management that has made a strong-willed decision to start creating a product. Then there are several departments, each of which must provide a part of the total product. They may not have their own specialists, which is why they have to hire people from outside. Those, in turn, can do the work themselves orentrust to someone else. That is, the basis of the company is literally a few blocks or departments. The rest is done by third parties. But the end result is already collected by the employees of the main company.
Functional structure
Above, we talked more about the process of organizing the work of an enterprise, although this is also directly related to project management. But the functional structure, which is the most common and popular along the way, is already a direct reference to projects. Its general principle was formulated by Max Weber back in the 20th century. Not much has changed since then. Such organizational structures of project management are distinguished by the presence of a strict hierarchy of subordination, division of powers, labor and functions. The standardization of all actions performed and the clear coordination of the entire process are actively applied. There is no binding of the personality of this or that employee to his functions, which makes it easy and simple to replace them with each other. The main positive features of this structure are the ability to stimulate specialization, reduce the total number of actions and significant savings in resources. At the same time, there are significant shortcomings. So, there is an isolation of different departments, the number of conflicts in the team increases, the overall efficiency of the entire production cycle decreases, and connections between horizontal departments gradually become more complicated, which had to be avoided. Basically, all this is due to the incompetence of the management team. This structure requires a minimum from a simple worker, but fromchiefs - maximum. They are required to respond to the smallest elements in a timely manner and ensure very clear interaction between horizontally located groups.

Functions of intermediaries
Since Max Weber was German, it is not surprising that such a system can work quite effectively for them. In conditions of mild or severe disorder of the leadership in domestic enterprises, connecting links are needed. In fact, they duplicate the functions of superiors, not having management rights, but having extensive control capabilities. As a result, the project work structure has acquired such a concept as intermediaries. These are special people (or entire departments) who regulate the interaction between horizontal groups. Ultimately, such coordinators give the final result to higher management at the same time as direct managers, whose function is reduced to the transfer of commands and general leadership. If they try to delve directly into the project and ensure the interaction of individual teams, the situation usually only gets worse.

Matrix structure
This is the next form that occurs as the number of intermediaries increases. This business project structure is called matrix. The main problem here lies precisely in the fact that those very coordinators receive much more management opportunities and, in terms of their functions, are closer to the heads of departments. It is very difficult to clearly distinguish whatmay indicate one leader, and what - another. For simplicity, they are divided into project and functional chiefs. The former provide a common system of interaction between departments. They are obliged to clearly and understandably convey the whole idea to subordinates, as well as understand the peculiarities of the work of units. They must establish communication between different employees and take into account their whims, desires and requests. Also, these bosses are responsible for possible unforeseen situations and the absence of conflicts. Functional managers, in turn, ensure the availability of the required resources, appoint the time and place of work, are responsible for the quality of manufactured products, as well as their compliance with the stated requirements. It is these people who are obliged to adapt very quickly to different conditions, including the most unfavorable ones for work. They must find a way out of difficult situations and ensure the production of products of the declared quality just in time.

Design type
This project structure is especially useful for those types of enterprises whose entire activity is tied to one or more projects. In this case, each of them has everything necessary to perform its functions. For example, there may be several accounting departments, financial departments, design bureaus, and so on for each of the projects separately. The rest of the units, which are not included in any of the groups, provide exclusively auxiliary, albeit very important, functions. The personnel department can be one and respond to applications from alldivisions. Such, for example, may be the structure of an investment project. It is inherent in the responsibility of each of the employees for the final result, very flexible and vague management and the absence of clearly regulated actions for each employee. Such structures can change their profile very quickly, respond to non-standard situations and fulfill orders in the shortest possible time.
Separation and features
All organizational structures of project management can be conditionally divided into two large groups - mechanistic and organic. The first is a functional system, and the second is a matrix system. Design is included in both categories at once, as it is very flexible. Mechanistic types of structures are distinguished by a clear vertical of power, strictly regulated functions and actions of employees, and so on. Organic, on the contrary, are very simple, flexible and do not have the ability to clearly indicate to each employee what and how to do. Both options are valid. The first is best suited for the production of specific products. For example, a car. When each worker performs only his own functions, nothing will distract him. But for more creative projects, it is more profitable to use a matrix structure, since sometimes it is “abnormal” interaction between employees that gives the maximum result at the lowest cost.

Creation
The structure of the project plan is difficult to draw up, because the entire subsequent production process depends on it. Practicallyit is impossible at the initial stage to set precise tasks and identify specific actions. First you need to choose the shape of the structure itself. It should correspond to the peculiarities of the interaction between all parties of the project, fit its content and work successfully within the existing external environment. The project management structure is usually created once in a long time, so it is better to spend more time on it and get the most effective result than to constantly rework it in the near future. The next stage is detailed planning for the current situation. At the very end, methodological, organizational, reference and other useful documentation is collected for each stage, department or group of employees. This also includes staffing, job descriptions, requirements for the availability of specialists, as well as the application of all this within the overall project budget.
Distribution by areas of responsibility
As mentioned above, the organizational structure of the project is based on the responsibility of all categories of employees. It is logical that the higher the personal interest of an individual employee, the more effective the overall process will be. It is necessary to convey to all groups of people participating in the project the importance of the actions they perform and the impact on the final result. Naturally, one should not forget about responsibility. It is necessary to explain how catastrophic the consequences will be if an employee fails to perform his functions. You can also designate rewards for correct work and pen alties for errors. Everyone should know all this, and the information itselfmust be as simple and accessible as possible. For example, somewhere in the job description it will be vaguely written that if the locksmith Sidorov does not work as it should, he will be punished. It's inefficient. It must be said directly that the detail that he makes is needed in order for the car to go. Without this, the project will fail and the company will suffer a loss of 1 million. And only he will be to blame. But if this locksmith does one more part in the same time, he will receive a bonus in the amount of half the salary. Everything is clear, understandable and accessible. The punishment is indicated and there is a reward.

Detail Features
In most cases, especially when a mechanistic project work structure is used, the maximum detail of any issue is required. You need to keep dividing blocks and elements until there are no parts left uncovered. In some cases, this process can take place already when the project starts its work, the main thing is that this does not affect the overall efficiency of the work. But there are also such enterprises in which an accurate description of actions and maximum detail can only interfere. This usually applies to creative teams. For example, the situation with the creation of a computer game was described above. If you give clear commands to all employees, the product will be created quickly and at minimal cost. However, great ideas or good comments from all project participants will be ignored, which could turn a mediocre game into a masterpiece worthy of many awards.
Result
In general, the project structure must be thought out in as much detail and precision as the current production process requires. It is impossible to apply uniform norms and examples to absolutely all enterprises without exception. You always need to take into account a lot of features and parameters that may not be obvious to most employees at the beginning of a project, but can become a significant problem closer to its end. And the main thing to remember is that the project structure is not a rigidly fixed scheme. It can and should be constantly refined, refined and deepened. Only in this way it will be possible to achieve the highest efficiency in the minimum amount of time and with little expenditure of resources.
Recommended:
Organizational structure of business and its development

The most important issue in any successful project is the structure of the business. After reading this article, you can easily evaluate your business development strategy and, if necessary, adjust it
The organizational structure of an organization is Definition, description, characteristics, advantages and disadvantages
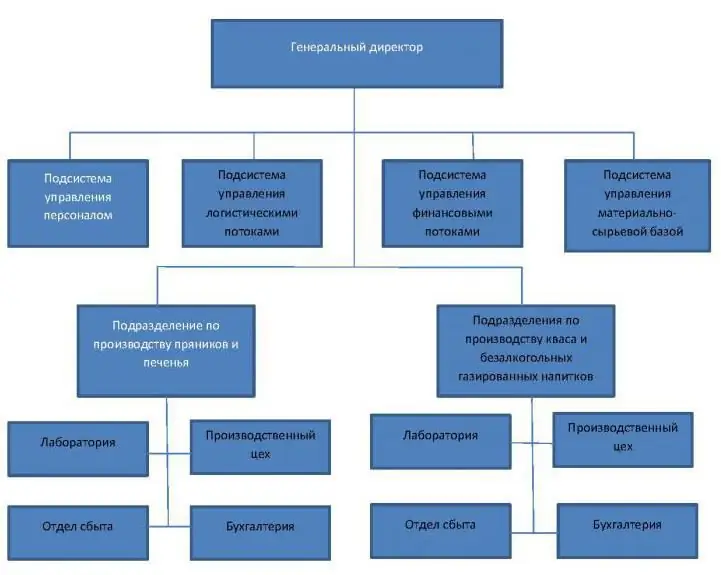
The article reveals the concept of the organizational structure of an enterprise: what it is, how and in what forms it is used in modern enterprises. The attached diagrams will help to visually illustrate the use of different types of organizational structures
Organizational structures of an enterprise - an example. Characteristics of the organizational structure of the enterprise
The implementation of plans and programs is achieved by building an organizational structure that allows you to effectively organize the joint activities of staff through the appropriate distribution of duties, rights and responsibilities. The article highlights the elements of the organizational structure, gives examples of its various types, highlights their advantages and disadvantages
Organizational structure of Russian Railways. Scheme of the management structure of Russian Railways. Structure of Russian Railways and its divisions

The structure of Russian Railways, in addition to the management apparatus, includes various dependent divisions, representative offices in other countries, as well as branches and subsidiaries. The head office of the company is located at: Moscow, st. New Basmannaya d 2
Centralized accounting: organizational structure, principle of operation

Centralized accounting acts as a specialized unit. At the initial stage, such institutions were formed under state and local bodies - managers of budget revenues. Currently, centralized accounting is a relatively independent legal entity

