2026 Author: Howard Calhoun | calhoun@techconfronts.com. Last modified: 2025-01-24 13:10:33
The modern construction market today is simply overflowing with a variety of thermal insulation materials. They differ not only in the features of manufacturing technology, but also in their properties, as well as their purpose. However, one of the most popular is extruded foam, which will be discussed below. It can be used not only for thermal insulation, but also to protect the building from external noise. To increase efficiency, you can lay the material in several layers.
Description
EP has unique thermal insulation qualities, and in appearance it resembles foam plastic, which is used today for facade insulation. Specifications far exceed those of traditional foam. It is made from polystyrene granules, which are melted under the influence of high temperature and form a viscous state. Under high pressure, carbon or freon is injected into the chamber, each of which is a foaming agent. The resulting mass is extruded through the extruder and forms a certain shape.

For reference
This technology allows you to create extruded foam, which has a cellular closed structure and resists the penetration of heat and moisture. It is resistant to aggressive environments such as alkalis and acids, and it can be used at extremely low temperatures, which can reach -50 ° C. If we are talking about the highest possible temperature, then it is kept at +70 ° С.

Material thickness
If you decide to purchase extruded foam, you should know what its thickness is. This parameter is different for different companies, so you can find plates on sale, ranging from 20 mm to 20 cm. This raises the question of what thickness to choose for certain work. To do this, you should know what is the resistance to heat transfer of materials from which objects are built that need insulation.
There are established codes and regulations that indicate the nominal heat transfer resistance in certain regions. For example, in the center of Moscow, the resistance of the wall will be 4.15 m2°C/W, while for the southern regions this figure will be a maximum of 2.8 m2 °C/Tue
Once you determine the norm of the region, you should calculate the resistance of the material and subtract it from the norm. The resulting value will indicate the resistance of the expanded polystyrene. If you have results, then according to the table you will be able to determine the desired thickness of thermal insulation.

Material density
Extruded foam, the density of which is from 28 to 40 kg/m3, is represented by the PBS-S-40 brand. Sometimes the manufacturer tries to mislead the buyer, because it will take less money to manufacture polystyrene foam of lower density. Therefore, you should not focus only on the number in the brand name, you need to ask about the technical characteristics that should be indicated in the certificates.
It will be great if you are told exactly how the material is made. If the density is 35kg/m3, then it is extrusion. In the usual way, you can achieve a density that does not exceed 17 kg/m3.

EC thermal conductivity
Extruded foam, the thickness of which was mentioned above, should be selected by the consumer not only on the basis of these data, but also taking into account thermal conductivity. The insulation described in the article is a huge amount of air bubbles that are separated by thin shells of polystyrene. In this case, the ratio is: 98% air and 2% polystyrene. The result is a kind of hard foam. The air is trapped inside the bubbles, thanks to which the material retains heat. An air gap without movement is an excellent heat insulator.
If we compare it with mineral wool, then its thermal conductivity will be higher. It will make indicators from 0.028 to 0.034 W / (m K). The denser it will befoam, the greater the value of the coefficient of thermal conductivity. Thus, for an extruded foam whose density is 45 kg/m3, this parameter is 0.03 W/(m·K). In this case, it should be taken into account that the ambient temperature should not be higher than +75 °С and lower than -50 °С.

Basic Features
Extruded foam, the thermal conductivity of which was mentioned above, has certain properties, including almost no water absorption and low thermal conductivity. Even if the plate is completely immersed in water for 10 days, the cells will not let moisture through, since they are insulated, only the side open cells will be filled. Thermal conductivity was discussed above, it should also be mentioned that this parameter is much smaller compared to other thermal insulation materials. Plasticity is also not so high, but the fragility is impressive, especially if we draw a parallel with expanded polystyrene.
The material has the ability to transmit light, and its compressive strength is quite high. Thermal insulation does not rot and is highly frost-resistant. Extruded foam is impact-resistant:
- acids;
- water;
- caustic alkalis;
- oils;
- bleach;
- saline solutions;
- dyes;
- alcohol;
- hydrocarbon;
- cement;
- acetylene;
- paraffin;
- propane;
- butane.
Nonot to mention the safety for humans.

Specifications
Extruded foam, the characteristics of which have been partially mentioned above, has a minimum water absorption that varies from 0.2 to 0.4%. The weight is quite small and can vary from 25 to 45 kg/m3. Among the disadvantages, one can single out poor vapor permeability, which is 5 times lower compared to traditional foam. This value is 0.013 Mg/(mhPa). This increases the requirements for the ventilation systems of the house, which will be insulated with extruded polystyrene foam.
Extruded foam, the technical characteristics of which will be of interest to the consumer, has another drawback, which is expressed in high flammability. The material belongs to the G3-G4 class, but today many manufacturers use special additives that have made it possible to achieve almost non-combustible characteristics. Therefore, this thermal insulation can sometimes be attributed to classes G1 and B1.
However, if you look at the sanitary norms and rules, it can be emphasized that extrusion boards, which have a high degree of flammability, can be used in building structures. If the building is subject to increased fire safety requirements, then extruded polystyrene foam should be used, which belongs to the combustibility group G3.
Conclusion
The federal law on combustible thermal insulation materials has recently been released, it contains information on indicatorstoxicity of combustion products. For high-quality polystyrene foams, toxicity does not exceed T2, which indicates that this thermal insulation is moderately dangerous. This indicator is inherent in wood materials, for example, parquet. The service life is comparable to the life of the building, and for quality manufacturers this figure reaches 40 years.
Recommended:
Foam block: foam block dimensions, history of appearance and application prospects

Each movement of the bricklayer is performed at a certain speed. An ordinary clay brick weighing about 3 kg or a large foam block of the same mass will be installed in the wall in the same time. But the dimensions of the foam block are eight or even twelve times the size of a brick, which dramatically increases the speed of masonry. Another important advantage of a light and warm building material is that it requires an adhesive rather than a complex cement-sand mortar
Thermal conductivity of concrete: features, coefficient and table

The thermal conductivity of concrete is determined by special formulas. For different types of material, this indicator may be different. Lightweight concrete retains heat better, heavy concrete worse
Thermal conductivity of sandwich panels: concept, main characteristics, dimensions, thickness, thermal conductivity coefficient, installation rules, pros and cons of operation
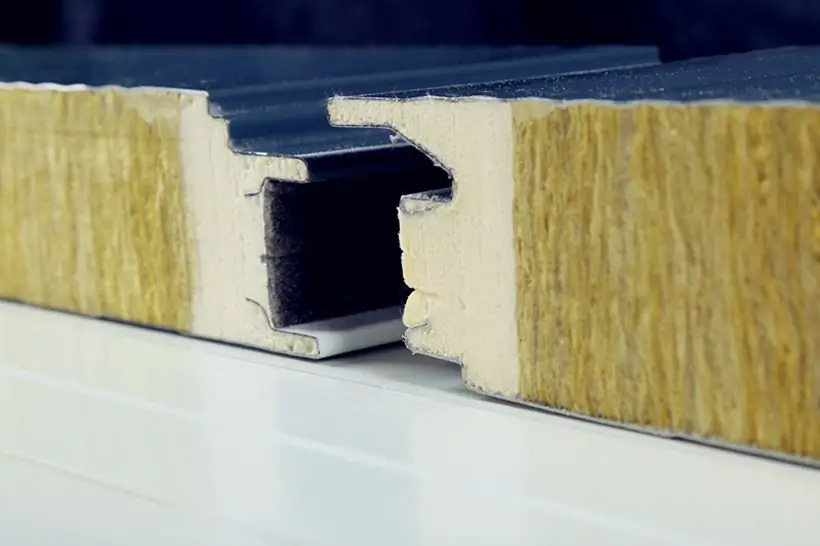
Thermal conductivity of sandwich panels will be the lowest if polyurethane foam is the basis. The parameter under consideration here varies from 0.019 to 0.25. The material is strong, dense and light. It is chemically resistant and does not absorb moisture. Rodents are indifferent to polyurethane foam, fungi and mold do not develop inside it. Working temperature reaches +160 ˚С
Expanded clay: thermal conductivity, properties and technical characteristics
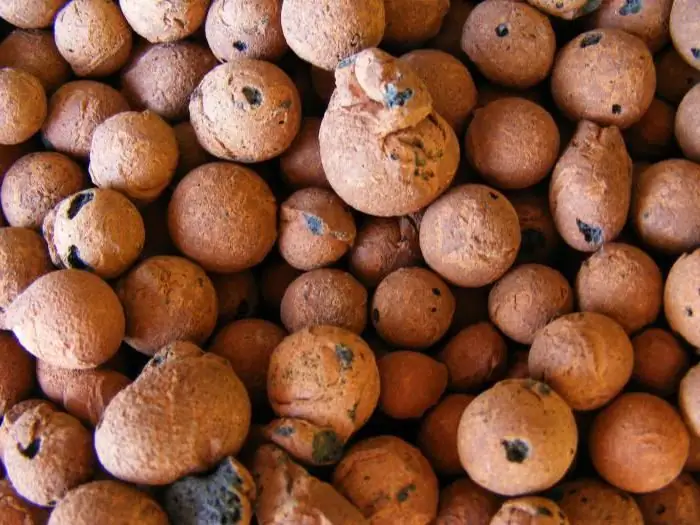

Expanded clay is made from slate and clay and is suitable for environmentally friendly and modern housing construction. Expanded clay is also used for decorative purposes, and at home it is suitable for solving the problems of growing cultivated plants
Thermal conductivity of mineral wool: properties and features

If you are looking for protection from the winter cold and summer heat, you can use mineral wool insulation. This material is presented for sale in several varieties, each of which has its pros and cons, so you need to study them before making a purchase

