2026 Author: Howard Calhoun | calhoun@techconfronts.com. Last modified: 2025-01-24 13:10:37
Today, in the era of a rapidly changing digital world, it is difficult to keep up with the pace of events. In order to do everything, it is necessary to correctly set tasks, goals, distribute and delegate authority. Logic and analysis are the best helpers in solving complex problems. One of the tools of logical construction is decomposition. Consider it in detail.

Definition
In a general sense, decomposition is the division of the whole into components. This is a fairly simple and understandable technique that helps to solve complex problems every day, presenting them as a sum of parts. In the system of logical constructions, decomposition is a scientific technique that solves a large problem by replacing it with several smaller and simpler problems.
As a rule, decomposition is carried out using a "problem tree", "goal tree", "decision tree", "work tree", in the construction of whicha clear hierarchical structure is formed, including vertical and horizontal subordination and feedback.
Features
The basis of any decomposition is structural subordination to all the rules of the method. Of the fundamental and governing the entire system of rules, the following can be distinguished:
1) The tier system must always be respected.
The decomposition method is based on the subordination of a lower level to a higher one. This is achieved by building a hierarchical structure using so-called "trees".

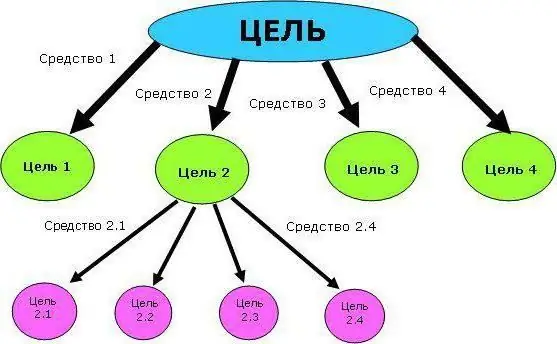
It is customary to build a tree of problems and a tree of goals first, in order to clearly and visually represent all the tasks that are currently available. At the same time, subordination should look in such a way that lower-level tasks reveal the essence of higher-level tasks, and all subtasks represent the entire project. Understanding the exact and complete picture of the percentage completion of a decomposition project comes only when the goal tree is 100% full.
With simple formal algebra and logic, you can also build AND trees and OR trees.
2) The dismemberment of the whole into parts should occur only on one basis.
This principle implies that all subtasks will be subordinated to a single idea and goal. A construction project can serve as an example of decomposition. A functional feature is taken as the main sign of splitting, then the project is divided into sections. For example, these can be the following main sections: constructionsreinforced concrete (KZh), architectural solutions (AR), metal structures (CM), heating and ventilation (OH), etc. In turn, these sections should also be broken down by functional features, that is, the essence of the main goals should be presented in the subgoals of the next level. For example, the heating and ventilation (HV) section is divided into an explanatory note, drawings, design, passing normative control and technical control, issuing documentation, architectural supervision, adjustments according to comments, etc.
Time frames (terms), subject characteristics, structural features, technological characteristics and others can also be used as a feature.
3) All decomposition subsystems should reveal the essence of the system.
If you represent the main task as 100%, then all subtasks should add up to the same 100%. At the same time, each subtask of the first level contains its own percentage, representing the sum of subtasks of the second level.

It is important to understand that all split subtasks of the same level should be independent of each other, while the hierarchy of tasks along one branch should be based on the principle of dependence and feedback: a task of a higher level depends on its subtask, and vice versa.
4) The depth of decomposition work should be determined at the initial stage.
Before you create a hierarchical structure, you need to decide what the last level of subtasks will be. In some cases, it is not necessary to create many levels, sinceThe purpose of decomposition is visibility. In the case when the hierarchy is created for accurate calculations, the number of levels should be such as to reveal the topic in as much detail as possible.
Classification
Today, several types of decomposition are known. You can also create your own techniques for a specific project. However, to one degree or another, they will relate to the main types, namely: decomposition of goals (the first and fundamental type), systems (the process of breaking the system into subsystems in order to work out and get the best result), process, work (drawing up a hierarchy of work to designate weak points and highlighting the main and paramount).

As a rule, all the listed processes are interconnected and as a whole represent a complete decomposition structure.
Decomposition of goals
To get started, a tree of problems and a tree of goals are compiled. The problem tree is a structural diagram of the main problem, divided into problems of the second and third levels. In this form, they become much easier to solve. After a detailed analysis of the problems, a goal tree is compiled, which is a resolved problem tree. That is, for every problem there is a solution. At the same time, the already prepared structure and interdependencies of subtasks are preserved.
Action analysis
Work decomposition is a logical construction that begins when all goals and problems are identified and is a hierarchical structure of all actions that need to be carried out to solve a particular task.
This logical scheme allows you to identify those stages of work at which problems arose. Since subtasks depend on high-level tasks, the work tree allows you to see where there are problems and shortcomings. Often, work at lower levels suffers from weaknesses in the first level of decomposition.
For example, if the purchaser did not submit an application for self-tapping screws, then the accounting department did not post invoices and did not purchase them. At the construction site, everything is at a standstill, because the installers do not have enough self-tapping screws to work.
Classic technique
To conduct a more detailed analysis of structures, identify their weaknesses, main goals and directions, tasks, projects and works, systems are decomposed.
The system is divided both horizontally and vertically into levels. They should form an overall picture of the structure. System decomposition is a general example of a hierarchy for any kind of decomposition.
Business Applications
To describe and analyze the activities of companies, as a rule, process decomposition is used. Using the hierarchy, you can identify the pain points of the company, the areas where failures occur.
Processes are summarized and analyzed, after which a detailed report on the company's activities is compiled.
Decomposition example
As an example, consider a project for the construction of a capital construction facility. Development is carried out in 2 stages: working documentation and project documentation. These will be subtasks of the first level. At the design stageworks will be represented by estimates and projects. At the working stage as well. These are subtasks of the second level. For example, a project is usually presented in the form of the following parts:
- general explanatory note;
- scheme of the planning organization of the land plot;
- architectural solutions;
- constructive and space-planning solutions.
Followed by subsections:
- power supply system;
- water system;
- water disposal system;
- heating, ventilation and air conditioning, heating networks;
- communication networks;
- gas supply system;
- technology solutions.
Sections and subsections of design and working documentation are subtasks of the third level.

Each section consists of certain stages and must contain information according to state standards. For example, the technological solutions section of the project necessarily includes a text part with a detailed description of the technological scheme and the accepted equipment, a graphic part (plans, sections, diagrams), a list of equipment, project design, site visits, passing normative control and technical control, and issuing documentation.
At each level, responsible executors are appointed, from whom the result is then required. In this decomposition example, the performers of the first level are the head of the project department, the second - the chief project engineer (CPI), the third - design engineers.
Briefly about the main things
Decomposition is a method of formal practical logic that involves a qualitative study of the main task in accordance with the main goal of the work. This approach ensures the involvement of personnel at all levels to solve multi-level tasks. This allows the project to be carried out most efficiently, with the least financial investments and labor costs.
Recommended:
What is the meaning of labor discipline? The concept, essence and meaning of labor discipline

It is difficult to overestimate the importance of labor discipline. Indeed, in labor relations, the employer and employee often face situations where both consider themselves right, but their opinions do not lead to agreement. Labor discipline legally regulates many points in which disputes and dissatisfaction among participants in labor relations simply do not arise. The next article is about the main points of labor discipline
The meaning of the word "irrigation". What is irrigation?

Russian speech is replete with terms that came from foreign languages. One of them is the word "irrigation". What is irrigation? From Latin, this term is translated as "irrigation". It is used with different meanings in different areas of life
What is the meaning of the word "offer"?

With the introduction of market relations in our country, the meaning of the word "offer" has become of interest to an increasing number of people. His understanding will be especially useful for those who start their own business. And also to those who participate in various kinds of promotions, which in fact turn out to be not so profitable for buyers. What is oferta, the meaning and interpretation of the word in Latin, will be discussed in the article
Who is the opponent? The meaning of the word "opponent"

"Opposition" is a word of Latin origin. More often used in a political context. Who is an opponent? In order to answer this question, it is worth watching any of the political shows that are regularly shown on television. The article considers the meaning of the word "opponent", as well as its synonyms
Soil appraisal is The concept, meaning, methodology, stages, goals and economic feasibility

Soil appraisal is an assessment of the condition of the soil in certain districts, regions or regions for its fertility. In the process of carrying out this procedure, specialists combine lands with similar characteristics into groups

