2026 Author: Howard Calhoun | calhoun@techconfronts.com. Last modified: 2025-01-24 13:10:38
It is known that metals with a high degree of purity (99, 99 and more percent pure substance) have low strength, which makes them difficult to use. The exceptions are aluminum and copper used in electrical engineering. Steels, in connection with their functionality, must have rigidity, wear resistance, hardness, and also, in some cases, ductility and elasticity, so pure iron is unsuitable for their creation.

Alloy steels differ from ordinary ones by the presence of artificially introduced additives that predetermine certain properties of the future alloy. So, in ordinary carbon steel, "grains" of ferrite, cementite and perlite are contained in various proportions. With the introduction of alloying elements, the amount of carbon in pearlite is most often reduced (the strength of steel increases).
Alloy steels due to the introduction of additional substances often have a distorted crystal lattice, which can provide additional toughness (when grindingpearlite and ferrite grains), reducing internal stress, reducing the likelihood of cracks during hardening or increasing the depth of annealing of the material, etc.
The properties of alloy steel are directly dependent on additional components. For example, chromium and nickel elements save metal parts from corrosion, manganese increases impact resistance, increases wear resistance and hardness. An element such as silicon allows products to better withstand the effects of acids, and cob alt increases heat resistance.

Alloy steels are divided by chemical composition into high-, medium- and low-alloyed (the content of additives is more than 10%, 2.5 - 10% and less than 2.5%, respectively). Medium-alloyed steels are mass-produced (additions are about 5-6%) with a pearlite structure. Other structural compositions of alloys (martensitic, carbide, austenitic, ferritic) are less common.

For materials of this type, as well as for other industrial products, there is a GOST. Alloy steels are classified according to state standards No. 4543 - 71, from which you can find out the number of additional components in steel of a particular grade. For example, a chromium-manganese-nickel alloy with titanium and molybdenum sample 25KhGNMT contains up to 0.29% carbon, up to 0.37% silicon, up to 0.8 percent manganese, up to 0.6% and 1.10% chromium and nickel (respectively), to half a percent molybdenum and up to 0.09 percent titanium. In addition to the range andtechnical requirements, GOST contains complete data on product testing methods, rules for acceptance, transportation, packaging, etc.
Alloy steels are also divided into several groups according to their purpose: structural (used in mechanical engineering, construction of bridges, wagons, oil and gas pipelines, springs, springs, etc.), tool (of which cutting tools are made, such as drills, files, saws, milling cutters, etc.) and special-purpose steels with high resistance to electrochemical type corrosion.
Recommended:
Steel weldability: classification. Weldability groups of steels

Steel is the main structural material. It is an iron-carbon alloy containing various impurities. All components included in its composition affect the properties of the ingot. One of the technological properties of metals is the ability to form high-quality welded joints
Density of steel in kg/m3. Carbon and alloy steels
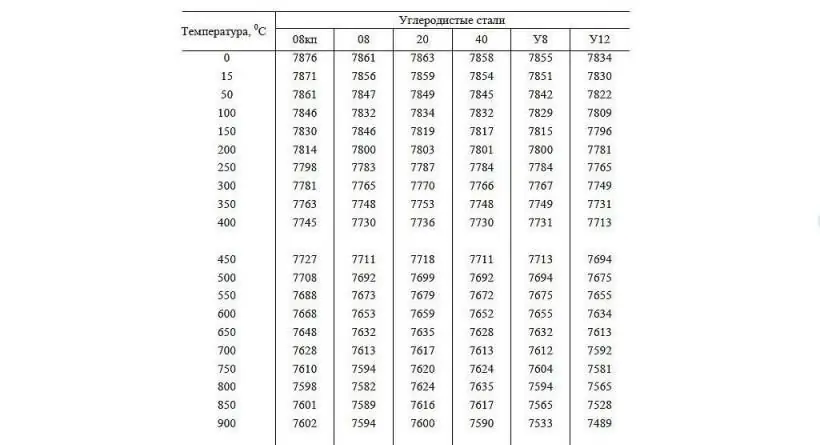
Steel is the most common metallic material in the industry, on the basis of which structures and tools with desired properties are made. Depending on the purpose of this material, many of its physical properties, including density, change. In this article, we will consider what steel density is in kg / m3
Heat resistance and heat resistance are important characteristics of steels
Ordinary structural steels, when heated, abruptly change their mechanical and physical properties, begin to actively oxidize and form scale, which is completely unacceptable and creates a threat of failure of the entire assembly, and possibly a serious accident. To work at elevated temperatures, materials engineers, with the help of metallurgists, created a number of special steels and alloys. This article gives a brief description of them
Heat-resistant alloys. Special steels and alloys. Production and use of heat-resistant alloys

Modern industry cannot be imagined without such material as steel. We encounter it at almost every turn. By introducing various chemical elements into its composition, it is possible to significantly improve the mechanical and operational properties
Spring steels: characteristics, properties, grades, GOST. Spring steel products
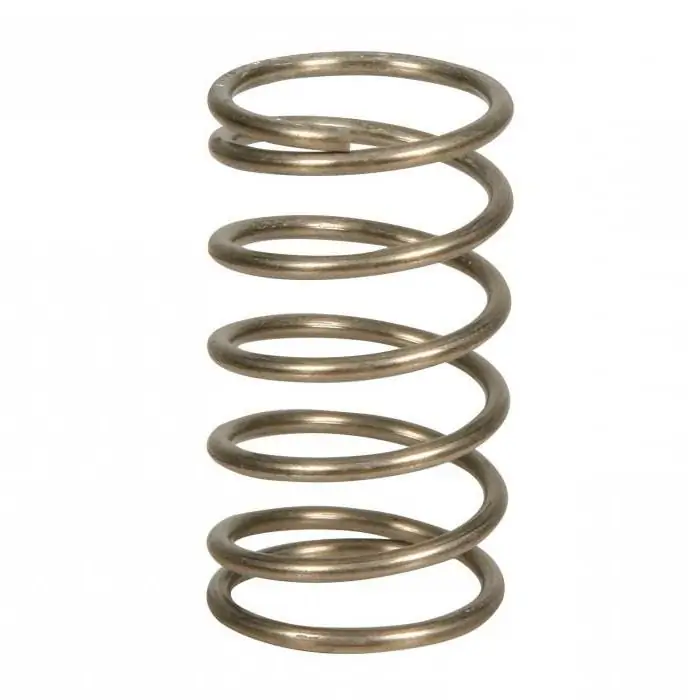

Currently, a lot of different equipment runs on springs, leaf springs, etc. High demands are placed on these details. Spring steels are the appropriate material for their manufacture

