2026 Author: Howard Calhoun | [email protected]. Last modified: 2025-01-24 13:10:30
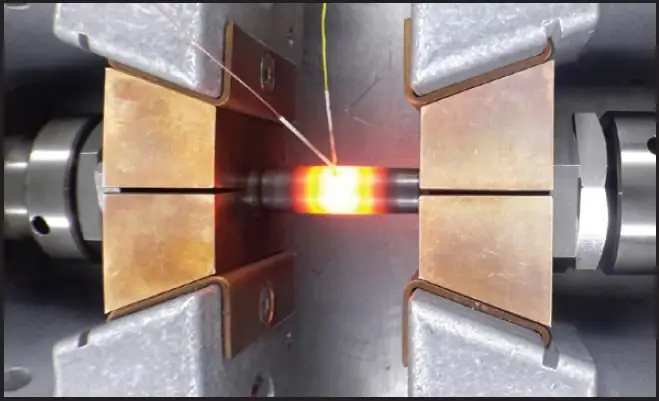
Heat resistance and heat resistance are very important characteristics. Some mechanical engineering products operate in very difficult conditions at elevated temperatures. Conventional structural steels, when heated, abruptly change their mechanical and physical properties, begin to actively oxidize and form scale, which is completely unacceptable and creates a threat of failure of the entire assembly, and possibly a serious accident. To work at elevated temperatures, materials engineers, with the help of metallurgists, created a number of special steels and alloys. This article gives a brief description of them.
Heat-resistant steels
Many people equate the concept of heat resistance with such a concept as heat resistance. Under no circumstances should this be done. Heat resistance is also called red brittleness. And this concept means the ability of a metal (or alloy) to retainhigh mechanical properties when working at elevated temperatures. That is, such a metal, even when heated to a red glow (it is typical for temperatures above 550 ° C), will not creep and retain sufficient rigidity.
In simple terms, heat resistance is the ability of a material to maintain performance when heated to high temperatures. Ordinary structural steels, even with slight heating, become ductile, which excludes the possibility of their use for the manufacture of products operating at high temperatures.
Different grades of metals and alloys have different heat resistance. This indicator depends on the chemical composition of the material. Heat resistance tests can be carried out over a long period of time. But most often, samples heated in an oven to a certain temperature are tensile tested for a short period of time.

Heat-resistant steels
Heat resistance, in contrast to heat resistance, is the ability of materials to resist the development of corrosion processes when working at high temperatures. Ordinary steels, if subjected to heat (with the exception of heat treatment in a protective atmosphere or in a vacuum), begin to oxidize. In addition, with prolonged heating, the carbon on the surface of the product begins to burn out. As a result, the surface is depleted of carbon, which leads to a sharp change in the mechanical properties (primarily hardness) on the surface. Wear resistance drops. Gets such a negative developmentphenomenon, like a bully. This group of steels can operate at temperatures around 550 °C.
In order to increase the heat resistance of steel, its melt is alloyed with silicon, aluminum and chromium. Sometimes it is enough to increase the heat resistance of the surface of the part. In this case, siliconizing or aluminizing (saturation of the surface layer with silicon or aluminum atoms, respectively) is resorted to in a powder medium.

High melting point materials
When operating at especially high temperatures, the considered materials cannot be used, since at a temperature in the region of 2000 ° C, melting begins to occur (a liquid phase is released). For these purposes, refractory metals are used: tungsten, niobium, vanadium, zirconium, and so on. These materials are quite expensive, but engineers have not yet found a worthy alternative for them.
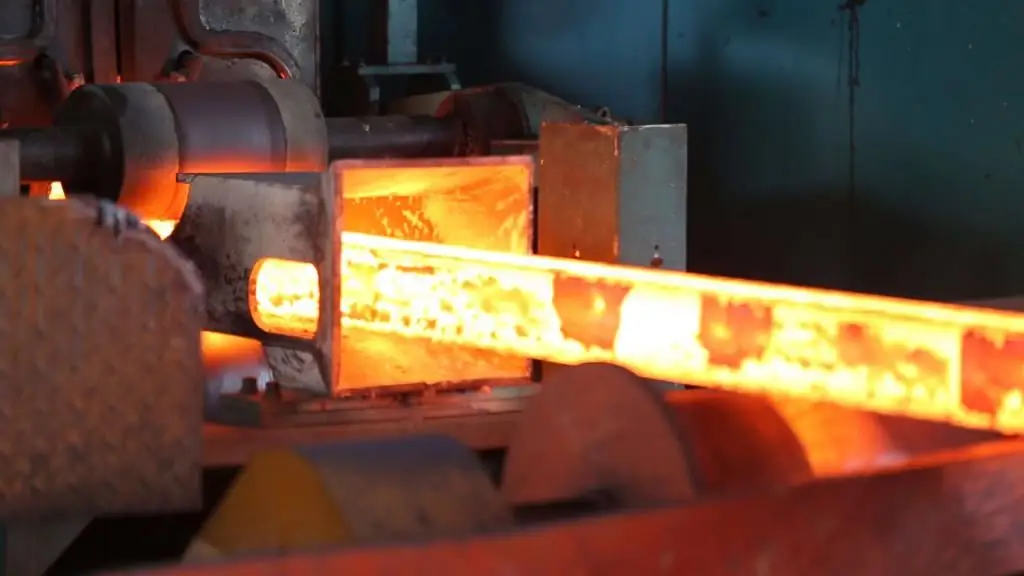

Characterization of chromium and nickel based alloys
Alloys with high heat resistance are in great demand in power engineering (blades of steam turbines, parts of aircraft engines, and so on). Moreover, the need for such materials is constantly growing. Moreover, the production requires scientists to obtain more and more advanced materials that can maintain their performance at very high temperatures. Therefore, work is constantly underway to increase the heat resistance. Nickel, or rather alloying steel with this element, contributes to this.
All heat resistant steelsare alloyed with nickel (not less than 65%). Chrome is a must. The content of this element should not be less than 14%. Otherwise, the metal surface will oxidize intensively.
Steels are additionally alloyed with aluminum, vanadium and other refractory elements. Aluminum, for example, even at room temperature is covered with a thin oxide film, which prevents corrosion from penetrating deep into the metal. That is, no scale is formed.
Recommended:
Heat energy tariff: calculation and regulation. Heat energy meter

Who approves and regulates heat tariffs? The main factors affecting the cost of the service, specific figures, the trend of increasing cost. Thermal energy meters and self-calculation of the cost of the service. Prospects for billing. Varieties of tariffs for organizations and citizens. Calculation of REC tariffs, documentation required for this
Heat-resistant alloys. Special steels and alloys. Production and use of heat-resistant alloys

Modern industry cannot be imagined without such material as steel. We encounter it at almost every turn. By introducing various chemical elements into its composition, it is possible to significantly improve the mechanical and operational properties
Spring steels: characteristics, properties, grades, GOST. Spring steel products

Currently, a lot of different equipment runs on springs, leaf springs, etc. High demands are placed on these details. Spring steels are the appropriate material for their manufacture
Support and resistance level. How to trade support and resistance levels correctly?
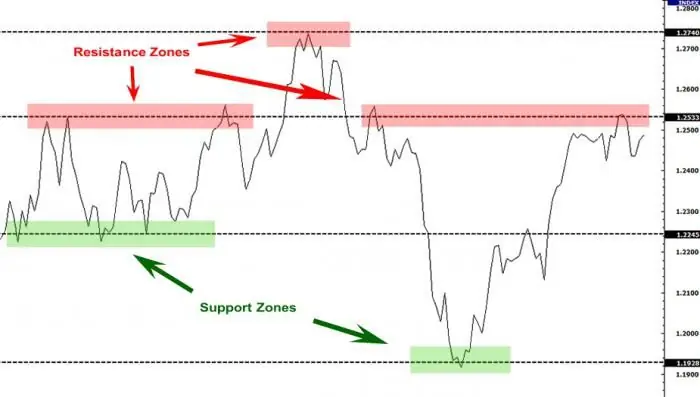
Support and resistance levels are the dominant concepts of the technical analysis of the foreign exchange market. Based on them, a large number of trading strategies have been developed, despite the fact that the lines belong to the category of inaccurate instruments
Types of heat transfer: heat transfer coefficient
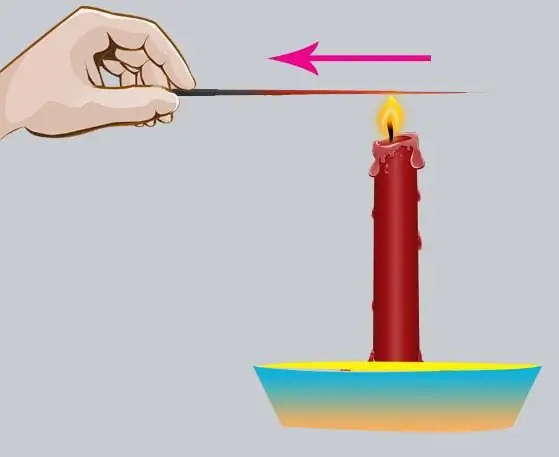
Because the heat of different substances may differ, there is a process of transferring heat from a hotter substance to a substance with less heat. This process is called heat transfer. We will consider the main types of heat transfer and the mechanisms of their action in this article