2026 Author: Howard Calhoun | calhoun@techconfronts.com. Last modified: 2025-01-24 13:10:26
To begin with, let's figure out what a transformer is for and what it is. This is an electrical machine designed to change the voltage. They are different depending on the destination. There are current transformers, voltage transformers, matching transformers, welding transformers, power transformers, measuring transformers. Everyone has different tasks, but they are unequivocally united by the principle of action. All transformers run on alternating current. There are no such DC devices. They all have primary and secondary windings.
What is called the primary and what is called the secondary winding?
The primary is the one to which the voltage comes, and the secondary is the one from which it is removed. Suppose we have a transformer that converts 220 V AC to 12 V. In this case, the primary winding is the one that is 220 V. But transformers can not only step down, but also step up the voltage. SoThus, by connecting 12 V AC to the previously indicated secondary winding, we can remove 220 V from the primary. Thus, they change places.
In some cases, there may be several secondary windings. For example, in old TVs there were devices with one primary winding and many secondary windings, the voltage on which varied from 3.3 to 90 V. In any case, the transformer serves to convert voltages and currents to optimal values.
The law of conservation of energy
It should be understood that this unit does not take energy from nowhere. For example, let's take a transformer with a primary voltage of 220 V and a current of 5 A. This means that its power is 1100 watts. From the secondary winding at 22 V, we can remove a current of no more than 50 A. Converting to watts, we get the same 1100 watts. We will not remove more power from the secondary winding. If you try to do this, the device will simply fail. Thus, it becomes clear what the transformer is for. To convert AC voltage to DC. Next, we will tell you more about each type of such devices.
Instrument transformers

Such devices serve to reduce the values to acceptable for measuring devices. They are used in instrumentation. You can also find such devices in microprocessor technology. There they work as a sensor that sends signals of different levels to the board, depending on which the latter "makes a decision" about further functioning.appliance.
They are generally highly accurate and not intended for consumer use. Examples of what instrument transformers are used for are the following devices for converting current and voltage. We will try to explain their purpose in as much detail as possible.
Current transformers

What are these devices for? They are designed to reduce the amount of current to an acceptable measurement equipment. In fact, they are intermediate equipment between the conductors, from which it is necessary to take the value of the value, and the measuring mechanism. Such transformers are used, as already mentioned, in measuring instruments, protection equipment and automation. They are connected in this way: the primary winding has several turns and is connected in series with the load, and the secondary winding is connected to the minimum possible resistance of the protective or measuring equipment.
Usually, these transformers are supplied with the equipment itself, since slight changes in load resistance will affect the measurement accuracy, and the protection equipment will not work properly. The design feature and method of connecting such devices make it impossible to power the consumer.
Voltage Transformers

This type of device is not used to power consumers, but is necessary to create a galvanic isolation between the high-voltage and low-voltage parts. The manufacturing method is nothingdifferent from the power types of devices with the same name. There are still primary and secondary windings, the wire cross-section is rather low, which does not allow it to be used to power consumers.
For example, take a kilovoltmeter. The fact is that it is too expensive to build a device that would hold high voltage. Therefore, a voltage transformer is installed between the measuring probes, which take the value of the quantities, and the device. It converts high values to acceptable by the measuring mechanism (approximately 100 V). This measure allows you not to make changes to the measuring mechanism. To some extent, this connection scheme allows you to protect the electrician who takes measurements.
They are also used for installation in various automated control and protection systems. Now you know what voltage transformers are for. Let's move on to the next type - welding devices of the same name.
Power transformers

These are more powerful devices that many of you have seen. Next, we will describe in detail what power transformers are used for. They are needed to increase / decrease the voltage through electromagnetic induction to the value that the consumer needs. In the case of these devices, the word “consumer” refers to factories and residential buildings.
The most striking example are devices that lower 6 (10) kV to an acceptable 380 V, which already feed a single phase in combination with the middle lineour houses need 220 V. And an example of such a step-up transformer can be found in the microwave, where one of the 220 V mains makes the 2 kV magnetron necessary for the operation. High voltage units (above 1000 V) are almost always three-phase, and they are classified into oil or air cooled units, as well as climatic modification and primary winding voltage.
A feature of three-phase transformers is that, depending on the inclusion of the windings (star-delta), you can change the operating voltage by 1.73 times. Suppose this unit, connected by a 6 kV delta, can operate on a 10 kV network, unless, of course, the manufacturer has taken care of this possibility from the insulation side. There are transformers, as mentioned above, three-phase and single-phase. Devices are designed to work with different capacities depending on the needs of the consumer.
Single-phase transformers, which were previously used as power supplies, are now being actively replaced by various electronic converters, which have greater efficiency, less weight and dimensions. Also, power devices can be divided according to the type of magnetic circuit design into rod and armored ones.
A transformer with a core magnetic circuit is designed in such a way that 2 coils are installed on a U-shaped part, and a yoke is closed on top. The advantage is that the elements do not actually touch each other.
In the armored magnetic circuit, the coil is installed on the W-shaped part. The section on which the conductors are located is usually wound firstas primary, and then, through a heat-resistant separator, as secondary. The advantage is the reinforced mechanical protection of the windings.
There are also toroidal cores, but they are made of ferrite rings, since it is unprofitable to build such a structure from a laminated magnetic circuit. Such units are usually used in electronics and operate at high frequencies.
Welding transformers

What are these devices for? In fact, they are independent units. That is, a welding transformer is not a harness that ensures the operation of any device, but it itself is a full-fledged device. The purpose of such a device is to lower the mains voltage to a relatively low, approximately 50-60 V, and provide a large current.
At this voltage, a rather short arc breaks through, but a truly huge current provides it with a lot of power. Thanks to the last parameter, metal is welded or cut.
Such transformers, as a rule, have current adjustment. This is necessary to change the diameter and type of the welding electrode. True, welding transformers for domestic use are increasingly being replaced by inverters. Which is not surprising, because the efficiency of the welding converter is lower. It strongly drops the mains voltage, consuming large currents on the primary winding, has a large weight, low mobility, and heats up quite a lot compared to inverter-type devices.

Now you know how a welding transformer works and what it is for.
Coordinator

This type of transformer is used in various multi-stage circuits to match the resistance between different parts of the circuit. You can find it in a tube audio amplifier. Usually in such devices it is a day off.
So what is the load matching transformer for? For example, the operating voltage of the lamps in the audio frequency amplifier is 70-90 V, but the current is scanty. Such a voltage cannot be applied to the speakers, which means that it is lowered to an acceptable voltage and, accordingly, the current increases.
The purpose of such a transformer is to lower the voltage or increase it to the value required by a particular node of the apparatus.
Conclusion
All devices for converting current and voltage are united by the principle of operation. Key parameters to pay attention to when buying: primary voltage, secondary winding, frequency, power factor and, accordingly, power and output current.
In everyday life, this unit is almost never used. After all, the welding transformer replaced the inverter, and its analogues in power supplies have already replaced electronic voltage converters. This is done due to the fact that devices usually have, in comparison with electronic ones, a lot of weight, and they are also not economically advantageous due to the high consumption of non-ferrous metal in production and expensive repairs. Will soon stay inproduction only transformer substations, but only in those places where it will not be possible to replace them with electronic components.
In this article, we tried to explain what transformers are for, and talked a little about their main types.
Recommended:
Derivative HPPs: description, principle of operation, where they are used

Hydrotechnical structures have been used since ancient times to generate energy. Nowadays, a separate direction of derivation stations is also successfully developing. These are structures characterized by a special drainage infrastructure that allows for more effective flow control even in difficult geographical conditions. At the basic level, the decoding of hydroelectric power stations is applicable to them - a hydrological power plant
Thermal imaging control of electrical equipment: concept, principle of operation, types and classification of thermal imagers, features of application and verification
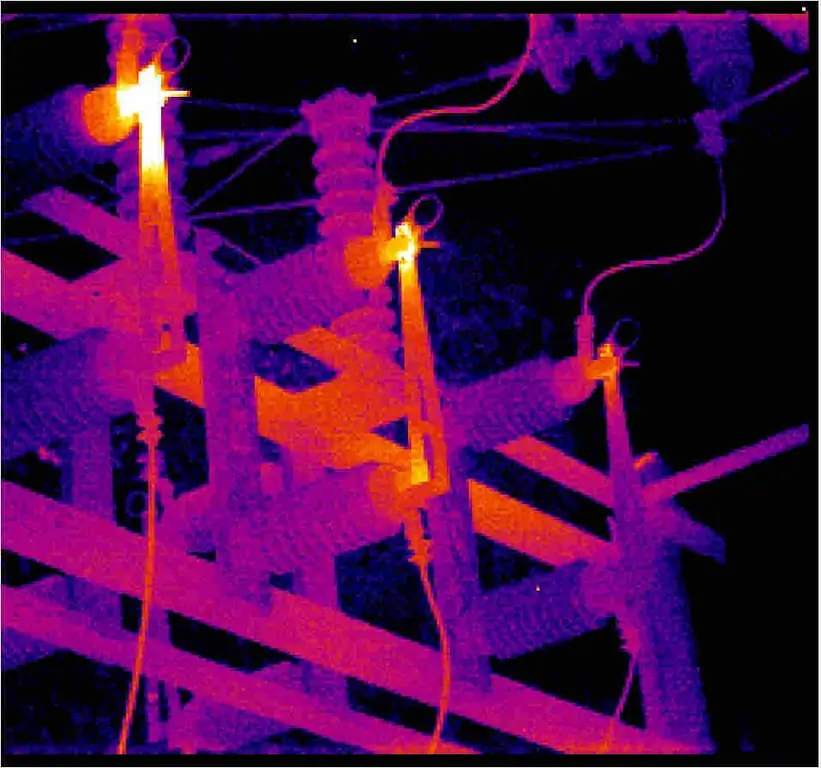
Thermal imaging control of electrical equipment is an effective way to identify defects in power equipment that are detected without shutting down the electrical installation. In places of poor contact, the temperature rises, which is the basis of the methodology
Electric locomotive 2ES6: history of creation, description with photo, main characteristics, principle of operation, features of operation and repair

Today, communication between different cities, passenger transportation, delivery of goods is carried out in a variety of ways. One of these ways was the railroad. Electric locomotive 2ES6 is one of the types of transport that is currently actively used
Low pressure heaters: definition, principle of operation, technical characteristics, classification, design, operation features, application in industry

Low pressure heaters (LPH) are currently used quite actively. There are two main types that are produced by different assembly plants. Naturally, they also differ in their performance characteristics
Mast transformer substation: principle of operation and purpose

The article is devoted to mast transformer substations. The device, principle of operation, types and purpose of such equipment are considered

