2026 Author: Howard Calhoun | calhoun@techconfronts.com. Last modified: 2025-01-24 13:10:38
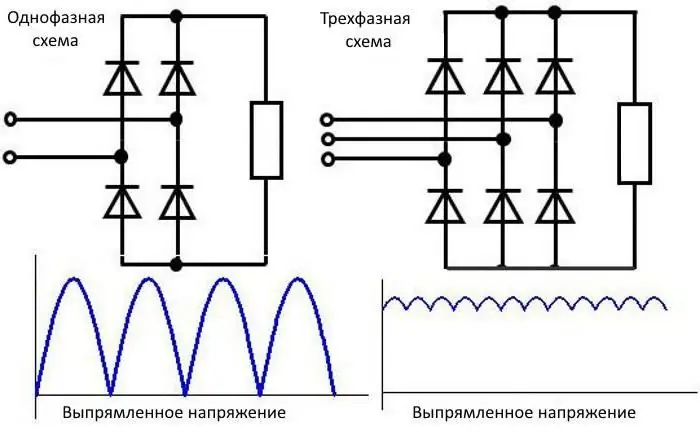
Alternating electric current is converted into a constant pulsating through the use of special electronic circuits - diode bridges. The rectifier diode bridge circuit is divided into 2 versions: single-phase and three-phase.

In the operation of the rectifier, the main element is the diode. Structurally, it is a plate of a semiconductor crystal with two zones of different conductivity. A feature is the one-sided transmission of electric current, depending on the direction of flow.
The design and operation of a rectifier diode are based on the features of the p-n junction between semiconductor zones. Its resistance depends on the polarity of the external voltage. In one case it is large, in the other it is insignificant.

Single-phase diode bridge
When the input is an alternating sinusoidal voltage, in each half-cycle, the current passes through one pair of diodes, and the other is closed. As a result, at the output of the rectifier diode bridge circuit,pulsating voltage, the frequency of which is twice that of the input.
Three-phase bridge circuit
This circuit uses diode half-bridge rectifiers. The output voltage here is obtained with less ripple.
How to smooth out ripple when rectifying the power?
The quality of the rectified voltage decreases as its ripple increases. To reduce it, elements are used that accumulate energy when it comes from the rectifier and give it away when it stops supplying.
In the diode bridge circuit of a rectifier with a capacitor, the latter is connected in parallel with the load. Its capacity is selected depending on the load current. When a pulse is applied, the capacitor is charged. Between pulses (when there are none), the voltage from it is given to the load.

As a result of smoothing, the output voltage of the filter becomes larger and approaches the amplitude of the rectified value.
The ideal voltage at the filter output cannot be obtained due to the discharge of the capacitor between pulses. Usually such ripples are acceptable. They can be reduced by increasing the capacitance of the capacitor.
If an inductor is used for smoothing, it is connected in series with the load. Combined filter circuits include chokes and capacitors.
Designs of diode bridges
The simplest bridge device is performed by soldering individual diodes. In industry, monolithic structures are produced, which are lesssizes and cheaper. In addition, diodes with similar characteristics are selected in them, which allows them to work with the same heating. This improves the reliability of the rectifier diode bridge circuit.
The advantage of diode bridges from individual elements is the possibility of repair when one of them fails. The assembly has to be replaced completely. Malfunctions in it rarely occur, since the elements are correctly selected.
Power Rectifiers
Devices that consume high current are usually powered by a 220 V network. Devices are not connected directly, since the voltage for electronic circuits is small and the current is constant. Then use the network adapter.
The voltage is reduced by a transformer, which also creates a galvanic isolation between the primary and secondary supply circuits. This reduces the risk of electric shock and protects the equipment if a short circuit occurs in the circuit.
Modern adapters in most cases work according to a simplified transformerless circuit without galvanic isolation, where excess voltage is absorbed by the capacitor.
12 volt diode bridge circuit: instructions and assembly
The power supply consists of two modules, where the first is a step-down transformer, and the second is a diode bridge that converts one type of voltage to another.
A suitable transformer is selected. The primary winding is located using a tester. Her resistance should be the greatest. By ringing with a multimeter in the resistance measurement mode, the necessaryends. Then other pairs are found and markings are made.
220 V is supplied to the primary winding. Then the tester is switched to the AC voltage measurement mode and the voltage on the remaining windings is measured. You should choose or wind one at 10V. It is important that the voltage is not 12V, because after the capacitive filter it increases by 18%.
The transformer is selected for the required power, after which a margin of 25% is taken.
4 diodes are twisted into a diode bridge and the ends are soldered. Then the circuit is connected, a 25 V and 2200 microfarad capacitor (electrolyte) is connected to the output and checked in operation.

Transformerless 24V rectifier diode bridge circuit
In amateur radio practice, low-power power supplies without transformers are widely used.

220V power is supplied through the ballast capacitor C1. The rectifier consists of diodes VD1, VD2 and zener diodes VD3, VD4. To eliminate current surges through the bridge, a 50-100 ohm current limiting resistor is installed in series with the capacitor when power is connected. To discharge the capacitor when the circuit is not working, a 150-300 kΩ resistor is connected to it in parallel.
A smoothing capacitor with a capacity of 2000 microfarads is installed at the output of the circuit.
Lack of galvanic coupling creates a risk of electric shock.
Application
Diode bridge applicationsextremely wide and varied:
- lighting fixtures (LED and fluorescent lamps);
- electricity meters;
- power supplies for electronic equipment;
- industrial power supplies, controls and chargers.

How to choose diodes for making a diode bridge?
The main selection criteria are the voltage and current at which the diode does not overheat. When turned on directly, a voltage of about 0.6 V drops across it, since it has internal resistance. The reverse voltage that the diode can withstand without entering the thermal and electrical breakdown mode has a certain limit. If it is designed for 220 V, then a margin of at least 25% is taken. But it is better to take it large enough to protect against accidental power surges.
The current is also taken with a margin. A cooling radiator is provided if required.
For the right choice, use the reference table of diodes and diode bridges.
Diode bridge manufacturers
Among the elements for lighting equipment, the rectifiers of the 1N4007 and MS250 series manufactured by Diotec stand out. They are designed for voltages up to 1000 V. In the first case, the diode bridge circuit consists of 4 diodes placed on a printed circuit board, and in the second it is presented as a compact assembly. While the 1N4007 series is reliable in operation, the MS250 assembly saves weight and footprint. Despite this, demand for the 1N4007 series remains strong as the price has droppedwhich is determined mainly by the cost of copper leads.

The manufacturing technology of MS series diode bridges continues. Now all 4 crystals of the bridge are installed together, which increases its heat resistance due to the uniformity of parameters.
The reliability of rectifiers decreases as the ambient temperature rises. This problem is solved by the B250S2A series, which is rated at 2.3A and passes 0.7A at 125°C.
Most manufacturers buy diodes and then assemble finished rectifiers. Diotec handles the entire production cycle, from crystal making to assembly and packaging.
Another leading global company - IRF - has unique technologies for reducing the dimensions of parts, improving heat transfer, and increasing the efficiency of semiconductor technology. It is the only one producing components for the entire energy conversion cycle.
Conclusion
The rectifier diode bridge circuit is used in all electronic equipment. Full-wave rectifiers should be used, the characteristics of which are much better than single-wave ones. You can check any of them yourself by ringing each diode.
Recommended:
Classification of engines. Types of engines, their purpose, device and principle of operation
Nowadays, most vehicles are powered by an engine. The classification of this device is huge and includes a large number of different types of engines
Electric motor with gearbox: features, device and principle of operation

Nowadays, it is difficult to find an industry that does not use geared motors. This unit is a kind of electromechanical independent unit in which the electric motor and gearbox work in pairs
Electric locomotive 2ES6: history of creation, description with photo, main characteristics, principle of operation, features of operation and repair

Today, communication between different cities, passenger transportation, delivery of goods is carried out in a variety of ways. One of these ways was the railroad. Electric locomotive 2ES6 is one of the types of transport that is currently actively used
Gas piston power plant: the principle of operation. Operation and maintenance of gas piston power plants

Gas piston power plant is used as a main or backup source of energy. The device requires access to any type of combustible gas to operate. Many GPES models can additionally generate heat for heating and cold for ventilation systems, warehouses, industrial facilities
Crucible induction furnace: principle of operation, diagram and reviews
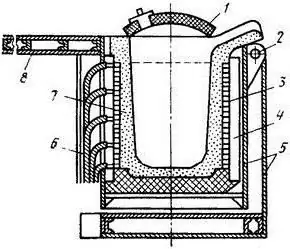
Induction heating can be used to work with any material: metal, slag, gas, etc. The main advantage of its use is non-contact heat transfer. Also, induction heating allows you to achieve almost any heating rate - it all depends on the power of the generator that feeds the furnace