2026 Author: Howard Calhoun | calhoun@techconfronts.com. Last modified: 2025-01-24 13:10:26
Classification of engines includes several large groups of these devices. It is worth noting that each individual group, in turn, is divided into several smaller ones. This is justified by the fact that today a huge number of different kinds of engines have been invented by man.
Method of preparing the mixture
Classification of internal combustion engines can also be carried out by the way in which the fuel was prepared for their operation. For example, there are two main types - these are with external mixture formation and with internal mixture formation. Mixing is the process by which fuel is obtained for the operation of the engine. External mixture formation is understood as the process of preparing fuel for engine operation outside its limits, that is, in a carburetor or in a mixer. Naturally, this group includes those types of these devices that are not capable of producing a mixture on their own.

Internal mixture formation refers to the case when the mixture production process occurs directly in the engine cylinder itself.
Liquid fuels
Liquid fuel engines are a type of rocket engines, that is, they are used to launch rockets. Such a device consists of the following parts:
- Combustion chamber with nozzle. These elements serve to convert the chemical energy of the fuel into thermal energy. After the completion of this process, the next one begins, the essence of which is the subsequent transformation of the already existing thermal energy into kinetic energy. It is important to note here that the combustion chamber, as well as the nozzle and the injection device, are considered a separate unit.
- Following elements are the fuel control valves, as well as the engine itself. The purpose of these valves, as the name implies, is to regulate the fuel supply. This is a rather important process, since the performance of an engine like this depends on the amount of fuel supplied. Depending on the amount of working substance entering the engine, its thrust will change.
Liquid fuel devices
In the classification of engines with a liquid substance as fuel, they are classified as rocket devices. It is important to note that a variety of fuels can be used as a working fluid. Here it is necessary to understand that the choice of mixture for starting the unit will depend on the characteristics, purpose, power, and also on the duration of the engine itself.

Among all the requirements that most often apply to this particular class of devices arethe lowest consumption of the working mixture or, what is the same, the maximum specific thrust. When it becomes necessary to choose a mixture for running an engine on liquid fuel, pay attention to such parameters as: ignition and burning rate, density, volatility, toxicity, viscosity, and several other important characteristics.

Solid fuel unit
Classification of engines includes another type of device. These units operate on a slightly unusual, solid fuel. It is important to note here that the scope of these engines is also rocket. Gunpowder became the main substance that is the fuel for this device. The peculiarity of the work is that the unit works until it has used up the entire stock to the end. The gunpowder itself is placed directly into the combustion chamber of the engine. Such devices became known as solid propellant rocket motors, or solid propellant rocket motors.

It is important to note here that this particular class of engines is one of the oldest. In addition, it was this type of device that was the first to find its practical application. Another important fact is that black powder was previously used as a fuel. With the development of technology, the type of mixture has also changed. Humans have succeeded in inventing smokeless gunpowder for use as rocket fuel.

Fuelless engine
One of the rather interestingunit classes is an engine that does not use any fuel mixture for its operation. Most often, these types of devices are used as rotation drives. This unit consists of such parts as: a disk or a flywheel, which is fixed on the axle. The same part has one or more permanent rotor magnets.
An important condition is that these magnets, like the disk itself or the flywheel, must be installed so that nothing interferes with their free rotation around its axis. Another important part of a fuel-free engine is a cylindrical permanent stopper magnet, which is fixedly mounted on a rod mounted parallel to the disk or flywheel. A permanent cylindrical magnet can move together with the rod to the area where at a given time there is a magnetic field created by the rotor magnets.
The principle of operation of a fuel-free unit
The principle of operation of this device lies in the fact that all its magnets are turned with the same poles towards each other. Since the magnetic poles of the same name will always repel each other, their movement will cause the disk or flywheel to rotate around its axis. In addition to this type of engine, there is another one that is very similar in its principle of operation to a fuelless one.
This device was a magnetic motor, which has a stator in the form of a permanent magnetic ring, as well as a rotor (or it is also called an anchor). This element is a bar permanent magnet, which is placed inside the stator in one plane.

The disadvantage of these types of engines is that they need a supply of electricity to carry out their work. Several goals were set for the invention of this type of device. It was necessary to achieve an environmentally friendly type of engine that would not have harmful emissions during its operation, and also worked without consuming any type of fuel and without supplying electrical energy from external sources. At the same time, it also should not have polluted the environment or atmospheric air.
Aircraft engines
Before starting to describe a specific class of engines, it is best to figure out on what basis they are divided. Currently, this group is classified into two fundamentally different types. The only distinguishing feature of one group from another was the ability of the device to operate outside the atmosphere. In other words, the first category of units requires the presence of an atmosphere for its operation, while the second is not tied to this indicator and can be operated outside of it. The first group was called atmospheric or air, while the second is called rocket.
It is worth noting that conventionally these types of devices are referred to as propeller-driven air engines and aircraft jet engines.
Reactive Device Group
The second category of devices, that is, reactive, includes such units as: turbojet air engines, ramjet engines. The main difference between these two types of devices is thatdirect-flow jet devices, air compression occurs due to the supply of mechanical energy to the engine tract. For the operation of this unit, it is necessary to create an increased static pressure. This effect is achieved by braking the air moving in the air intake inlet.

Dual-circuit jets
The jet engine of this type of aircraft - a bypass turbojet - was born due to the fact that people needed to create a device that would have an increased traction efficiency. It was necessary to achieve an increase in this indicator at huge subsonic speeds. The principle of operation of this device looks something like this.
Air flow runs into the engine, then it enters the air intake, where it is divided into several parts. One part passes through the high pressure device located in the primary circuit. The second part of the intake air passes through the fan blades in the secondary circuit. It is worth noting here that the principle of constructing the primary circuit in the turbofan engine is similar to that used in the circuit of its predecessor, the turbofan, and therefore it works accordingly. But the action of the fan located in the second circuit of the engine is similar to how a multi-bladed propeller operates, which rotates in an annular channel.
It can be added that the turbofan engine can also be used at supersonic speeds, but for this it is necessary to provide for the presence of a fuel combustion system in its secondary circuit,to increase the traction of the device.
Recommended:
Driver controller: purpose, device and principle of operation
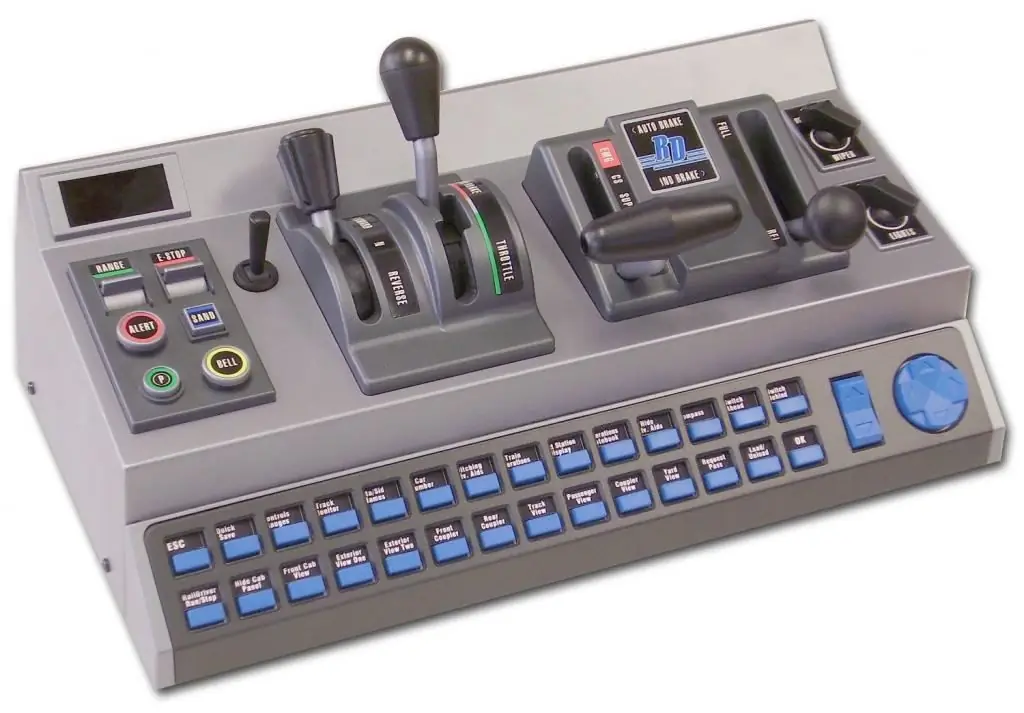

The use of a variety of vehicles today is very active. They all have in common that they need to be managed. The driver's controller is also designed for control. With it, you can remotely control the traction motor in braking or traction mode
Turboprop engine: device, scheme, principle of operation. Production of turboprop engines in Russia

A turboprop engine is similar to a piston engine: both have a propeller. But in every other way they are different. Consider what this unit is, how it works, what are its pros and cons
General purpose engines: device, principle of operation, application, photo

Automotive equipment is mainly equipped with standardized internal combustion engines (ICEs), the design of which is focused on placement in the engine compartment. However, there is a great demand for power units of this kind in the garden equipment segments, from manufacturers of snowplows, snowmobiles, etc. Moreover, the requirements for integration and operational parameters in such cases differ sharply from automotive standards
Magnetohydrodynamic generator: device, principle of operation and purpose
Not all alternative energy sources on planet Earth have been studied and successfully applied so far. Nevertheless, humanity is actively developing in this direction and finding new options. One of them was obtaining energy from an electrolyte, which is in a magnetic field. Typical operation cycle and main classifications of MHD generators. List of main characteristics. Perspective and applications
A burner is Description, device, principle of operation, classification, photos and reviews
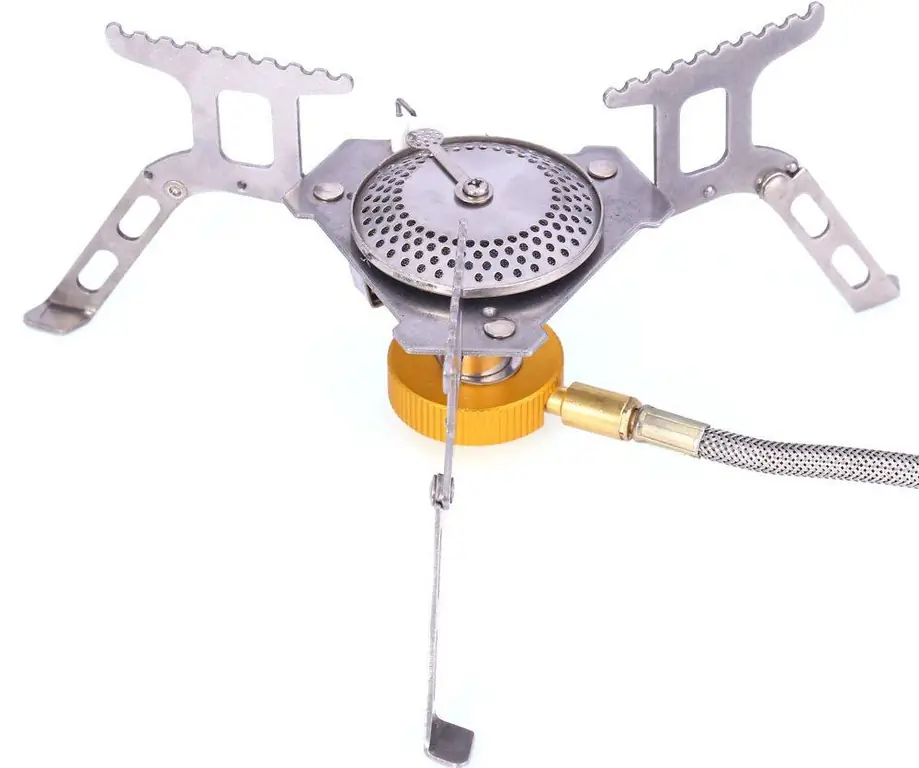

By burning the resulting mixture, a variety of tasks are solved - from the release of thermal energy to thermal cutting action. The simplest tool for carrying out such operations is a burner - this is a small-sized apparatus in which a torch flame is formed from burning fuel