2026 Author: Howard Calhoun | calhoun@techconfronts.com. Last modified: 2025-01-24 13:10:39
Many inexperienced fur breeders often wonder why rabbits die on the farm. These small animals can die for various reasons. However, most often a lunge in a herd occurs due to various kinds of infectious diseases. One of the most dangerous infections affecting rabbits is pasteurellosis.
This unpleasant disease can damage the he alth of almost all farm animals: pigs, sheep, poultry, cattle. But it is in rabbits, who by nature do not differ in good he alth, that hemorrhagic septicemia is most often found. Treatment of animals with pasteurellosis should be started immediately after the first signs of it appear. Otherwise, the drop in the herd will be very large (up to 75%).

What causes hemorrhagic septicemia
The causative agent of such a dangerous disease as rabbit pasteurellosis is the bacterium Pasteurella multocida (sometimes gemolitica). It is a polymorphic, short, immobile rod that does not form spores. In water,in manure and soil, this bacterium can remain viable for 2-3 weeks, and in the corpses of dead animals - up to 4 months. At the same time, direct sunlight kills Pasteurella multocida in just a few minutes.
How the disease is transmitted
This bacterium can get into the rabbitry in several ways:
- with stale or simply contaminated food and water;
- with chicks or sires purchased from another farm;
- airborne.
Very often chickens become the carrier of this infection. Pasteurellosis in birds is of the same nature as in rabbits. That is why cages and aviaries are recommended to be built away from chicken coops. Sometimes the Pasteurella multocida stick gets into the rabbitry and on the clothes of the owners. You can also bring this infection to the farm on the back or wheels of a car after visiting a farm that is unfavorable in terms of animal disease.

Clinical picture of the disease
Pasteurellosis in rabbits can be acute or chronic. This disease poses a great danger to animals, among other things, because its symptoms are not pronounced. Outwardly infected rabbits look relatively he althy. The only thing is that the animals feel a little depressed and are not too willing to eat. Therefore, inexperienced breeders often simply skip the first stage of the disease without taking any action. Meanwhile, animals can be saved only by starting their treatment in time.
Pasteurellosis is the most commonthe answer to the question of why rabbits die on the farm. The incubation period of this disease in acute form lasts about 5 hours. Animals die approximately 5 days after infection. Sometimes the disease also becomes chronic.

Pasteurellosis symptoms
To determine the presence of infection in the herd, in addition to depression and loss of appetite, you can use the following signs:
- increase in body temperature of animals up to 41-42 gr.;
- slightly labored breathing;
- bloating of the gastrointestinal tract;
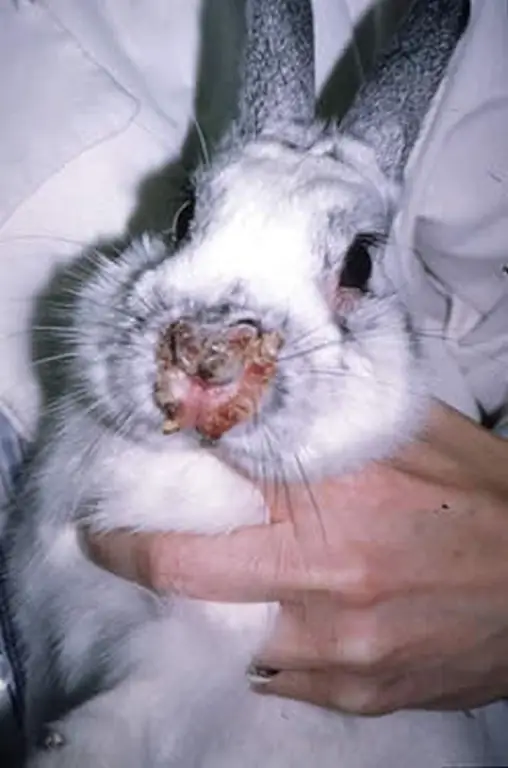
- discharge of pus from the nasal cavity.
Infected rabbits can develop conjunctivitis and ear infections, among other things. By the end of the disease, just before death, the body temperature of the animal drops sharply (up to 35-33 degrees). With chronic pasteurellosis, rabbits may experience symptoms such as depression, otitis media, and purulent discharge from the eyes and nose.
Pasteurellosis of rabbits: drug treatment
At the initial stage of the development of the disease, rabbits are usually prescribed sulfa drugs or antibiotics. It can be, for example, tetracycline, levomycin, biomycin, norsulfazol, etc. These drugs are supposed to be administered intramuscularly. Rabbits are given injections twice a day. In this case, the first 3 days usually use sulfa drugs, and the next three days - antibiotics. At the final stage, the first group of funds is again used. In total, therefore, the treatment of rabbits lasts about 9 days.
The method described abovemainly used to rescue adults. Young animals aged 45-90 days are given a special remedy - formol vaccine. This drug is able to completely rid the animal of pasteurellosis in the shortest possible time. However, unfortunately, it does not have such an effect on adult rabbits.

Disease prevention
The main ways to prevent the spread of infection such as rabbit pasteurellosis are:
- keeping cleanliness in aviaries and cages;
- keeping newly acquired individuals for several days in a quarantine department.
Before starting work on the farm, the owners should always wash their hands with soap and water. Also, do not enter the rabbitry in dirty shoes and clothes.
If there is a farm with already sick animals near the farm, the rabbits should be examined without exception. Suspicious individuals from the herd must be isolated. All animals, without exception, should also immediately receive intramuscular injection of terramycin at a dose of 20 mg per kg of body weight.

Pasteurellosis vaccine: use
Of course, the best preventive measure against pasteurellosis is vaccination. Vaccination of rabbits against this disease is not done in all farms. It is carried out only on those farms that are located close to disadvantaged ones. Adults older than 2 months are usually injected with an extract-formol vaccine intended for rabbits. Serum is administered to young animals against suchdiseases such as pasteurellosis in birds and pigs (every 5-7 days). Then the vaccine is also used. Sometimes serum is administered to animals older than 2 months.
What to do if rabbits are already sick
In addition to the treatment of animals, when an infection appears in the rabbitry, a thorough disinfection should be performed. The meat of rabbits slaughtered or dead from pasteurellosis should not be eaten. Under certain circumstances, this disease can be transmitted to humans. You can not give the meat of dead rabbits and dogs. Carcasses, according to the regulations, are supposed to be burned. Skins are allowed to be handed over to workshops, but only after thorough disinfection.

Disinfection in an infected rabbitry should be done not only in cages and aviaries, but also in the clothes of the farm staff. As disinfectants, it is allowed to use only products designed specifically to remove the Pasteurella bacterium. The fact is that not all disinfectants kill her. It is possible to treat rabbitry during an outbreak of a disease such as rabbit pasteurellosis, for example, with formalin (1%), lysol (5%), caustic soda (2%), carbolic acid (3%). All these drugs can be used both separately and simultaneously. Carry out the treatment of rabbitry using a sprayer.
Recommended:
Cattle fascioliasis: causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment and prevention
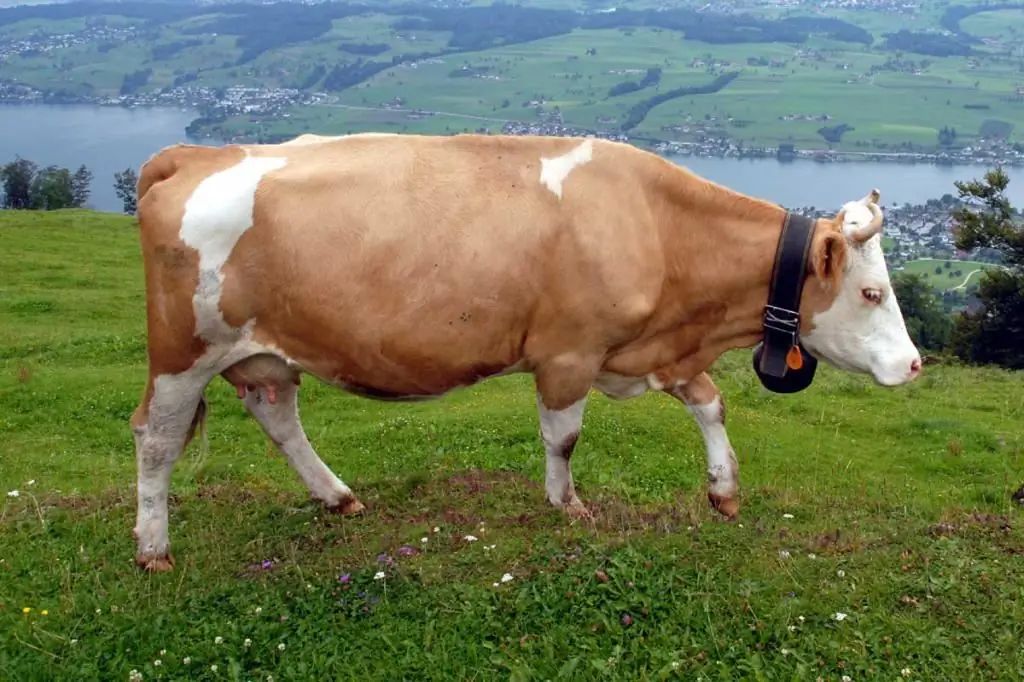

Cattle fascioliasis is a disease that can bring great material damage to the farm. In an infected cow, milk yield drops, weight decreases, and reproductive function is impaired. To protect livestock, it is necessary to carry out anthelmintic treatment in a timely manner and carefully approach the choice of pastures
Diseases of rabbits: symptoms and their treatment. Disease prevention in rabbits
Rabbit diseases can destroy most of the livestock in a matter of days. In order to provide assistance to animals in time, it is necessary to be able to determine the disease, as well as vaccinate in time, follow the rules of care
Fruit rot: causes, first signs and symptoms of infection, methods of treatment and improvement of the garden

It happens that the gardener does not have time to collect the fruits - they rot right on the branches and fall off. At the same time, in appearance, apples and pears look quite he althy, but from the inside, an insidious enemy of all stone fruit and pome crops lurks - fruit rot. Despite the fact that this dangerous adversary is well studied and can be defeated, amateur gardeners often do not notice signs of infection in the early stages of the disease
Eimeriosis of rabbits: causes, symptoms, treatment methods

Eimeriosis, or coccidiosis, is the most common invasive disease of young rabbits that damages the digestive organs. Mortality among young animals reaches almost one hundred percent. Most often, rabbits are exposed to the disease from one to five months. Due to eimeriosis, many farms are closed and the number of animals is significantly reduced
Breeds of rabbits with photos and names. Giant rabbits. Meat breeds of rabbits
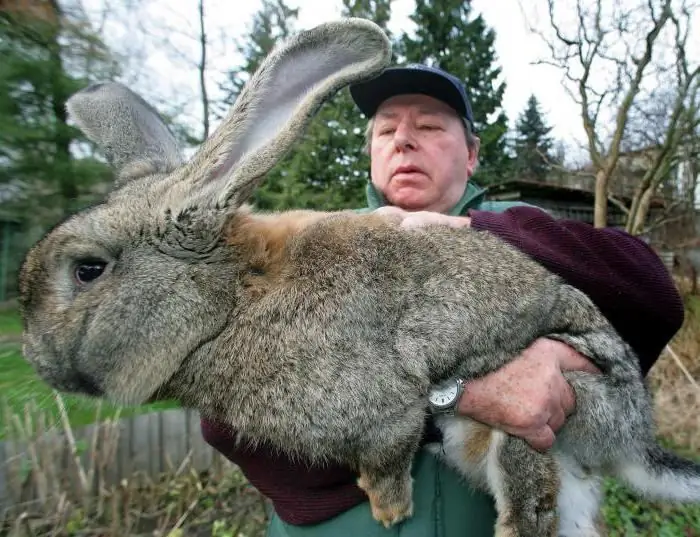

The rabbit was tamed by man a long time ago. This is mentioned in the written sources of ancient Roman history. From that time to the present, many new breeds have been created by rabbit breeders. Rabbits are bred to obtain dietary meat, fur, fluff. Fur products are highly durable, and the quality of the down prevails over the wool of the merino and angora goats. This article will present rabbit breeds with names and photos

