2026 Author: Howard Calhoun | calhoun@techconfronts.com. Last modified: 2025-01-24 13:10:33
Rabbits are valued for their beautiful fur, excellent taste of meat. But growing them is not as easy as it seems at first glance. Breeding breeders face a variety of challenges. After all, these animals are very demanding on the conditions of detention and often get sick. Rabbit diseases can destroy most of the livestock in a matter of days. In order to provide timely assistance to animals, it is necessary to be able to determine the disease, as well as vaccinate in time, follow the rules of care.

Sick or he althy rabbit
Some diseases of rabbits do not have a pronounced clinical picture. But even in such cases, it is possible to distinguish a sick animal from a he althy one. And in order not to miss the first signs of ailments, it is necessary to conduct periodic examinations of all individuals. Usually this is done before mating, after birth. When the rabbits appear, they are examined daily until two weeks of age.
He althy animals are always active, they have a good appetite. They are characterized by:
- Shiny, beautiful, even coat.
- Absencedischarge from the nose, eyes.
- Smooth breathing (about sixty breaths per minute).
- Smooth pulse (120-160 beats per minute).
- Body temperature between 38 and 39.5 degrees.
Examine stools daily. They can assess the state of the gastrointestinal tract. The norm is the feces of a dark brown or black shade in the form of peas.
In an unhe althy animal, behavior changes: it becomes inactive, may refuse to eat or eat with reluctance. Also, a sick rabbit can lie with its eyes closed.
In some diseases, the frequency of breathing changes, there is a strong thirst. Ulcers may occur on the skin, discharge from the nose and eyes can be observed. Sometimes rabbits develop diarrhea or constipation, and bloating is visible. When touched, wool falls out: it loses its attractiveness. In some diseases, rabbits shake their heads, scratch their ears and other parts of the body. There are ailments that can cause paralysis, convulsions, trembling.
Rabbit diseases require immediate treatment. But before proceeding with therapy, you should consult with your veterinarian. He will analyze the feces, take scrapings from the wool, the lesions, take the material for analysis in the presence of discharge. All this will help to accurately diagnose and prescribe the right treatment.

How diseases happen
Types of rabbit diseases, symptoms and their treatment determine the possibility of recovery of animals. There are diseases that are not amenable to therapy, and sick individuals are destroyed. There are illnessesthe treatment of which does not cause problems.
There are many diseases of rabbits. For convenience, they were divided into groups: infectious or infectious, non-infectious or non-infectious. Let's consider them in more detail. The most dangerous are precisely infectious pathologies, since they are able to quickly move from one animal to another, infecting the entire livestock. It is worth noting that some diseases are dangerous for humans.
In a separate group of rabbit diseases, parasitic diseases are distinguished. Penetrating into the body, parasites can spread to all organs and systems, affecting different areas. This species includes helminths, ticks and others.
Scabies or psoroptosis
Rabbit diseases, symptoms and their treatment, started on time, can be determined independently, without the participation of a veterinarian. Such ailments include psoroptosis or ear scabies. What it is? Its causative agent is a scabies mite that lives in the auricle. The parasite causes inflammation. The rabbit begins to comb the ears. Ticks begin to move to other areas, penetrating deeper into the tissue.
The incubation period for scabies lasts up to five days. Usually the clinical picture is very pronounced: the rabbit shakes its head, scratches its ears. There are scratches on the inner surface of the auricle.
With timely treatment, the disease is easy to defeat. The surface of the auricle is treated in all infected rabbits. To do this, use turpentine, dust or special drops for scabies, sold in veterinary pharmacies.

Rickets
Ricketsmanifests itself in rabbits from an early age. Such individuals lag behind in growth, practically do not gain weight. They show deformity of the limbs: the paws resemble an oval. Rickets rabbits have a huge belly.
Treatment is carried out by prescribing a course of vitamin D in drops, as well as calcium and phosphorus. The drugs are added to the feed.
Coccidiosis
Coccidiosis in rabbits is caused by parasites that infect the gastrointestinal tract. According to statistics, approximately 70% of rabbits die from this disease. To prevent this from happening, they carry out the prevention of coccidiosis.
This disease is of two types: hepatic and intestinal. In the latter case, parasites develop very quickly. Rabbits die in a week or two.
In the hepatic form, the pathology develops slowly. Animals gradually lose weight and develop diarrhea.
The incubation period for coccidiosis is about three days. The main manifestations of the disease are loose stools, the presence of bloody discharge, jaundice. For an accurate diagnosis, a laboratory study of the animal's feces is necessary. Rabbits can get sick at any age. But young animals aged from one and a half to four months suffer the greatest susceptibility.
When detecting coccidiosis in rabbits, treatment is carried out by the method of drinking with drugs dissolved in water. It can be sulfanilamide drugs: "Sulfadimezin", "Sulfadimetoksin". Rabbits are fed twice a day for five days. There is a three-week break between courses.
Good results are obtained by drinking with an iodine solution: for adultsprepare a 0.01% solution (dose 100 ml per animal / day for ten days), for rabbits, the dosage is 50 and 100 ml.
In the veterinary pharmacy you can buy special preparations for the treatment and prevention of coccidiosis. They are used in accordance with the instructions.

Myxomatosis
Myxomatosis in rabbits is a dangerous disease caused by viruses. Outbreaks of the epidemic are recorded in the summer-autumn period. Carriers of infection are mice, rats, blood-sucking insects.
Myxomatosis in rabbits shows the following symptoms:
- Swelling of the nose, ears, lips.
- Discharge appears from the eyes and nose.
- Seals form on the paws, ears.
- Apathy appears, and the rabbit's hair falls out.
As the disease progresses, the animal's ears droop, it falls into a coma and dies. The disease proceeds very quickly and is always fatal. All individuals are disposed of, the carcasses are not suitable for human consumption. The rabbitry is disinfected, the remaining animals are vaccinated.
Pododermatitis
Pododermatitis or plantar dermatitis in rabbits occurs in individuals kept in cages with mesh floors. Because of this, ulcers appear on the paws, into which the infection enters. As a result, the process of suppuration begins: the disease becomes acute.
Most often, pododermatitis affects animals with a large body weight, with legs not lowered. A side factor is the unsatisfactory condition of the cells, polluted air, highhumidity.
Clinically, the disease is manifested by a lack of appetite, the animal almost does not move, more lies. On examination, damage to the legs is visible. Treatment of pododermatitis is carried out by lubricating the lesions with zinc ointment or Vishnevsky liniment.

Conjunctivitis
If a rabbit has watery eyes, then this may indicate conjunctivitis. Pathology occurs when dust gets into the eyes from contaminated hay, grass, feed. The disease manifests itself in the form of redness, swelling of the eyelids, tearing. Subsequently, the discharge becomes purulent, the eyes stick. The rabbits try to tear them apart with their paws, making the situation even worse.
Treatment is carried out by daily eye treatments with a solution of boric acid, "Levomycetin", strong brewing of black tea. The eyes are treated throughout the week.
Worm infestations
Worms in rabbits can lead to the death of the animal. They not only cause inflammation, but are also dangerous for the eared.
When infected with helminths, the following symptoms are observed:
- Increased thirst. Rabbits drink a lot: they go to the bowl of water more often than usual.
- Greenish mucus can be seen in the feces. Diarrhea and constipation in rabbits alternate.
- The fur grows dull, loses its luster, begins to fall out in large quantities.
- The sclera of the eyes become cloudy.
- Rabbits get lethargic, lie down a lot.
- The worms cause itching in the anus, forcing to drive on the floor.
Treatment of helminths is carried out usingspecial preparations. It can be "Shustrik", "Gamavit", "Albendazole", "Tetramizol", "Pirantel" and other anthelmintic drugs available in the veterinary pharmacy. Funds are used strictly according to the instructions.

Poisoning
Rabbits are very sensitive to food: if the feed is not properly selected, the animal can get poisoned. Such a phenomenon can be caused by such herbs as dope, potato tops, caustic buttercup and other poisonous plants.
When poisoning, the following symptoms occur: profuse salivation, vomiting, diarrhea, impaired coordination of movement. With these signs, it is necessary to drink the rabbit with a decoction of rice or oats, replace the food.
Rhinitis or pasteurellosis
The disease affects animals at any age. With pathology, nasal discharge is observed. They can be purulent or mucous, body temperature rises, diarrhea occurs. Rabbits are depressed, refuse food, water. Patients are immediately isolated and their cells are disinfected.
For treatment, it is necessary to drip "Furacilin", a solution of "Penicillin" into the nose. The antibiotic is diluted with water in a ratio of 1 to 1. After recovery, the rabbits are slaughtered. These are not left for knitting.
Diseases of the respiratory system
If rabbits live in a draft, then they may have problems with the respiratory system: pneumonia, bronchitis. With these ailments, wheezing, oppressed breathing, and body temperature rise. For treatment, it is necessary to inject intramuscularly "Penicillin", a solution of "Sulfidin" 0.3 g eachfor one individual. Be sure to add vitamins to the feed. Rabbits are moved to warm, draft-free cages.
Heatstroke
If cages with rabbits stand all day in the sun, the animals can overheat and get heat stroke. Large individuals do not tolerate heat and high temperatures.
When overheated, they refuse food and water, stretch to their full height in the cells. Their breathing quickens and they may experience convulsions.
Help is to move the animals to a cool place. It may be some kind of room where it is colder than in cages. A cold compress can be applied to the head.
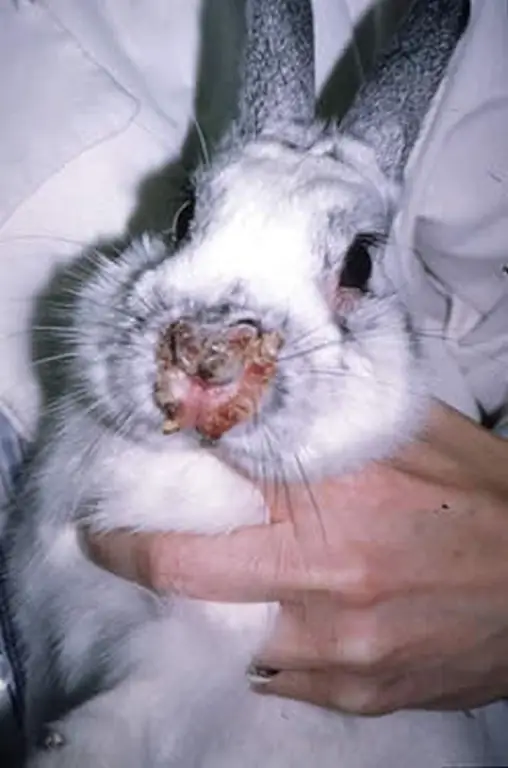
Stomatitis or "wet muzzle"
Young animals are often exposed to infectious stomatitis or "wet muzzle" disease. It is caused by viruses.
The disease affects the mucous membrane, causing salivation, diarrhea, inflammation. Secondary signs of the disease are: increased humidity of the integument, sudden changes in temperature.
The main clinical manifestations are:
- Appearance on plaque tongue: first white, then grayish red.
- Ulcer formation.
- The animal loses its appetite, becomes lethargic.
- Champing is heard while eating.
When such symptoms are detected, treatment should be started immediately. The oral cavity is washed with a solution of potassium permanganate or copper sulfate. Streptomycin gives good results. Powder treatment is carried out by falling asleep in the oral cavity, 0.2 g once a day for three days.

Vaccination
The main prevention of disease in rabbits is vaccination. It helps protect livestock from the most dangerous diseases that can destroy the entire economy in a matter of days.
What vaccinations does a rabbit need and when are they given? The first injection is done at the age of 45 days, with a weight of at least 500 grams. The following vaccinations are performed every six months throughout the life of the individual. If a break between vaccinations is allowed, then disease prevention must be resumed, regardless of the age of the rabbit.
Vaccination can be done as follows:
- The first vaccination is given at 45 days of age with an associated vaccine.
- Revaccination is carried out after 3 months.
- Further, vaccinations are done every six months.
Another pattern looks like this:
- The first vaccination is given with a single HBV vaccine at the age of one and a half months.
- Vaccination against myxomatosis in two weeks.
- Another two weeks later, revaccination of VGBK is carried out.
- Two weeks later - revaccination against myxomatosis.
- After 3 months, the associated vaccine is vaccinated.
- Six months later, revaccination with all three vaccines is carried out.
When vaccinated according to any scheme, a two-week quarantine is mandatory. It helps to avoid possible infection of the pet during the period of immunity development. At this time, it is recommended to feed the animal with sprouted grain, mountain ash, fish oil, pumpkin.
Timelyvaccination and proper treatment will help save the rabbit population, as well as prevent outbreaks of dangerous infections.
Recommended:
Pasteurellosis of rabbits (hemorrhagic septicemia): ways of infection, symptoms, treatment, prevention

Rabbit pasteurellosis is a most dangerous disease that can cause enormous damage to a farm. Measures to cure animals should be taken immediately after the appearance of its first symptoms. In addition, it is necessary to carry out various preventive measures aimed at preventing infection of rabbits
Cucumber powdery mildew disease and others: prevention and treatment

Cucumber disease is an extremely unpleasant phenomenon. Plants affected by a fungus or virus die off, resulting in a significant reduction in yield. Appropriate preventive measures must be taken to prevent infection
The most common bird diseases: description, symptoms, treatment and prevention

Farming poultry is not only profitable, but also affordable. With proper housekeeping, you can not only provide your family with meat and eggs, but also earn decent money. However, as in every business, there are pitfalls, and here they are. The main problem in poultry breeding are diseases that, in the absence of adequate treatment and preventive measures, can cause serious damage to the farm
Newcastle disease in poultry: causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment and prevention

Today, livestock farmers have faced a huge number of different ailments. Many of them can be cured with effective drugs, but there are those that are exclusively fatal. Newcastle disease is a viral disease that mainly affects birds
Why do rabbits sneeze: causes, possible diseases, treatment, prevention, advice from veterinarians and rabbit breeders

Rabbit breeders often face animal diseases. This is due to the fact that rabbits are weak species and are often subjected to various pathologies. One of the pathologies is a runny nose. As soon as it begins to appear, new breeders ask different questions: why do rabbits sneeze, how dangerous is it, how to treat it?