2026 Author: Howard Calhoun | calhoun@techconfronts.com. Last modified: 2025-01-24 13:10:45
Insurance is a way to distribute possible losses from current income. It is used to protect the property interests of legal entities and individuals in the event of the occurrence of certain events thanks to the monetary funds that were formed from the contributions paid.
Introduction
Where and how are the legal foundations of insurance in the Russian Federation? This issue is regulated at the highest level. It is enshrined in Law No. 4015-І dated November 27, 1992 "On the organization of insurance business in the Russian Federation" with numerous changes, as well as a number of other regulatory documents. A number of concepts of interest are also discussed there. Considering them is not superfluous:
- Insurance is a system (method) for protecting the property (material) interests of market entities (individuals and legal entities), for which there is always a certain threat, but it is not mandatory. Note: this will not allow you to avoid problems, but you can count on compensation.
- Insurance product is an action from whichprotection is purchased.
About the system of ensuring material interests and confirmation of rights

The very fact that protection is required is associated with a threat to the existence of rights. If we consider individual owners, then the risk to material interests is small. But according to the law of large numbers it is quite real. Hence the need to insure existing risks arises. This is expressed in the form of specific products. Each of them is aimed at a specific object of insurance, reasons, cost, payment terms. The documentary form is a policy. The legal basis for insurance requires that it always be. After all, it confirms the existence of a contract, which is always substantive, addressed to the participants in the transaction and contains the main parameters. At the same time, it is also a full-fledged legal document. It should be noted that contributions are always less than compensation. This is the specificity of insurance products. This position makes them attractive in supply markets and increases demand for them.
How then do they make money on this?

Although at first glance it seems that this relationship is unprofitable for sellers, this does not mean that he is losing money. Why? The fact is that the number of policies (buyers of products) usually exceeds the number of insured events by an order of magnitude. This situation remains almost always (except for force majeure). Initially, the financial obligations of the participants in the process are equated. But sincethe law of large numbers is in effect, then the obligations of insurers are lower than the volume of policies sold. This is solved by establishing a certain ratio between payments and payments (the larger the contributions, the larger compensation you can count on). It should be noted that the dynamics of insured events is uneven. Because of this, it is difficult to establish balance equality. Further complicating the situation is the need for prices to be low enough to sell and high enough to cover costs and generate profits.
Legal bases of insurance: what is included in this concept?
In general, the information has been considered. But there is also pension, social, medical insurance. How to ignore them? They also have separate regulations. For example, the legal basis for compulsory social insurance is laid down by Law No. 165-FZ of 1999-16-06. In addition, we should also remember about civil law. It is he who is entrusted with the regulation of property obligations that arise between project participants. Chapter 48 "Insurance" of the Civil Code deals with the procedure for concluding a contract and subsequent relationships. At the same time, the activities of legal entities offering products are regulated by the supervisory and licensing bodies of insurance activities. In order to comply, they need to form and place certain reserves, control the validity of tariffs, and also ensure solvency. All this is regulated by administrative law. Handles financial mattersTax code.
How does the government regulate and oversee?

Speaking of what the organizational and legal basis of insurance is, it should be noted here:
- Direct participation of the state in the formation and development of a system aimed at protecting property interests.
- Legislative support and protection of the national market.
- State supervision of insurance activities.
- Protection of fair competition and prevention and suppression of monopolies.
Why is government involvement necessary?

Can't it just lay the legal foundations for insurance? His active participation is due to the following factors:
- It is necessary to provide social security. The legal framework is good, but the protection of certain groups of the population requires the use of budgetary funds.
- Defining the bases and procedures for participation in non-commercial risk insurance. For example, protecting investments, securing export credits.
- Provision of additional guarantees for those insurers that place the collected funds in the form of special non-marketable securities with guaranteed income issued by the state.
- The state creates targeted reserves that are used to compensate for the insolvency of individual organizations, and helps them fulfill their obligations.
Ohpension insurance
The social impact of the activity matters a lot. Therefore, the legal framework for pension insurance requires careful state oversight. And this state of affairs is not without reason. After all, this is a tool for shaping sources of pensions in the future. A distinction is made between compulsory and voluntary insurance. The first covers all categories of the population. Each citizen has his own individual personal account, to which the contributions transferred by the employer are credited. They form the labor pension. It should be noted that a citizen has the right to transfer the funded part under the management of various non-state structures. Voluntary pension insurance is a system of savings, which is based on the same principles as the mandatory one. Only the amount of contributions, conditions, and participation in general depend on the citizens themselves. You can safely choose an organization that will deal with assets, a software program and many other things. At the same time, the state does not influence them in terms of choosing a strategy, but carries out careful and very multifaceted supervision of their activities.
Some nuances
We should also touch upon the legal foundations of compulsory insurance. It is regulated by articles 927, 935-937, 969 of the Civil Code. Their essence can be reduced to:
- To ensure social interests for civil servants of certain categories, compulsory state insurance of life, he alth and property is established. This is done with funds fromfederal budget.
- All actions must be based on current laws, as well as other legal acts affecting the topic of insurance. This applies to the procedures, the process itself and the payments for these services. Payment is made in the amount established by law.
As you can see, the legal framework for compulsory insurance applies not only to pension savings.
About the medical aspect

It should be noted that insurance in this area has the minimum necessary legal basis. The changes are caused by the catastrophic state of he alth care. The legal foundations for compulsory he alth insurance were laid back in the early 1990s, and not much has changed since then. More common is the activity of the private sector. Although the legal basis for he alth insurance provides for the participation of state organizations.
About essence
Practically any activity has a risky nature. This is due to the fact that it is always possible to incur certain financial losses that are caused by adverse events or, alternatively, their consequences. The reason for such a development of events can be either completely dependent on the will of a person, or be associated with natural factors. Throughout our lives, we face many dangers that threaten our lives, he alth and property. Realizing this, a person expresses them in the concept of "risk". And here the essence exerts its influence. A society built on commoditymonetary relations, transfers the risk from household to economic category. In this role, the concept of probability is used to characterize it, as well as the uncertainty of the development of the situation. In fact, any event has three development options depending on the result:
- Auspicious. Receiving winnings.
- Does not entail changes. There is a null result.
- Negative. Turns into losses.
About Functions

What can be said based on the economic essence of insurance? Just this:
- Risk function. It lies in the fact that the essence of insurance allows you to create a risk transfer mechanism. And to be more precise, their financial consequences.
- Warning feature. It allows you to provide measures to prevent an insured event, as well as to minimize damage. Implemented through preventive solutions - requirements for the facility to reduce the occurrence of risks and the consequences that follow.
- Control function. They consist in the exclusively targeted formation and use of the insurance fund.
- Savings function. It is realized when using certain products aimed at providing life. An insurance organization both provides protection and functions as a savings institution.
About Forms
There is a wide variety of them. So, depending on the legal form, they distinguish:
- State insurance. Present when the government can directly influence the decisions of the organization.
- Non-government insurance. Also known as equity or mutual. In this case, legal entities with any organizational and legal form, which is only provided for by law, and not subject to the government, act as insurers.
Depending on the form of implementation:
- Voluntary.
- Required.
There is also an industry classification, which was introduced by the law "On the organization of insurance business in the Russian Federation":
- Private.
- Property.
You can select a number of forms, depending on a number of points. For example, what property rights are protected and the like.
Conclusion

This is what the legal foundations of insurance are, their essence, forms and types. It should be noted that this topic is extremely broad, and an attempt to cover it all can only be of a generalizing nature. And this is not surprising, because a qualitative analysis of the topic will require a detailed consideration of not only definitions, but also examples, special cases, comparisons with other approaches to implementation, and much more.
Recommended:
Classification of management functions: definition of the concept, essence and functions

Management is a complex and multifaceted process. Why is it needed and what is its essence? Let's talk about the concept and classification of control functions, consider approaches to this problem and characterize the main functions
A bank statement is The concept, necessary forms and forms, design examples
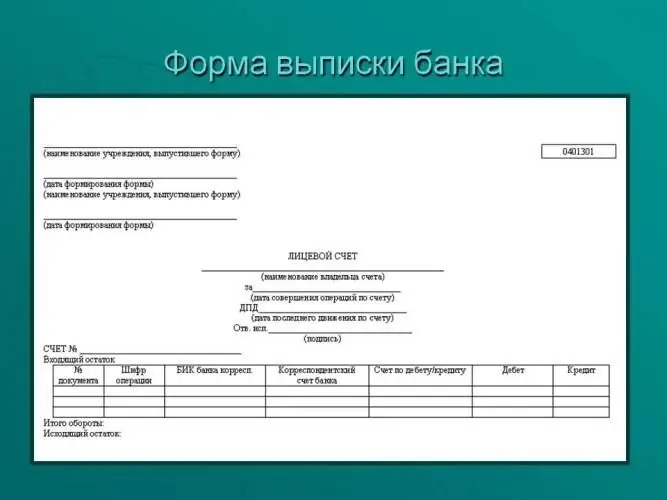
When purchasing any banking product, any client, sometimes without knowing it, becomes the owner of an account with which you can carry out income and debit transactions. At the same time, there must certainly be a certain tool that allows any client to exercise control over the movement of their own funds. This is a bank statement. This is a document that is usually issued upon request to the client. However, not everyone is aware of this possibility
Entrepreneurship, its types and forms. Concept, essence and signs of entrepreneurship

This article discusses in detail the concept of "entrepreneurship", given its concepts, essence, features, forms and types, and analyzed the personality of the entrepreneur. The main features of small, medium and large types of entrepreneurship are highlighted
Individual entrepreneur - legal form. Types of organizational and legal forms

Most often, an individual entrepreneur is registered (the legal form of "individual entrepreneur"). In addition, LLCs (limited liability companies) and CJSCs (closed joint-stock companies) are often registered. Each of the forms has both its advantages and disadvantages, which you need to know about before the stage of setting up a business
Insurance: essence, functions, forms, concept of insurance and types of insurance. The concept and types of social insurance

Today, insurance plays an important role in all spheres of life of citizens. The concept, essence, types of such relations are diverse, since the conditions and content of the contract directly depend on its object and parties

