2026 Author: Howard Calhoun | calhoun@techconfronts.com. Last modified: 2025-01-24 13:10:47
Sometimes in step-down transformer installations, a breakdown discharge between the low and high voltage windings may occur, as well as a significant increase in the potential difference on the low voltage windings. In connection with such cases, it became necessary to use protective devices, such as blowout fuses. Now almost all step-down transformer substations use these protective devices.
Blowout fuse
In the event of emergency situations in transformers between the high and low voltage windings, a breakdown occurs and a significant increase in voltage on the transformer plates, which can disable all connected equipment. This phenomenon is called transient voltage, in which the voltage from the high side passes to the low side, destroying its insulation, since the low side may not be designed forhigh voltages. To avoid this, they use special equipment - a blowout fuse.

There are several options for connecting the low side windings. When connecting the low side windings to a star, the transformer blowout fuse is connected to the neutral and then to ground. When connecting the windings of the low side into a triangle, the fuse is connected to one of the ends of the winding and then to ground.
What is the fuse made of
The punching fuse consists of two metal electrodes separated by a mica plate. The dimensions of the plate vary depending on the power and voltage of the low side windings of the transformer. Special holes are made in the plates for the passage of the discharge. Why this is needed - we will explain below.
One of the fuse electrodes is connected to the neutral, or to one of the phases of the transformer if there is no neutral. The use of these fuses greatly simplifies the control and maintenance of transformer substations.
Operation principle
When a junction voltage occurs in transformers, the voltage rises on the low side windings. In this case, a spark breakdown occurs, the discharges pass through the holes in the mica plate between the electrodes of the breakdown fuse, thereby switching between them and the increased voltage goes through the ground. As mentioned above, the dimensions and thickness of the mica plate itself, as well as the holes in it, depend onrated operating voltage of the high side of the transformer.

Such fuses are used when the voltage on the high side is above 3000 V, but if the voltage is lower than 3000 V, then simply blind grounding is used, or fuses by special order of the customer-consumer.
Features
At present, breakdown fuses with a rated operating voltage of 400 to 690 V are manufactured and used (in rare cases, fuses for a normal operation voltage of 230 V are made on special orders), the breakdown voltage limits vary from 300 to 1000 V. Discharge gap between electrodes varies from 0.08 to 0.3 mm, depending on the junction voltage.
The fuse during breakdown withstands ground current up to 200 A for 30 minutes. In this case, welding of the working electrodes during breakdown often occurs. During the porcelain insulation test, a voltage of 2000 V is applied to the ends of the fuse electrodes for 1 minute. Normal insulation resistance should not be lower than 4 ohms. After passing the test, the operating voltage is marked on the bottom of the porcelain case. All current-carrying parts of the fuse are nickel-plated, and the joints and fasteners are zinc coated.

During installation, this protective device must be installed strictly symmetrically to the vertical axis. When outdoor installation of transformers from above, the fuses are coveredspecial cover to protect against dust and moisture. Fuses are a one-time means of protection, that is, if a breakdown occurs through a mica plate, it should subsequently be replaced with a new one, especially if during the test of the breakdown fuses it was revealed that the electrodes were welded together.
Application
When calculating the power supply of any area of energy consumption, many special protection devices for electrical installations are necessarily introduced in order to avoid their failure. As described above, one of these devices is a blowout fuse. It is used to protect low voltage windings in a transformer installation with a voltage on the high side of 3000 V.

The main advantage of this type of fuse is their ease of manufacture, low cost, and ease of maintenance. Sometimes, according to the technical requirements of the client's conditions, installation organizations use analogs of blowout fuses.
Recommended:
Indicators without delay and redrawing: types, principle of operation, pros and cons of application, expert advice

There is a wide variety of different tools in trading: graphical constructions, technical indicators, automated programs, trading signals and much more. To successfully apply them in trading, you need to understand how they work. Indicators without delay and redrawing are especially popular with traders
Ion implantation: concept, principle of operation, methods, purpose and application
Ion implantation is a low-temperature process by which the components of a single element are accelerated into the solid surface of a wafer, thereby changing its physical, chemical or electrical properties. This method is used in the production of semiconductor devices and in metal finishing, as well as in materials science research
Electric locomotive 2ES6: history of creation, description with photo, main characteristics, principle of operation, features of operation and repair

Today, communication between different cities, passenger transportation, delivery of goods is carried out in a variety of ways. One of these ways was the railroad. Electric locomotive 2ES6 is one of the types of transport that is currently actively used
Low pressure heaters: definition, principle of operation, technical characteristics, classification, design, operation features, application in industry

Low pressure heaters (LPH) are currently used quite actively. There are two main types that are produced by different assembly plants. Naturally, they also differ in their performance characteristics
Gas piston power plant: the principle of operation. Operation and maintenance of gas piston power plants
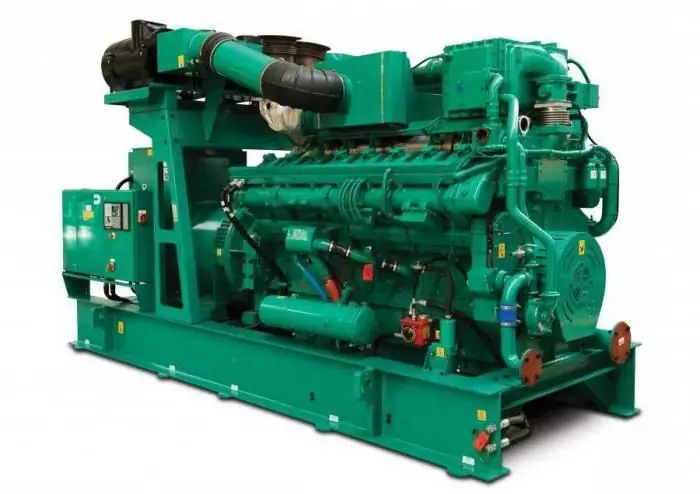

Gas piston power plant is used as a main or backup source of energy. The device requires access to any type of combustible gas to operate. Many GPES models can additionally generate heat for heating and cold for ventilation systems, warehouses, industrial facilities

