2026 Author: Howard Calhoun | calhoun@techconfronts.com. Last modified: 2025-01-24 13:10:49
Protection of the electric motor against overload today is one of the main tasks that must be solved in order to successfully operate this device. These types of engines are used quite widely, and therefore many ways have been invented to protect them from various negative effects.
Protection Levels
There is a wide variety of devices to protect this equipment, however, all of them can be divided into levels.
- External short circuit protection level. Most often, various types of relays are used here. These devices and the level of protection are at the official level. In other words, this is a mandatory item of protection that must be installed in accordance with the safety rules on the territory of the Russian Federation.
- The motor overload protection relay will help to avoid a variety of critical damage during operation, as well as possible damage. These devices also belong to the outer level of protection.
- An inner layer of protection prevents possibleoverheating of engine parts. For this, external switches are sometimes used, and sometimes overload relays.

Causes of equipment failures
Today, there is a wide variety of problems that can affect the performance of an electric motor if it is not equipped with protection devices.
- Low electrical voltage or, conversely, too high a supply level can cause failure.
- Possible damage due to changing the frequency of the current supply too quickly and often.
- Incorrect installation of the unit or its components can also be dangerous.
- The temperature rises to a critical value or higher.
- Too little cooling also leads to breakdowns.
- Elevated ambient temperature has a strong negative effect.
- Few people know that low pressure or setting the engine much above sea level, which causes low pressure, also has a negative effect.
- Naturally, it is necessary to protect the motor from overloads that may occur due to power failures.
- Frequent switching on and off of the device is a negative defect that also needs to be eliminated with the help of protection devices.

Fuses
The full name of the protective equipment is the fusible safety switch. This device combines and automaticswitch and fuse, which are located in the same housing. The switch can also open or close the circuit manually. The fuse is the protection of the electric motor against overcurrent.
It is worth noting that the design of the emergency switch provides for a special casing that protects personnel from accidental contact with the terminals of the device, as well as the contacts themselves from oxidation.
As far as the fuse is concerned, this device must be able to distinguish between an overcurrent and a short circuit in the circuit. This is very important, as short-term overcurrent is quite acceptable. However, the motor overload protection should trip immediately if this parameter continues to increase.

Short circuit fuses
There is a type of fuse that is designed to protect the unit from a short circuit (short circuit). However, it is worth noting here that the fast-acting fuse may fail if a short-term overload occurs during the start-up of the device, that is, an increase in the starting current. For this reason, such devices are usually used in networks where such a jump is not possible. As for the motor overload protector itself, the fast blow fuse can handle up to 500% more than its rated current if the difference lasts less than a quarter of a second.

Delay fuses
The development of technology has led to the fact that it was possible to create a device for protection against both overload and short circuit at the same time. This tool was a fuse with a delay. The peculiarity is that it is able to withstand a 5-fold increase in current if it lasts no more than 10 seconds. An even larger increase in the parameter is possible, but for a shorter period before the fuse blows. However, most often an interval of 10 seconds is enough to start the engine, and so that the fuse does not work. Protection of a single-phase electric motor against overloads, against short circuits, as well as another type of electric motor by such a device is considered one of the most reliable.
It is also worth noting here how the response time of this protection device is determined. The response time of a fuse is the length of time for which its fusible element (wire) melts. When the wire is completely melted, the circuit opens. If we talk about the dependence of the disconnection time on overload for these types of protective equipment, then they are inversely proportional. In other words, the current overload protection of the electric motor works like this - the higher the current strength, the faster the wire melts, which means that the time for disconnecting the circuit is reduced.

Magnetic and thermal appliances
Today, automatic thermal devices are considered the most reliable and economical devices for protecting an electric motorfrom thermal overload. These devices are also capable of withstanding large current amplitudes that may occur during instrument start-up. In addition, thermal fuses protect against problems such as a locked rotor, for example.
Protection of asynchronous electric motors from overload can be carried out using automatic magnetic switches. They are highly reliable, accurate and economical. Its peculiarity lies in the fact that the temperature limit of its operation is not affected by changes in the ambient temperature, which is very important in some operating conditions. They are also different from thermal themes, they have a more precise response time.

Overload relay
The functions of this device are quite simple, however, and quite important.
- Such a device is able to withstand a short current surge during engine start without breaking the circuit, which is the most important.
- Opening the circuit occurs if the current increases to the value when there is a threat of breakage of the protected device.
- After the overload is removed, the relay can reset automatically or can be reset manually.
It is worth noting that the current protection of the electric motor against overloads using a relay is carried out in accordance with the response characteristic. In other words - depending on the class of the device. The most common are classes 10, 20 and 30. The first group are relays thatoperate in the event of an overload, within 10 seconds and if the numerical value of the current exceeds 600% of the nominal. The second group is triggered after 20 seconds or less, the third, respectively, after 30 seconds or less.

Fuse protection and relays
Nowadays, it is quite common to combine two means of protection - fuses and relays. This combination works as follows. The fuse must protect the motor from a short circuit, and therefore it must have a sufficiently large capacity. Because of this, it cannot protect the device from lower but still dangerous currents. It is to eliminate this drawback that relays are introduced into the system that respond to weaker, but still dangerous current fluctuations. The most important thing in this case is to set the fuse so that it blows before any damage occurs.
Outdoor protection
Currently, advanced systems of external motor protection are used quite often. They can protect the device from overvoltage, phase imbalance, are able to eliminate vibrations or limit the number of on and off. In addition, such tools have a built-in thermal sensor, which helps to control the temperature of the bearings, the stator. Another feature of such a device is that it is able to perceive and process a digital signal that a temperature sensor creates.
The main purpose of external protective equipment- this is the preservation of the efficiency of three-phase motors. In addition to being able to protect the motor during a power failure, such equipment also has several other benefits.
- An outdoor unit can generate and signal a fault before it affects the machine.
- Diagnoses problems that have already occurred.
- Enables relay testing during maintenance.
Based on the foregoing, it can be argued that there is a wide variety of devices for protecting an electric motor from overload. In addition, each of them is able to protect the device from certain negative influences, and therefore it is advisable to combine them.
Recommended:
Electric motor with gearbox: features, device and principle of operation

Nowadays, it is difficult to find an industry that does not use geared motors. This unit is a kind of electromechanical independent unit in which the electric motor and gearbox work in pairs
Thermal imaging control of electrical equipment: concept, principle of operation, types and classification of thermal imagers, features of application and verification
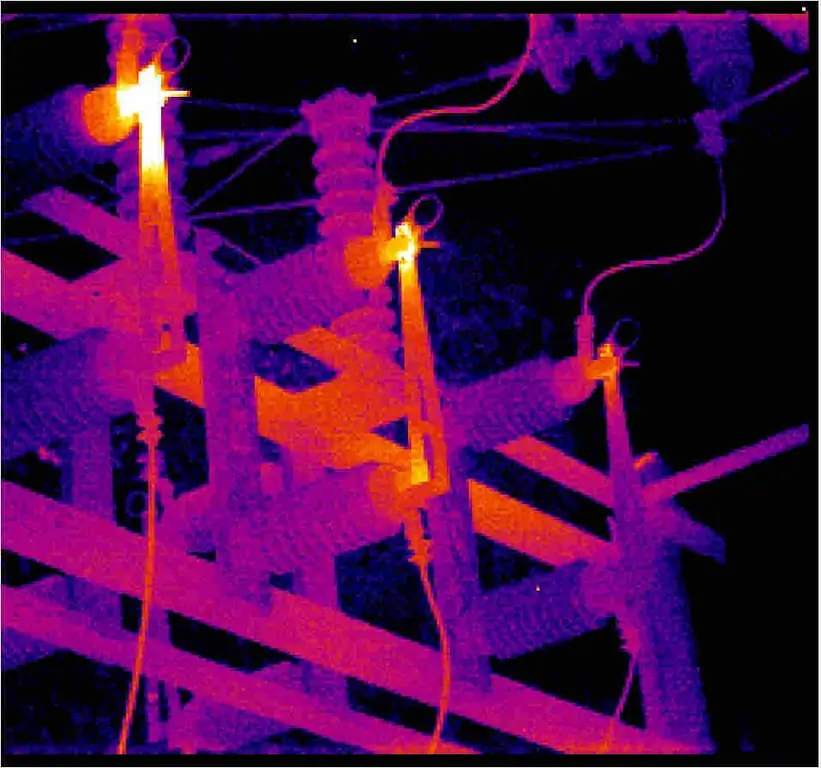
Thermal imaging control of electrical equipment is an effective way to identify defects in power equipment that are detected without shutting down the electrical installation. In places of poor contact, the temperature rises, which is the basis of the methodology
Electric locomotive 2ES6: history of creation, description with photo, main characteristics, principle of operation, features of operation and repair

Today, communication between different cities, passenger transportation, delivery of goods is carried out in a variety of ways. One of these ways was the railroad. Electric locomotive 2ES6 is one of the types of transport that is currently actively used
Low pressure heaters: definition, principle of operation, technical characteristics, classification, design, operation features, application in industry

Low pressure heaters (LPH) are currently used quite actively. There are two main types that are produced by different assembly plants. Naturally, they also differ in their performance characteristics
Protection devices: purpose, types, classification, specifications, installation, features of operation, settings and repair

Protection devices are currently in operation almost everywhere. They are designed to protect both electrical networks and electrical equipment, various machines, etc. It is very important to properly install and follow the operating rules so that the devices themselves do not cause a fire, explosion, etc

