2026 Author: Howard Calhoun | calhoun@techconfronts.com. Last modified: 2025-01-24 13:10:25
In the application of compact, productive and functional drive mechanisms today, almost all areas of human activity from heavy industry to transport and households are interested. This is also the reason for the constant improvement of traditional concepts of power units, which, although they are improving, do not change the fundamental device. The most popular basic systems of this type include an electromagnetic drive, the working mechanism of which is used both in large-format equipment and in small technical devices.
Drive Assignment
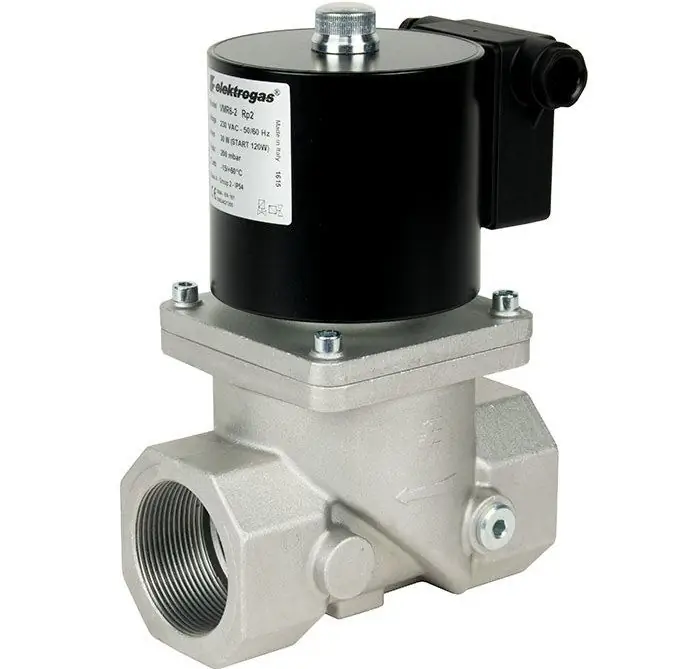

In almost all target applications, this mechanism acts as the executive body of the system. Another thing is that the nature of the function performed and the degree of its responsibility within the framework of the overall work process may change. For example,in shut-off valves, this drive is responsible for the current position of the valve. In particular, due to its effort, the overlap assumes the position of a normally closed or open state. Such devices are used in various communication systems, which determines both the principle of operation and the protective characteristics of the device. In particular, the electromagnetic smoke exhaust drive is included in the infrastructure of the fire safety system, structurally docking with the ventilation ducts. The drive housing and its critical working parts must be resistant to high temperatures and harmful contacts with thermally hazardous gases. As for the command to execute, the automation usually works when signs of smoke are detected. The drive in this case is a technical means of regulating the flow of smoke and burning.
A more complex configuration for the use of electromagnetic actuators takes place in multi-way valves. These are a kind of collector or distribution systems, the complexity of which lies in the simultaneous control of entire groups of functional units. In such systems, an electromagnetic valve actuator is used with the function of switching flows through nozzles. The reason for closing or opening the channel can be certain values of the working medium (pressure, temperature), flow intensity, program settings for time, etc.
Design and components
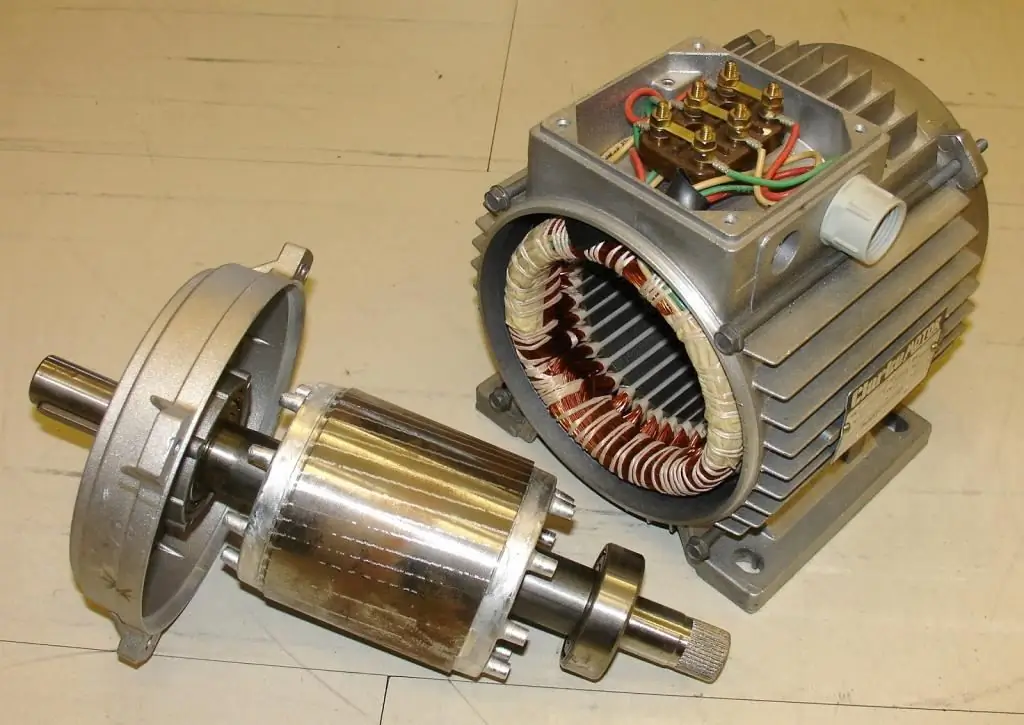
The central working element of the drive is the solenoid block, which is formed by a hollow coil andmagnetic core. Communication electromagnetic connections of this component with other parts are provided by small internal fittings with control impulse valves. In the normal state, the core is supported by a spring with a stem that rests on the saddle. In addition, a typical electromagnetic drive device provides for the presence of a so-called manual understudy of the working part, which takes over the functions of the mechanism in moments of sudden changes or a complete absence of voltage. Additional functionality may be provided, provided by means of signaling, auxiliary locking elements and fixators of the position of the core. But since one of the advantages of this type of drives is their small size, in order to optimize, developers try to avoid excessive saturation of the design with secondary devices.
The principle of operation of the mechanism
In both magnetic and electromagnetic power devices, the role of the active medium is performed by the magnetic flux. For its formation, either a permanent magnet or a similar device is used with the possibility of a point connection or disconnection of its activity by changing the electrical signal. The executive body begins to operate from the moment the voltage is applied, when the current begins to flow through the circuits of the solenoid. In turn, the core, as the activity of the magnetic field increases, begins its movement relative to the cavity of the inductor. Actually, the principle of operation of the electromagnetic drive just comes down to the conversion of electrical energy intomechanical by means of a magnetic field. And as soon as the voltage drops, the forces of the elastic spring come into play, which returns the core to its place and the drive armature takes its original normal position. Also, to regulate the individual stages of force transmission in complex multi-stage drives, pneumatic or hydraulic drives can be additionally switched on. In particular, they make possible the primary generation of electricity from alternative energy sources (water, wind, sun), which reduces the cost of the equipment workflow.
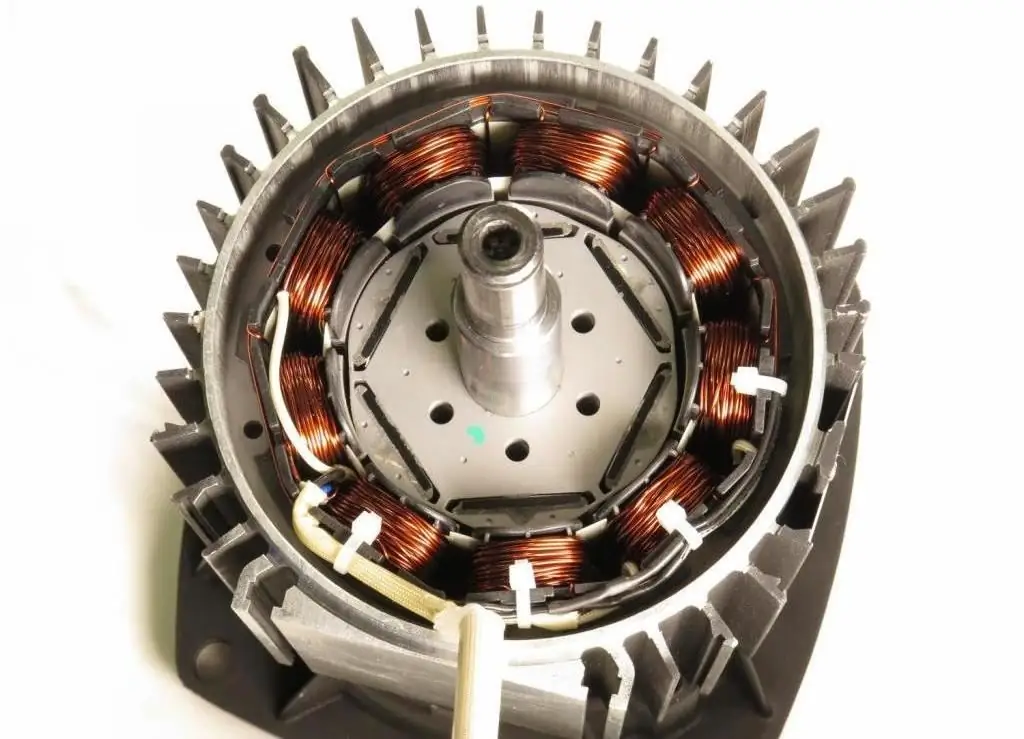

Electromagnetic actuator action
The movement pattern of the drive core and its ability to work as an output power unit determine the features of the actions that the mechanism can perform. It should be noted right away that in most cases these are devices with the same type of elementary movements of the executive mechanics, which are rarely supplemented with auxiliary technical functions. On this basis, the electromagnetic drive is divided into the following types:
- Rotary. In the process of applying current, a power element is activated, which makes a turn. Such mechanisms are used in ball and plug valves, as well as in butterfly valve systems.
- Reversible. In addition to the main action, it is able to provide a change in the direction of the power element. More common in control valves.
- Pushing. This electromagnetic actuator performs a pushing action, which is also used in distribution andcheck valves.
From the point of view of the structural solution, the power element and the core may well be different parts, which increases the reliability and durability of the device. Another thing is that the principle of optimization requires the combination of several tasks within the functionality of one technical component in order to save space and energy resources.
Electromagnetic fittings
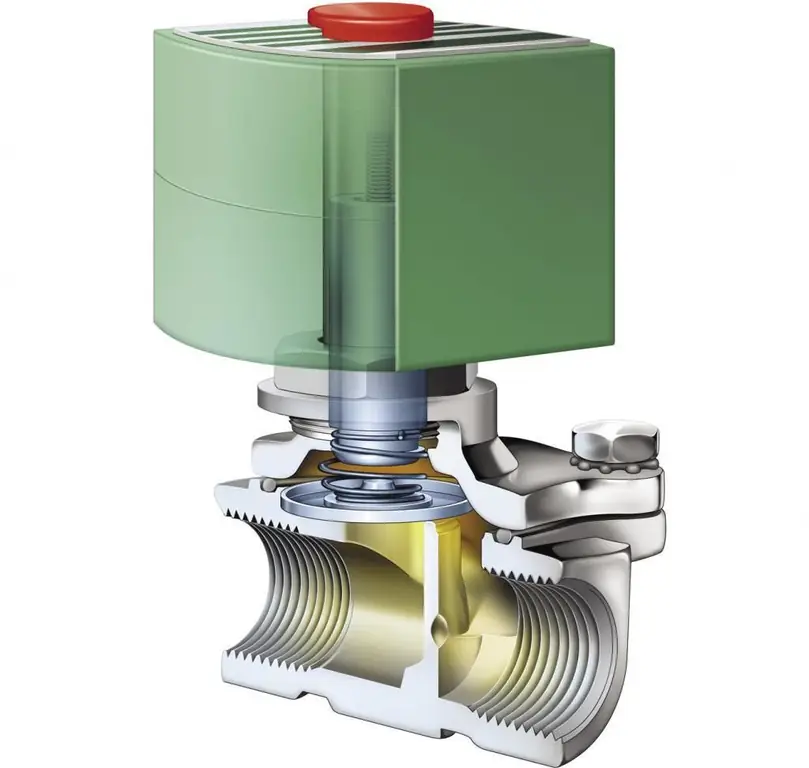

The executive bodies of the drive can work in different configurations, performing certain actions required for the operation of a particular working infrastructure. But in any case, the function of the core or strength element alone will not be enough to provide a sufficient effect in terms of fulfilling the final task, with rare exceptions. In most cases, a transition link is also required - a kind of translator of the generated mechanical energy from the directly driven mechanics to the target device. For example, in an all-wheel drive system, an electromagnetic clutch acts not just as a force transmitter, but as an engine that rigidly connects the two parts of the shaft. Asynchronous mechanisms even have their own excitation coil with pronounced poles. The leading part of such couplings is made according to the principles of the rotor winding of an electric motor, which gives this element the functions of a converter and force translator.
In simpler systems with direct action, the task of transmitting force is performed by standard ball bearing devices, swivel and distribution units. Specificthe execution and configuration of the action, as well as the relationship with the drive system, is realized in different ways. Often, individual schemes for interfacing components with each other are developed. In the same electromagnetic drive clutch, an entire infrastructure is organized with its own metal shaft, slip rings, collectors and copper bars. And this is not counting the parallel arrangement of electromagnetic channels with pole pieces and contours of the direction of the magnetic field lines.
Drive operating parameters
The same design with a typical scheme of operation may require the connection of different capacities. Also, typical models of drive systems differ in power load, type of current, voltage, etc. The simplest solenoid valve actuator operates on 220 V, but there may also be models with a similar design, but requiring connection to three-phase industrial networks at 380 V. Power supply requirements are determined by the size of the device and the characteristics of the core. The number of revolutions of the motor, for example, directly determines the amount of power consumed, and with it the insulation properties, windings and resistance parameters. Concretely speaking about the industrial electrical infrastructure, the heavy-duty drive integration project should consider the traction force, grounding loop characteristics, circuit protection device implementation diagram, etc.
Modular drive systems
Most commonthe structural form factor for the production of drive mechanisms based on the electromagnetic principle of operation is block (or aggregate). This is an independent and somewhat isolated device that is mounted on the body of the target mechanism or also a separate actuating unit. The fundamental difference between such systems is that their surfaces do not come into contact with the cavities of the transitional power links and, moreover, the working elements of the executive bodies of the target equipment. At least, such contacts do not necessitate the adoption of any measures to protect both structures. The block type of an electromagnetic drive is used in cases where functional units need to be isolated from the negative influence of the working environment - for example, from the risks of corrosion damage or temperature exposure. To provide a mechanical bond, the same insulated armature like a stem is used.
Integrated drive features

A kind of electromagnetic power drives that act as an integral part of the working system, forming a single communication infrastructure with it. As a rule, such devices have compact dimensions and low weight, which allows them to be integrated into a variety of engineering structures without a significant impact on their functional and ergonomic characteristics. On the other hand, sizing optimization and the need to expand the possibilities for tying (direct connection to the equipment) limits the creators in providinghigh degree of protection of such mechanisms. Therefore, typical budget-friendly insulating solutions are being thought out, like separating hermetic tubes, which help protect sensitive elements from the aggressive effects of the working environment. Exceptions include vacuum valves with an electromagnetic drive in a metal case, to which fittings made of high-strength plastic are connected. But these are already specialized enlarged models that have comprehensive protection against toxic, thermal and mechanical factors.
Application areas of the device
With the help of this drive, the tasks of power mechanical support of different levels are solved. In the most critical and complex systems, glandless fittings are used to control electromagnetic devices, which increases the degree of reliability and performance of equipment. In this combination, the units are used in transport and communication pipeline networks, in the maintenance of storage facilities with petroleum products, in the chemical industry, at processing stations and plants in various industries. If we talk about simple devices, then in the domestic sphere, an electromagnetic fan drive for supply and exhaust systems is common. Small format mechanisms also find their place in plumbing fixtures, pumps, compressors, etc.

Conclusion
Provided that the structure of the drive mechanism is properly designed, on the basis of electromagnetic elements, you can get quite profitablesource of mechanical force. In the best versions, such devices are distinguished by a high technical resource, stable operation, minimal power consumption and flexibility in terms of combination with various actuators. As for the characteristic weaknesses, they manifest themselves in low noise immunity, which is especially pronounced in the operation of the electromagnetic drive of the circuit breaker on high-voltage power lines with a voltage of 10 kV. Such systems, by definition, need special protection against electromagnetic interference. Also, due to the technical and structural complexity due to the use of a hinged-lever mechanism with a pusher and a holding latch in the switch, additional connection of protective electrical devices is required to eliminate the risks of short circuits in the circuits.
Recommended:
Classification of engines. Types of engines, their purpose, device and principle of operation
Nowadays, most vehicles are powered by an engine. The classification of this device is huge and includes a large number of different types of engines
Universal drive: types, device and purpose

Today, the development of technology has advanced quite widely, and those operations that were previously performed by two different devices can be performed by just one machine. A striking example of such progress was the universal drive
Differential pressure gauge: principle of operation, types and types. How to choose a differential pressure gauge

The article is devoted to differential pressure gauges. The types of devices, the principles of their operation and technical features are considered
Clutch flywheel: description, types, purpose and principle of operation

Everyone knows that the main task of an engine is to convert energy into torque. Its transmission is carried out through a special flywheel of the clutch disc. This node is available in any car. How is it arranged and functioning? All this and more - further in our article
Scraper conveyor: principle of operation, types, purpose and features

Scraper conveyors have become widespread in the coal industry. They can move the load along a fixed chute with the help of scrapers, which are connected by a movable chain. These conveyors are used to transport dusty, granular and lumpy goods

