2026 Author: Howard Calhoun | calhoun@techconfronts.com. Last modified: 2025-01-24 13:10:37
Pressure in gaseous and liquid media is one of the most important indicators, the measurement of which is required for the maintenance of communication and technological systems. Work objects include various filters, pipeline systems, air conditioning and ventilation devices. Using a differential pressure gauge, the user not only identifies the characteristics of the actual pressure, but also gets the opportunity to record the difference between dynamic indicators. Knowledge of this data facilitates system monitoring and improves operational reliability. In addition, differential pressure gauges are also used to measure the flow of liquid, gas or compressed air.
Working principle

In most pressure gauges, the technology for determining and calculating data is based on deformation processes in special measuring blocks, for example, in a bellows. This element acts as an indicator that perceives pressure drops. The block also becomes a pressure difference converter - the user receives information in the form of moving the pointer on the device. In addition, data can be presented in Pascals, coveringthe entire measuring spectrum. This way of displaying information, for example, is provided by the Testo 510 differential pressure gauge, which, during the measurement process, relieves the user of the need to hold it in his hand, since special magnets are provided on the back of the device.
In mechanical devices, the main indicator is the location of the arrow, controlled by the lever system. The movement of the pointer occurs until the moment when the drops in the system cease to exert the influence of a certain force. A classic example of this system is the 3538M Series DM Differential Pressure Gauge, which provides proportional delta (differential pressure) conversion and provides the result to the operator as a unified signal.
Classification

Due to the complexity of pressure measurement processes, the characteristics of working media and further conversion, there are several options for differential pressure gauges to work in different conditions. By the way, the differential pressure gauge, the principle of operation of which is largely determined by its design, is oriented in its design to the possibility of application in specific environments - therefore, classification is made from this. So, manufacturers produce the following models:
- Group of liquid differential pressure gauges, which includes float, bell, pipe and ring modifications. In them, the measuring process takes place on the basis of indicators of the liquid column.
- Digital pressure gauges. They are considered the most functional, since they make it possible to measure not only the characteristics of pressure drops, but also the speed of compressed air flows, indicators of humidity and temperature. A prominent representative of this group is the Testo differential pressure gauge, which is also used in environmental monitoring systems, in aerodynamic and environmental studies.
- Category of mechanical devices. These are bellows and diaphragm versions providing measurement by monitoring the characteristics of the pressure sensitive element.
Two-pipe models
These devices are used to measure pressure indicators and determine the differences between them. These are devices with a visible level, which is usually presented in a U-shape. By design, such a differential pressure gauge is an installation of two vertical communicating tubes, which are fixed on a wooden or metal base. A mandatory component of the device is a plate with a scale. In preparation for the measurement, the pipes are filled with the working medium.
Next, the supply of the measured pressure begins in one of the pipes. At the same time, the second pipe interacts with the atmosphere. During the delta measurement, both tubes are subjected to a measurable pressure. Two-pipe liquid-filled differential pressure gauge is used to measure vacuum, pressure of non-corrosive gases and air media.
Single-pipe models

Single tube differential pressure gaugescommonly used when high precision results are required. In such devices, a wide vessel is also used, which is subjected to pressure with the highest coefficient. The only tube is fixed to a plate with a scale showing these differences, and communicates with the atmospheric environment. In the process of measuring pressure drops, the smallest of the pressures interacts with it. Fluid is poured into the differential pressure gauge until zero level is reached.
Under the influence of pressure, a certain proportion of the liquid flows into the tube from the vessel. Since the volume of the working medium that has moved into the measuring tube corresponds to the volume that has left the vessel, a single-tube differential pressure gauge provides for measuring the height of only one liquid column. In other words, the measurement error is reduced. However, devices of this type are not without drawbacks.
Deviations from the optimal values may be due to thermal expansion in the measuring components of the device, the density of the working medium and other errors, which, however, are typical for all types of differential pressure gauges. For example, a digital differential pressure gauge, even with corrections for density and temperature coefficients, also has a certain margin of error.
Diaphragm differential pressure gauges

The main subtype of mechanical differential pressure gauges, which is also divided into devices with metallic and non-metallicmeasuring elements. In devices with a flat membrane made of metal, calculations are based on fixing the deflection characteristics in the measuring component. A differential pressure gauge is also common, in which the membrane acts as a dividing wall for the chambers. At the moment of deformation, the counteracting force is formed by a cylindrical spiral spring, which unloads the measuring element. This is how two different pressures are compared.

Also, some modifications of membrane devices are provided with protection against one-sided impact - this design feature allows them to be used in measuring overpressure indicators. Despite the active introduction of electronics into the metrology industry as a whole, membrane measuring instruments remain in demand and even indispensable in some areas. For example, the high-tech differential pressure gauge DMTs-01m of digital type, despite its ergonomics and high accuracy, has a number of limitations for use in conditions where operation of membrane devices is possible.
Bellow versions
In such models, the measuring element is a corrugated metal box, supplemented with a spiral spring. The plane of the device is divided by a bellows into two parts. The greatest impact of pressure falls on the chamber outside the bellows, and the smallest - in the internal cavity. As a result of exposure to pressures with different forces, the sensitive element is deformed in accordance with a value proportional to the desired indicator. itclassic differential pressure gauges showing the results of measurements by an arrow on the dial. But there are other representatives of this family.
Other mechanical versions
Less common are ring, float and bell devices for measuring differential pressure. Although among them there are relatively accurate scaleless and self-recording models, as well as devices with contact electrical devices. Data transmission in them is provided remotely, again, by means of electrical communication or due to pneumatics. To determine consumption indicators based on variable differences, mechanical devices are also produced with summing and integrating additions.
Digital pressure gauges

Devices of this type, in addition to the basic functions of measuring the difference in pressure, are able to determine the dynamic performance of working media. Such devices are marked DMC-01m. A digital differential pressure gauge, in particular, is used in ventilation control systems of production facilities, it allows you to calculate gas consumption indicators, taking into account temperature corrections, as well as keep records of average consumption for measured positions. The device is equipped with a microprocessor that automatically keeps records of measurements and accumulation of information on the flue. All received information about the results of the work is displayed on the display.
Recommendations for selection

Calculation operations with pressure indicators requireusing a reliable device that best suits the operating conditions. In this regard, it is important to determine the list of functions that the device will perform. For example, the Testo 510 differential pressure gauge is able to provide accurate, temperature compensated readings and provide data on a digital display. In some cases, a signaling model is required, so this option should be taken into account.
For the most correct data, you must first compare the characteristics of the device with the possibility of operation in a specific working environment. Not all devices can be used in oxygen, ammonia and freon environments. At the very least, their accuracy may be poor.
Recommended:
Indicators without delay and redrawing: types, principle of operation, pros and cons of application, expert advice

There is a wide variety of different tools in trading: graphical constructions, technical indicators, automated programs, trading signals and much more. To successfully apply them in trading, you need to understand how they work. Indicators without delay and redrawing are especially popular with traders
Thermal imaging control of electrical equipment: concept, principle of operation, types and classification of thermal imagers, features of application and verification
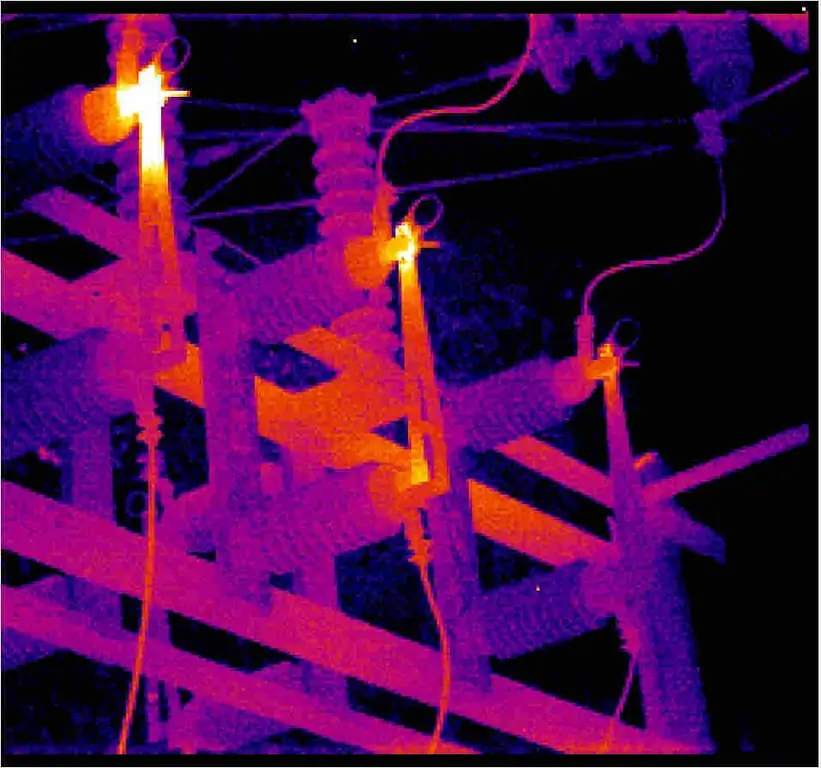
Thermal imaging control of electrical equipment is an effective way to identify defects in power equipment that are detected without shutting down the electrical installation. In places of poor contact, the temperature rises, which is the basis of the methodology
Electric locomotive 2ES6: history of creation, description with photo, main characteristics, principle of operation, features of operation and repair

Today, communication between different cities, passenger transportation, delivery of goods is carried out in a variety of ways. One of these ways was the railroad. Electric locomotive 2ES6 is one of the types of transport that is currently actively used
Low pressure heaters: definition, principle of operation, technical characteristics, classification, design, operation features, application in industry

Low pressure heaters (LPH) are currently used quite actively. There are two main types that are produced by different assembly plants. Naturally, they also differ in their performance characteristics
Gas piston power plant: the principle of operation. Operation and maintenance of gas piston power plants
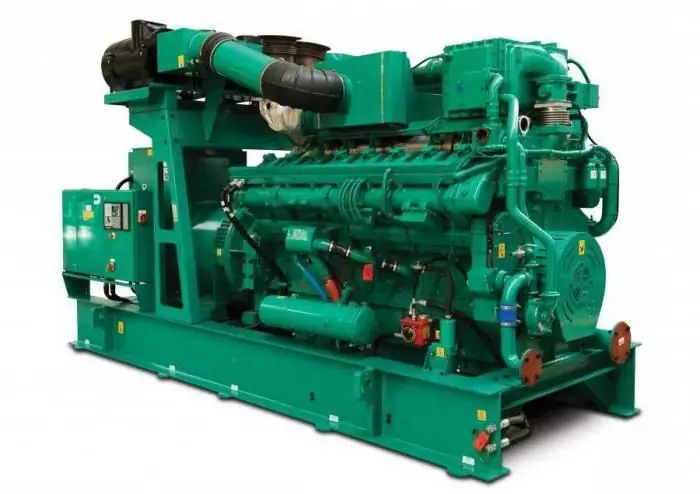

Gas piston power plant is used as a main or backup source of energy. The device requires access to any type of combustible gas to operate. Many GPES models can additionally generate heat for heating and cold for ventilation systems, warehouses, industrial facilities

