2026 Author: Howard Calhoun | calhoun@techconfronts.com. Last modified: 2025-01-24 13:10:41
Electric machines perform the critical function of energy conversion in working mechanisms and generating stations. Such devices find their place in different areas, supplying the executive bodies with sufficient power potential. One of the most popular systems of this type are AC machines (ACMs), which have several varieties and differences within their class.
General information about MAT
The segment of MPT or electromechanical converters can be conditionally divided into single-phase and three-phase systems. Also, at the basic level, asynchronous, synchronous and collector devices are distinguished, while the general principle of operation and design design have much in common. This classification of AC machines is conditional, since modern electromechanical conversion stations partially involve workflows from each group of devices.
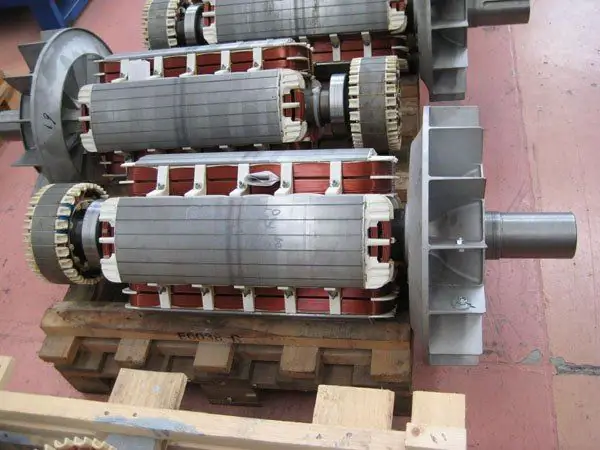
As a rule, the MPT is based on a stator and a rotor, between which an air gap is provided. Again, regardless of the type of machine, the work cycle is based on the rotation of the magnetic field. But if in a synchronous installation the movement of the rotor corresponds to the direction of the force field, then in an asynchronous machine the rotor can move in a different direction and with different frequencies. This difference also determines the features of the use of machines. So, if synchronous can act both as a generator and as an electromechanical motor, then asynchronous ones are mainly used as motors.
As for the number of phases, single- and multi-phase systems are distinguished. Moreover, from the point of view of practical use, representatives of the second category deserve attention. These are for the most part three-phase AC machines, in which the magnetic field just performs the function of an energy carrier. Single-phase devices, on the other hand, due to operational impracticality and large sizes, are gradually disappearing from the practice of application, although in some areas the decisive factor in their choice is low cost.
Differences from DC machines
The fundamental structural difference lies in the location of the winding. In AC systems, it covers the stator, and in DC machines, the rotor. In both groups, electric motors differ in the type of current excitation - mixed, parallel and series. Today, AC and DC machines are used in industry, agriculture and the domestic sector, but the firstoption is more attractive in terms of performance. Alternators and AC motors benefit from improved design, reliability and high energy efficiency.
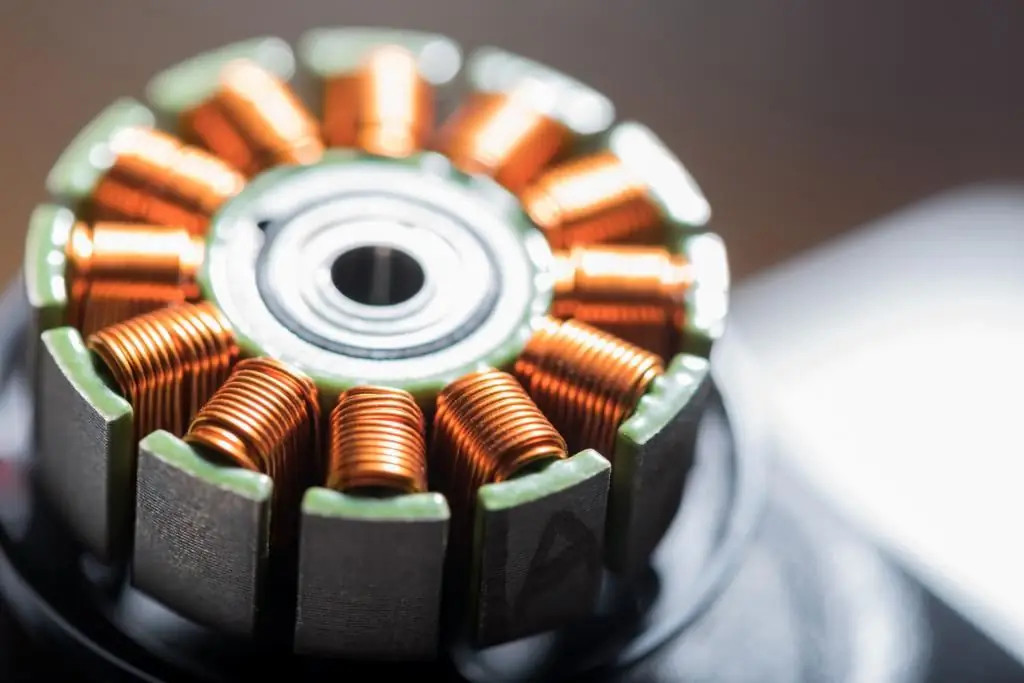

The use of direct current devices is widespread in areas where the requirements for the accuracy of regulation of operating parameters come to the fore. These can be transport traction mechanisms, machine tools and complex measuring instruments. In terms of performance, DC and AC machines have a high efficiency, but with different possibilities of technical and structural adjustment to specific application conditions. DC operation gives more options for speed control, which is important when servicing servo and stepper motors.
Asynchronous MPT device
For the technical basis of this device in the form of a rotor and a stator, sheet steel is used, which is coated with an insulating oil-rosin layer on both sides before assembly. In low-power machines, the core can be made of electrical steel without additional coating, since in this case the natural oxide layer on the metal surface acts as an insulator. The stator is fixed in the housing, and the rotor on the shaft. In asynchronous high power AC machines, the rotor core can also be mounted on the housing rim with a sleeve mounted on the shaft. The shaft itself must rotate on the bearing shields, which are also fixed to the base of the housing.
The outer surfaces of the rotor and the inner surfaces of the stator are initially provided with grooves to accommodate the winding conductors. In the stator of AC machines, the winding is often three-phase and connected to the appropriate 380 V network. It is also called primary. The rotor winding is similarly performed, the ends of which usually form a connection in a star configuration. Slip rings are also provided, through which a rheostat for adjustment or a three-phase starting element can be additionally connected.
It is also important to note the parameters of the air gap, which acts as a damper zone that reduces noise, vibration and heat during operation of the device. The larger the machine, the larger the gap should be. Its value can vary from one to several millimeters. If it is structurally impossible to leave enough space for the air zone, then an additional cooling system for the unit is provided.
The principle of operation of asynchronous MPT
The three-phase winding in this case is connected to a symmetrical network with a three-phase voltage, as a result of which a magnetic field is formed in the air gap. Regarding the armature winding, special measures are taken to achieve a harmonic spatial distribution of the field for the damping gap, which forms a system of rotating magnetic poles. According to the principle of operation of an alternating current machine, a magnetic flux is formed at each pole, which crosses the winding circuits, thereby provoking the generation of electromotivestrength. A three-phase current is induced in the three-phase winding, which provides the motor torque. Against the background of the interaction of the rotor current with magnetic fluxes, an electromagnetic force is formed on the conductors.
If the rotor, under the action of an external force, is set in motion, the direction of which corresponds to the direction of the fluxes of the magnetic field of the AC machine, then the rotor will begin to overtake the rate of rotation of the field. This occurs when the stator speed exceeds the rated synchronous frequency. At the same time, the direction of movement of electromagnetic forces will be changed. In this way, a braking torque with a reverse action is formed. This principle of operation allows the machine to be used as a generator operating in the mode of active power output to the network.
Design and principle of operation of synchronous MPT

In terms of design and location of the stator, a synchronous machine is similar to an asynchronous one. The winding is called an armature and is performed with the same number of poles as in the previous case. The rotor is provided with an excitation winding, the energy supply of which is provided by slip rings and brushes connected to a direct current source. A source is a low-power generator-exciter mounted on a single shaft. In a synchronous AC machine, the winding acts as a generator of the primary magnetic field. During the design process, designers strive to create conditions so that the inductive distribution of the excitation fieldon the surfaces of the stator was as close to sinusoidal as possible.
At increased loads, the stator winding generates a magnetic field with rotation in the direction of the rotor with the same frequency. Thus, a single field of rotation is formed, in which the stator field will affect the rotor. This device of AC machines allows them to be used as electric motors, if a three-phase current is initially supplied to the synchronous winding. Such systems create conditions for the coordinated rotation of the rotor with a frequency corresponding to the stator field.
Salient and non-salient synchronous machines
The main difference between salient pole systems is the presence of protruding poles in the design, which are attached to special protrusions of the shaft. In typical mechanisms, fixation is carried out with the help of T-shaped tail fasteners to the rim of the cross or the shaft through the bushing. In the device of low-power AC machines, the same problem can be solved by bolted connections. As a winding material, strip copper is used, which is wound on an edge, insulating with special gaskets. In lugs with poles in the grooves, the winding rods for starting are placed. In this case, a high resistivity material like brass is used. The winding contours at the ends are welded to the short-circuiting elements, forming common rings for a short circuit. Salient-pole machines with a power potential of 10-12 kW can be performed in the so-called inverted design, when the armature rotates and the inductor poles remain stationarycondition.

In non-salient pole machines, the design is based on a cylindrical rotor made of steel forging. There are grooves in the rotor to form an excitation winding, the poles of which are calculated for high speeds. However, the use of such a winding in electrical machines with high power alternating current is impossible due to the high degree of rotor wear in harsh operating conditions. For this reason, even in medium-power installations, high-strength components made of solid forgings based on chromium-nickel-molybdenum or chromium-nickel steels are used for rotors. In accordance with the technical requirements for strength, the maximum diameter of the working part of the rotor of a non-salient synchronous machine rotor cannot exceed 125 cm. elements. The maximum length of the rotor is 8.5 m. Non-salient pole units that are used in industry include various turbogenerators. With their help, in particular, they connect the working moments of steam turbines with thermal power plants.
Features of vertical hydro generators
A separate class of salient-pole synchronous MPTs provided with a vertical shaft. Such installations are connected to hydraulic turbines and are selected according to the power of the served flows according to the rotation frequency. Most AC machines of this type are low-speed, but at the same time they havea large number of poles. Among the critical working components of a vertical hydro generator, one can note a thrust bearing and a thrust bearing, which bears the load from the rotating parts of the engine. The thrust bearing, in particular, is also subjected to pressure from the flow of water, which acts on the turbine blades. In addition, a brake is provided to stop rotation, and guide bearings are also present in the working structure that perceive radial forces.
In the upper part of the machine, along with the hydro generator, auxiliary units can be placed - for example, a generator exciter and a regulator. By the way, the latter is an independent AC machine with a winding and poles for permanent magnets. This setting provides power to the motor for the automatic governor function. In large vertical hydro generators, the exciter can be replaced by a synchronous generator, which, together with the excitation units and mercury rectifiers, provides power to the power devices serving the working process of the main hydro generator. The vertical shaft machine configuration is also used as a drive mechanism for heavy duty hydraulic pumps.
Collector MPT

The presence of a collector unit in the design of the MPT is often determined by the need to perform the function of converting the rotational speed in the electrical connection of different-frequency circuits on the rotor and stator windings. This solution allows you to equip the device with additionaloperational properties, including automatic regulation of operating parameters. AC collector machines that are connected to three-phase networks receive three brush fingers in each segment of the double pole division. The brushes are connected to each other in a parallel circuit with jumpers. In this sense, collector MPTs are similar to DC motors, but differ from them in the number of brushes used on the poles. In addition, the stator in this system may have several additional windings.
The closed armature winding when using a collector with three-phase brushes will be a three-phase complex winding with a delta connection. During the rotation of the armature, each phase of the winding maintains an unchanged position, however, the sections alternately pass from one phase to another. If a six-phase set of brushes with a shift of 60 ° relative to each other is used in an AC commutator machine, then a six-phase winding is formed with a polygon connection. On the brushes of a multi-phase machine with a collector group, the current frequency is determined by the rotation of the magnetic flux relative to the fixed brushes. The direction of rotation of the rotor can be either counter or matched.
Use of MAT
Today, MPTs are used everywhere where, in one form or another, the generation of mechanical or electrical energy is required. Large productive units are used in the maintenance of engineering systems, power stations and lifting and transport units, and low-power units are used in ordinary householdequipment from fans to pumps. But in both cases, the purpose of AC machines is reduced to the development of energy potential in sufficient volume. Another thing is that structural differences, the implementation of the internal configuration of the stator and rotor, as well as the control infrastructure are of fundamental importance.
Although the general MPT device retains the same set of functional components for a long time, the increasing requirements for the operation of such systems force developers to introduce additional controls and controls. At the present stage of technological development, especially in the context of the use of AC machines in the industrial sector, it is difficult to imagine the operation of such motors and generators without high-precision means for regulating operating parameters. For this, a variety of control methods are used - pulse, frequency, rheostat, etc. The introduction of automation into the regulatory infrastructure is also a characteristic feature of modern MPT operation. The control electronics is connected to the power plant on the one hand, and on the other - to the software controllers, which, according to a given algorithm, give commands to set specific parameters of the mechanism.
Conclusion

Power generators and electric motors are an indispensable power component in today's industry. Due to their function, machine tools, transport, communication installations and other electrical units and devices that require power supply operate. AtIn this case, there is a huge array of types and subspecies of AC and DC electrical machines, the features and characteristics of which ultimately determine the niche for their operation. The technical and operational features of the MPT include a simpler structural device and relatively low maintenance requirements. On the other hand, DC machines turn out to be a more attractive solution to power supply problems in complex critical power systems. The domestic production segment of power industrial equipment has vast experience in the design and production of both types of electrical machines. Large enterprises are increasingly focusing on the development of individual solutions with structural and operational features. Deviations from standard designs are often associated with the need to connect auxiliary functional units and equipment such as cooling systems, protective equipment against overheating and mains fluctuations, additional and backup power. In addition, the external operating environment has a considerable influence on some of the structural properties of electrical machines, which is also taken into account at the stages of designing and creating equipment.
Recommended:
Mobile gas station: description, device, principle of operation, application

Mobile gas station is quite a popular business idea these days. Therefore, the achievement of any success in this area can only be possible if you pay maximum attention to the various key points that are described in this article
Industrial flotation machines for wastewater treatment: types, device, principle of operation
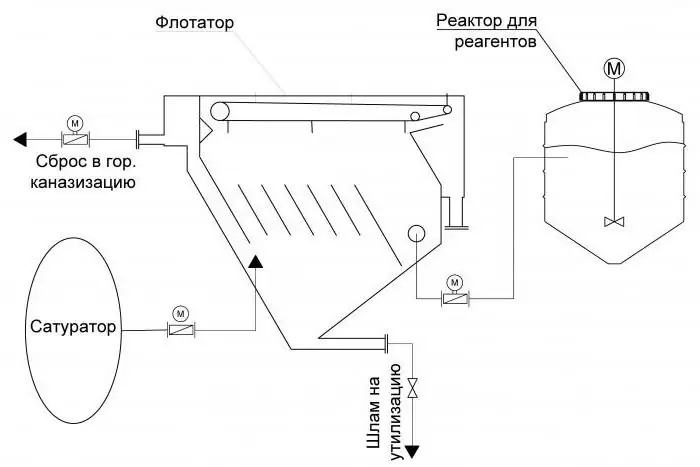
2017 has been declared the year of environmental protection in Russia, and therefore environmental education is one of the tasks for this year. Wastewater generated during the economic activities of enterprises contains a large amount of pollutants in concentrations exceeding the permissible and normative ones. As a rule, we are talking about heavy metals (iron, nickel, copper, lead, mercury, cadmium, etc.), oil products, suspended solids, aluminum, and surfactants. These substances, getting into water bodies, violate the norms
Cylinders "Rockwool" (Rockwool): description, device, principle of operation, application, photo

The service life of pipes is reduced due to their use in conditions of low temperatures and high humidity. This problem, however, can be solved by using modern protective materials made of mineral wool. Among the huge variety of proposals on the market, Rockwool cylinders are not the last. The company started its activity more than a century ago in Denmark. During its existence, it has achieved consumer recognition
Low pressure heaters: definition, principle of operation, technical characteristics, classification, design, operation features, application in industry

Low pressure heaters (LPH) are currently used quite actively. There are two main types that are produced by different assembly plants. Naturally, they also differ in their performance characteristics
General purpose engines: device, principle of operation, application, photo

Automotive equipment is mainly equipped with standardized internal combustion engines (ICEs), the design of which is focused on placement in the engine compartment. However, there is a great demand for power units of this kind in the garden equipment segments, from manufacturers of snowplows, snowmobiles, etc. Moreover, the requirements for integration and operational parameters in such cases differ sharply from automotive standards

