2026 Author: Howard Calhoun | calhoun@techconfronts.com. Last modified: 2025-01-24 13:10:26
The modern world economy is increasingly characterized as a service economy. This is primarily due to the increase in the service sector in the economies of most developed and developing countries. The growth of the service sector is one of the indicators of a country's economic progress.
Economic history tells us that all developing countries necessarily make the transition from agriculture to industry, and then to the service sector. This transition has also led to a change in the definition and characteristics of goods and services.

What are services
There are a huge number of definitions of services, the two most clearly describing the concept:
- A service is a type of activity, the results of which have no material expression, are realized and consumed in the course of this activity.
- A service is a benefit provided not in the form of physical objects, but in the form of activity (intangible goods).
Product definition
The product is a product of nature and human labor or only human labor intangible and intangible substance and in the form of services, which, due to its properties, is capable of satisfying existing or perceived social needs and is intended for exchange and trade.
A commodity is a product of labor, produced not for own consumption, but for sale, tangible and intangible assets, as well as securities and derivatives used in any operations, except for operations for their release (issue) and redemption.
Item properties:
- The ability to meet a specific human need.
- Suitable for exchange for other goods.
The difference between goods and services
The following are fundamental differences between physical goods and services.
Products |
Services |
| Physical item | Process or activity |
| Material | Intangible |
| Homogeneous | Heterogeneous |
| Consumption occurs after production and delivery | Production, supply and consumption are simultaneous processes |
|
May be stored |
Cannot be stored |
| Transfer of ownership possible | Property transfer not possible |
Classification of services
There are three types of services: business services,personal services and social services.
Business services are services that support the day-to-day activities of a business but are not a commodity, such as IT services. Other services that a business may need to run and manage its operations include banking, warehousing, insurance, communications, transportation, and more.
Personal services are commercial activities provided to individuals according to their individual needs. The service here is personalized for the client. Some examples of personal services are cosmetics, food, hotel and lodging, medicine, any artistic service.
Social services are important public services. They are provided by the government or non-profit organizations. These services are aimed at achieving social equality in society and are not provided with a profit motive. Social services include: education, medical facilities and so on.

A more detailed classification and description of services is given below.
By field of activity, services are divided into:
- Material.
- Intangible.
By the nature of the provision:
- Paid or market.
- Free or non-market.
For purpose:
- Production.
- Consumer.
By consumption pattern:
- Public.
- Customized.
- Mixed.
According to the form of ownership of their producers:
- State.
- Private.
By funding source:
- Budget.
- Self-financed.
- Mixed.
By legal status:
- Legal.
- Illegal.
At the place of provision of services:
- Domestic.
- External.
By economic sector:
- Financial.
- Non-financial.
By industry origin: management, science, culture, he alth care and so on.
By type of service: management, information, transport and so on.
Key features of services
The following characteristics apply universally to any service. The most important characteristics of the services are:
- Lack of ownership.
- Intangibility.
- Inseparability.
- Impermanence.
- Fragility.
- Interchangeability.

Lack of ownership is one of the most obvious characteristics of services. You may not own or store the service; it can be done. Unlike goods that have a material form, a service is not property. This feature is closely related to several other characteristics of services such as intangibility, inseparability and perishability.
Intangibility means that the service cannot be picked up, touched. For example, airline passengers have only a ticket and a promise that they will be at a certaintime at the destination. The problem of intangibility is vital for potential customers, because it is difficult to assess the quality of the services provided in advance.
The characteristics of services include inseparability, which means that services are produced and consumed at the same time. It also implies that services cannot be separated from their providers. Unlike services, physical goods are produced, then stored, then sold, and later consumed. Services are first sold, then produced and consumed at the same time.
Variability or variability refers to the fact that the quality of services can vary greatly depending on who provides them, when, where and how. Due to the labour-intensive nature of services, there is great variation in quality, and they may be provided by different people or even by the same providers at different times.
Perishability means that services cannot be stored for later sale or use. This is one of the most important characteristics of services, as it can have a significant impact on financial results. Service companies use various methods to create a better match between supply and demand.
Fungibility refers to the fact that goods can replace services that satisfy similar needs, and vice versa. As a result, there is competition between services and goods.
Definition of service quality
Quality of service (SQ) in its modern conceptualization is a comparison of the expected result (E) with the actu althe result is a characteristic of the service (P), which leads to the equation SQ=P - E.

A high-quality service business will meet or exceed customer expectations while remaining cost-competitive. Empirical evidence shows that improving service quality improves profitability and long-term economic competitiveness. Improvement in the quality of service can be achieved by improving operational processes; identification of problems and their solution; setting valid and reliable service performance metrics and measuring customer satisfaction and other outcomes.
Characterization of the quality of services is considered in two aspects:
- Technical quality: what the customer receives as a result of the interaction (for example, a meal in a restaurant, a room in a hotel).
- Functional quality: how the customer receives the service; the nature of the service (e.g. courtesy, attentiveness, promptness).
Technical quality is relatively objective and therefore easy to measure. However, there are difficulties when trying to assess functional quality.
Service Life Cycle
Every product or service goes through a specific life cycle. Lifecycle management is a key task of marketing and sales management. The model shown below describes the relationship between sales volume and profit from a product or service. The model defines five life cycle stages:
- Development stage - a product or service is being developed, it has not yet entered the market, therefore, the enterprise incurs costs.
- Introduction stage - product or service is placed on the market, sales are slowly growing, profits still do not cover costs.
- Growth stage - sales are growing, profits are turning into positive numbers.
- Maturity stage - sales continue to rise but profits start to decline (falling price).
- Declining stage - gradual decline in sales and profits.

Then the organization either changes the marketing system, improves the characteristics of the products or services, and sales increase again. Either the project dies.
Service Marketing
Service marketing is a broad category of marketing strategies aimed at providing services. This includes everything from personal services such as medical care and spa treatments to rental of vehicles and facilities. Any method that creates benefits for a service company is a valid approach, including informational content, promotional offers, advertisements, and many other marketing materials.
Characteristics of the service market
Segmentation, targeting and positioning are the strategic foundations of marketing used to create competitive advantages that shape an organization's success story. The definition of the market is the basis for setting up a service delivery organization. Characteristics of goods and servicesdifferent in the market.

Market segmentation is a strategy that recognizes the need to "specialize" according to the needs of a market segment and then attempts to become a leader in that segment. Service market segmentation is defined as the process of dividing the market into separate groups that share common service performance characteristics and customer needs or consumption patterns.
Why market segmentation matters
- Defining a market niche leads to more efficient use of resources.
- Segmentation improves market manageability by dividing it into smaller parts.
- Defining the market helps improve a company's ability to meet customer needs.

The importance of the services market for the global economy
Without a doubt, the service market has grown in recent years and contributed to the global economy. Today, services account for more than 65% of the gross world product. In developed countries, the service sector contributes more to economic growth than any other.
Recommended:
The main object of commercial activity is the product. Classification and characteristics of goods

For an average person who is not related to business, the concept of an object of commercial activity is unfamiliar. However, this term indirectly applies to all spheres of our life. According to the theory, objects of this kind include everything that can be bought or sold, that is, property of any purpose, including goods. Let's find out what is meant by this concept. In addition, we will reveal the main characteristics of the product and its classification
Heat-treated wood: main characteristics, production technology, pros and cons

Almost every one of us has come across such a concept as heat-treated wood. However, few have thought about what it really means. Meanwhile, this material can be considered innovative. Due to the high temperature - from +150 °C to +250 °C - the material is strong and durable
How to manage a housing and communal services management company? Licensing, organization and activities of the management company in the field of housing and communal services

Today, there is no competition in the field of housing management in the modern domestic market. And most of those companies that exist are often lacking initiative or even problematic. And this despite the fact that the management company, on the contrary, is designed to improve this area and ensure the rational use of funds. It is the question of how to manage a housing and communal services management company that this article is devoted to
Thermal conductivity of sandwich panels: concept, main characteristics, dimensions, thickness, thermal conductivity coefficient, installation rules, pros and cons of operation
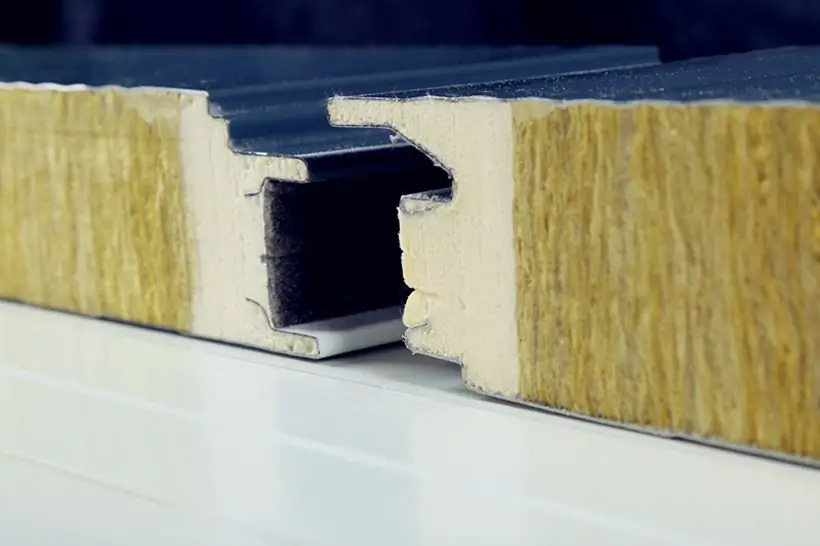
Thermal conductivity of sandwich panels will be the lowest if polyurethane foam is the basis. The parameter under consideration here varies from 0.019 to 0.25. The material is strong, dense and light. It is chemically resistant and does not absorb moisture. Rodents are indifferent to polyurethane foam, fungi and mold do not develop inside it. Working temperature reaches +160 ˚С
Characteristics and features of hotel services, specifics and constituent elements

The hotel industry is an independent branch of the hospitality industry. The content and features of the hotel service as a product of the hotel business are due to the economically viable activities of commercial enterprises that are in demand among customers who need the necessary conditions for accommodation and food

