2026 Author: Howard Calhoun | calhoun@techconfronts.com. Last modified: 2025-01-24 13:10:28
Cash is what all organizations engaged in the sale of goods and services carry out their activities for. Making a profit is the main goal of any business company in the conditions of market relations. From the money received, all market participants must pay tax fees in favor of the state. And for the accuracy of the calculation of these amounts requires accurate accounting and reporting. For these purposes, there are many forms of reporting documents, one of which is the balance sheet. This article discusses issues such as the types of funds in the balance sheet, cash and non-cash funds, their equivalents, accounting accounts, rows in the table, as well as analysis tasks.

A few words about the balance sheet
The balance sheet is the most important reporting document of an organization. It reflects summary information about all the assets of the company, the sources of their formation, obligations to other companies and government agencies. Hisalso called Form No. 1 of financial statements. Presented in the form of a table, it is divided into two columns - asset and liability. The first part contains all the property and investments of the company, expressed in monetary terms, that is, the assets of the organization. The second part contains information about where the funds came from for this property - equity, reserves, long-term and short-term obligations to other participants in the economic process. This article will focus on cash in the balance sheet. This line refers to the balance sheet asset, namely to its second section - current assets. In the same part there are several other types of property.

What is contained in the asset
Cash in the balance sheet is only part of the asset. In the same column, next to the company's money, the following types of values are listed: fixed assets and assets that do not have a material form, objects under construction, financial investments in other organizations and income funds, deferred tax assets, raw materials used in production, materials for collateral for the organization, manufactured products, debts of other companies, VAT on acquired valuables and other types of property of varying degrees of liquidity. Cash on the balance sheet is by far the most liquid part of assets.

Tasks of cash balance analysis
Cash in the balance sheet is not just a number. This is the guarantee of stableactivities of the company, its ability to meet its debts, as well as to provide for internal needs and the production cycle. For an economist and accountant, conducting analytics and structuring funds is a very important part of the work. Its completeness and reliability is necessary for a number of further actions, management decisions, as well as for external users such as financial institutions, banks, depositors, sponsors and others.
Analysis of the state of cash accounts implies such activities as monitoring the turnover of financial flows, circulation time, determining the optimal amount of liquid funds in accounts, forecasting upcoming financial cycles, drawing up and distributing budgets.

Accounts for which assets are kept
All tangible goods and intangible assets are accounted for in accounting accounts specifically designed for each specific category of funds, property or transactions. The code numbering of accounts is the same for all companies operating in the territory of the Russian Federation, and is set out in the Chart of Accounts. Cash in the assets of the organization's balance sheet is accounted for using the following list of BU accounts:
- 01 - fixed assets - an account that reflects assets used in business activities for more than 12 months.
- 04 - Intangible assets - property that does not have a material form (for example, a patent or software).
- 10 - Materials - everything that is used in the production processor managerial activities.
- 43 - Manufactured products - what is already waiting for sale in the warehouse.
- 45 - Shipped products - products that have been sold but not yet paid for.
- 50 - Cash - cash for the needs of the organization and salaries, as well as receipts from customers.
- 51 - accounts used for settlements, organization's money for various needs.
- 52 - money in foreign currency accounts in ruble terms.
- 55 - special accounts in financial institutions, such as deposits.
- 57 - Transfers in transit - funds that were sent through special services, but have not yet reached the organization.
- 58 - investments in shares, authorized capitals of other companies and other profitable placements of funds.
All these accounts are active, that is, the debit reflects the income, the credit - the expense. They are also called inventories. The meaning of this name is that the presence or absence of these funds can be checked during the inventory.

Lines in Form 1
If the company is on the simplified tax system (it is also "simplified"), the totality of all funds located on accounts 51, 50, 52, 55 and 57 is reflected in the debit of line 1250 in the balance sheet. That is, the total amount as of December 31 of the year includes the cash balance, currency and settlement accounts, special purpose accounts, as well as transfers in transit. If the money is placed in a bank on a deposit account and brings a certain percentage of income to the company, itreflected as a financial investment. In the balance sheet, these are lines numbered 1170 or 1240.
If an organization uses the general taxation system, its balance sheet has a slightly different line numbering. Then the company's funds in the balance sheet will be reflected in line 260. Short-term deposits with accrued interest - in line 250, and long-term - 140.

Money in current account
In order to reflect the processes associated with the receipt and disposal of funds on settlement accounts, organizations use accounting account 51. The account is active, it can correspond with several other accounts of the accounting chart of accounts. So, when carrying out operations with the receipt of funds, the accounting reflects the correspondence of the debit of account 51 with the credit of the following plan accounts:
- 50 - cash deposit from the cash desk to the settlement account.
- 62 - receipt of money for goods or services from buyers.
- 90.1 - revenue reflection.
- 91.1 - a reflection of the money that the organization received in the event of the sale of materials, funds and other assets that were not originally intended to be sold in the main line of business.
- 66 - short-term loan.
- 67 - getting a long-term loan.
- 55 - crediting the balances of special accounts to the settlement account.
- 76 - receiving debt from a debtor.
- 78 - repayment of the shortage by the client.
When spending money from a current account, use the following correspondence, in which 51 accountsreflected on the credit, and on the debit the listed codes:
- 50 - withdrawal of money from the current account to the cashier, for example, to pay salaries.
- 60 - payment for goods and services to counterparties and contractors.
- 68 - payment of taxes, duties, other fees to the state.
- 91.2 - settlements with banks for interest on loans.
- 67 - payment of long-term loans.
- 66 - payment of short-term loans.
- 69 - payment to social funds for employees.
- 58 - financial investments.
- 76 - payment of accounts payable.
To carry out operations, the company provides the bank servicing its settlement account with the following documents: an announcement for a cash deposit, a cash receipt for issuance, a payment order or, if the counterparty requests money, a demand. In some cases, the bank writes off funds on its own. For example, if a request was received to write off tax debts from the relevant government service.

Contents of the cash desk of the organization
Cash in the balance is not only bank accounts, but also the contents of the cash register. They also need to be correctly accounted for, written off and accepted, drawn up and reflected in the accounting analytics. The following correspondence of accounts of the BU plan is used upon receipt at the cash desk, where 50 accounts are reflected on the debit, and listed below on the credit:
- 51 - receipt from settlement accounts;
- 71 - refund from accountable persons;
- 66 - short-term loan;
- 55 - admissionfunds from a special account to the cashier;
- 90.1 - Posting proceeds.
Expense from the cash register is issued by the following correspondence, where the fiftieth account is reflected in the credit, and in the debit - the following codes:
- 70 - payment of salaries to employees;
- 71 - issuance of funds to the accountant;
- 26 - payment of household needs in cash;
- 51 - announcement of a cash deposit to the bank;
- 66 - repayment of a short-term loan from the cash register.
All transactions for depositing and withdrawing funds from the cash desk are documented: cash receipts and debit orders, an announcement for a cash contribution, a receipt, a cashier's check.
Cash reporting
In addition to the balance sheet, the organization must draw up other forms of documents in which it reports on incoming and outgoing funds. Among such documents are: appendix to the balance sheet, income statement, cash book, cash flow statement, book of purchases and sales. All these documents are compiled by the accountant at the end of the reporting period. In some cases, there is a need to report in interim periods. If the end of the period is December 31 of the current year, reports must be submitted no later than January 15. Intermediate periods - the end of the quarters of the year, that is, March 31, June 30, September 30. Quarterly reports are submitted no later than half a month following the end of the period.
The set of reporting forms gives an idea about the activities of the company, its financial situation, the ability to meet obligations. If the organization does not submitreporting, submits it at the wrong time or with erroneous data, it may be subject to pen alties, unscheduled tax audits, blocking of accounts, prohibition of activities, forced bankruptcy proceedings. In some situations, punishment is provided for the leadership of the organization - criminal and administrative.
Recommended:
Net sales in the balance sheet: string. Sales volume in the balance sheet: how to calculate?

Annually, enterprises prepare financial statements. According to the data from the balance sheet and income statement, you can determine the effectiveness of the organization, as well as calculate the main planned indicators. Provided that the management and finance department understand the meaning of terms such as profit, revenue and sales in the balance sheet
General concepts of the balance sheet: assets, liabilities, balance sheet currency

The balance sheet contains important information for assessing the company's financial results. Each section of the asset, liability, as well as the balance sheet currency is necessary to calculate many financial indicators
Formula of net assets on the balance sheet. How to calculate net assets on a balance sheet: formula. Calculation of net assets of LLC: formula

Net assets are one of the key indicators of the financial and economic efficiency of a commercial firm. How is this calculation carried out?
Liquidation balance sheet is Definition of the concept, approval, form and sample of filling out the liquidation balance sheet
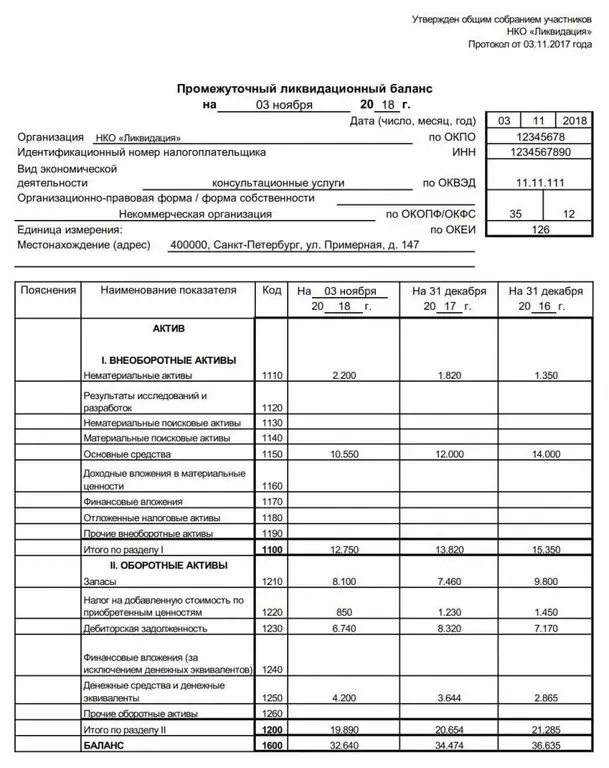
The liquidation balance sheet is an important financial act drawn up during the closing of an organization. It can be intermediate or final. The article tells what is the purpose of these documents, what information is entered into them, as well as how and when they are approved and submitted to the Federal Tax Service
Balance: types of balance. Types of balance sheet
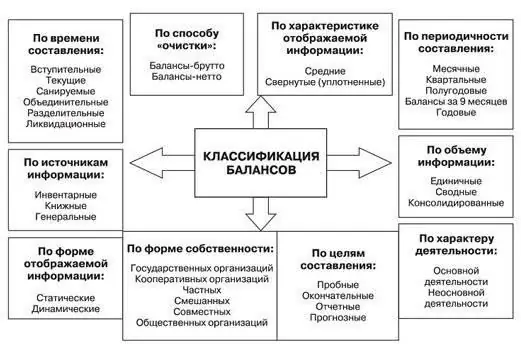
The balance sheet is the most important accounting document of an institution. What is it, what are the rules for filling it out, types and classification

