2026 Author: Howard Calhoun | calhoun@techconfronts.com. Last modified: 2025-01-24 13:10:26
Annually, enterprises prepare financial statements. According to the data from the balance sheet and income statement, you can determine the effectiveness of the organization, as well as calculate the main planned indicators. Provided management and finance understand the meaning of terms such as profit, revenue and sales on the balance sheet.
Terminology
The sales volume of products in the balance sheet is the amount of revenue received for the sale of goods in the reporting period. In this case, the form of calculations does not matter. Products can be sold on credit, for cash, with a deferred payment or at a discount. Therefore, for a more accurate calculation, the formula for calculating the net sales volume in the balance sheet is used, when the received revenue is adjusted for the amount of goods shipped on credit.

Sales volume reflects the amount of funds received by the company. Therefore, it should be calculated by all organizations. The indicator can be expressed asgoods sold, the amount of funds received, the monetary value of the goods sold, etc.
Revenue
First of all, you need to determine the revenue:
Revenue=Production: output x Price.
A company that is a monopolist in the market, the price of goods does not change. That is, the volume of sales depends only on the number of manufactured products. To determine how efficiently the company operates, it is necessary to subtract the total expenses from the amount of revenue received. Costs increase as output increases. This nuance should be taken into account when planning production.

Scope of work
Work is an action aimed at development. The volume of production is measured in the number of manufactured products of each type. And how to calculate this indicator, for example, in construction? It is necessary to first familiarize yourself with the design materials, divide them into underground and surface works. Then the amount of work required to complete each task is calculated: laying the foundation, heating system, water supply, all floors and building elements. The consumption rate of materials is indicated in the project documentation. The calculated amount of work is multiplied by its cost.
Expenses
The amount of production costs in the BU is called the cost. It includes labor costs, material, logistics costs, interest on loans. All costs are divided into fixed and variable. The first do not depend on the efficiency of production. This is the sumfixed costs, such as rent, taxes, depreciation, etc. Variable costs change in proportion to the change in the quantity of manufactured products. Most of the funds are directed to the purchase of materials and the payment of wages.

Profit calculation
Profit is one of the performance indicators. Therefore, when analyzing the work of the organization, it is necessary to correlate the level of profit received with the costs incurred. There are several types of profits.
1. The income received from the sale is called revenue or sales volume.
2. Gross profit is the amount of sales adjusted for the amount of production costs incurred:
VP=Sales - Cost
3. Net income is the gross profit, net of all other expenses:
PE=VP - Expenses

Example 1
In April, the company sold goods worth 200 thousand rubles. The cost of production amounted to 90 thousand rubles. Overhead costs in the form of wages, rent, taxes amounted to another 30 thousand rubles. Counting:
- VP=OP - S/S=200 - 90=110 thousand rubles.
- PE=VP - Expenses=110 - 30=90 thousand rubles.
Next, let's look at how we can determine the net sales in the balance sheet.
Formula
Sales volume can be calculated like this:
FC=(Fixed Cost + Profit): (Unit Price - Variable Unit Cost)
To determine the target sales volume, use the following formula:
- OP=(Fixed Costs + Earnings Before Interest): Contribution.
- MP=Price - Variable cost per unit.
As mentioned earlier, in order to determine the efficiency of the enterprise, it is more expedient to calculate net sales in the balance sheet. How to count? It is necessary to adjust the BP for the amount of returned goods, as well as those that were sold at a discount, provided by the consumer. The formula looks like this:
HRE=(Net Profit x 100%): (RP - Returned Products)

Example 2
Based on the results of the month of work, the company received 1.32 million rubles. arrived. Products are sold at a price of 250 rubles. a piece. Variable costs per unit are 98 rubles, and fixed costs for the entire volume of production - 0.38 million rubles. Let's determine the volume of sales in the balance sheet.
1. First you need to find the contribution margin:
MP=Price - Variable costs=250 - 98=152 rubles.
2. Calculate sales volume:
FC=(Fixed Costs + Earnings Before Interest): Marginal Profit=(380,000 + 1,320,000): 152=11,250 pieces
How to determine the sales volume in the balance sheet
With accounting data, you can calculate all the main financial indicators. You can, for example, determine the volume of sales. There is no balance formula as such. Since these data are reflected in the "Profit and Loss Statement". Line 2110 indicates the amount of products sold in monetary terms after deducting VAT. This includes all production and shipping costs.products: line 2120 + line 2210 + line 2220. The organization may have other contingencies (line 2350) and income (line 2340).
So you can calculate net income or net sales in the balance sheet:
Line 2400=2110 - (2120 + 2210 + 2220) + 2340 - 2350 - 2410, where 2410 is the income tax amount.
Net sales in the balance sheet can be calculated by subtracting retained earnings (uncovered loss) at the end of the period from the value at the beginning of the period. A positive difference indicates a net profit, and a negative difference indicates a loss.

Profitability
The efficiency of the enterprise in the reporting period is calculated by the ratio of various indicators of profitability and costs. There are several indicators of profitability. Consider the main ones.
Sales performance is determined by the ratio of profit to revenue. If the numerator of the fraction uses gross profit, then this indicator is called the gross margin of sales.=:
GPM=Gross Margin: Revenue=(Sales - Gross A/R): (Price x Number of Products)
Operating return on sales is calculated as follows:
ROS=EBIT: Revenue=line 2300 + 2330: (2110 - (2120 + 2210 + 2220))
Sales profitability by balance:
- RP=Profit: Revenue=line 050: line 010 (form No. 2).
- RP (from f. No. 2)=2200: 2110.
Most often, to determine the effectiveness of sales, the netprofitability:
NPM=Net income: Revenue
These formulas determine the share of different types of profit in revenue. After analyzing the value of the coefficient in dynamics, you can determine what changes have occurred in the activities of the organization.

Explanations to reporting
Each type of accounting report is accompanied by an explanatory note. It contains information:
- about the chosen method of accounting for fixed assets, goods and materials;
- description of some balance sheet items (debt repayment terms, rent payments, etc.);
- shareholder information, capital structure;
- merger, acquisition, liquidation data;
- off-balance sheet items.
Often an explanatory note gives more information about the financial situation than reports. According to the data from the balance sheet and f. No. 2, you can get information about the current state of affairs and the effectiveness of activities. Having false information is worse than not having it. Therefore, it is important that financial statements are properly prepared.
Unfortunately, even accountants make mistakes. The use of technical means makes it possible to avoid arithmetic errors, but not methodological ones. Also, reporting may be distorted due to the low skills of a specialist.
It is important to understand that the data in the balance sheet reflect the state of affairs at the reporting date. The very next day, these figures change. In the last weeks of the reporting period, the organization is trying to defer payments, but in the first days of the new year, the funds will be used to repaydebt. Therefore, reporting is always done "with a margin." In the registries, you can always find costs that will reduce the rate of profitability. For example, writing off more inventories, non-current assets, or bad debts. After all, it is always easier to lose profit than to increase it.
According to accounting rules, all transactions must be recorded at historical cost. But assets and liabilities enter the balance sheet at different times. Therefore, the carrying costs of the acquisition do not reflect the true value of the assets. You should also consider currency fluctuations if you have assets or liabilities denominated in foreign currencies.
Conclusion
Financial reporting data is used to calculate sales volume. However, you should not rely entirely on the balance and Form No. 2. They contain only part of the important information. Profitability and real value of assets are usually underestimated in reporting.
Recommended:
General concepts of the balance sheet: assets, liabilities, balance sheet currency

The balance sheet contains important information for assessing the company's financial results. Each section of the asset, liability, as well as the balance sheet currency is necessary to calculate many financial indicators
Formula of net assets on the balance sheet. How to calculate net assets on a balance sheet: formula. Calculation of net assets of LLC: formula

Net assets are one of the key indicators of the financial and economic efficiency of a commercial firm. How is this calculation carried out?
Liquidation balance sheet is Definition of the concept, approval, form and sample of filling out the liquidation balance sheet
The liquidation balance sheet is an important financial act drawn up during the closing of an organization. It can be intermediate or final. The article tells what is the purpose of these documents, what information is entered into them, as well as how and when they are approved and submitted to the Federal Tax Service
Active sales - what is it? Nikolay Rysev, "Active sales". Active sales technology

In the business environment, there is an opinion that the locomotive of any business is the seller. In the United States and other developed capitalist countries, the profession of "salesperson" is considered one of the most prestigious. What are the features of working in the field of active sales?
Balance: types of balance. Types of balance sheet
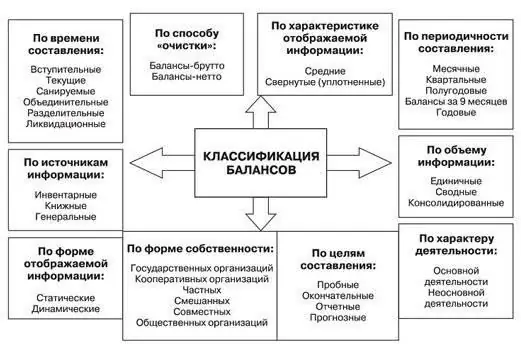
The balance sheet is the most important accounting document of an institution. What is it, what are the rules for filling it out, types and classification

