2026 Author: Howard Calhoun | calhoun@techconfronts.com. Last modified: 2025-06-01 07:12:56
The concept of a bill of exchange has been used for several centuries. He came from Europe. And since that time, the promissory note as an IOU has been valued more than other options, such as an IOU.
Bills were issued loans to the population, personal debts were paid, goods and services were purchased. If the one who was supposed to pay the bill could not do it at the appointed time, then he could actually start selling his property.
But, like any security or debt paper, a bill has its own special characteristics.
Promissory note concept
A bill of exchange is a strictly established form that certifies the unconditional obligation of the person who issued the bill to pay the other party (the one who holds it) the specified amount of money at the agreed place within the specified payment period.
Promissory note obligation can be described as unilateral, abstract, formal and formal.
This financial document is considered from two positions: on the one hand - as a security, on the other- as a fact of existence of obligations of the parties. You can also associate a bill with the concept of a transaction.
It is one-sided. From the document follows the obligation of the debtor on it to pay the amount of money to the holder of the bill. On the contrary, as a creditor, he has the right to demand payment.

The obligation under the note is considered to be abstract, that is, it does not depend on the business transaction that was the basis for issuing the debt paper. The debtor must pay the bill only because the latter is presented for it.
Promissory note obligation is formal. It is always approved in writing, subject to all the details established by law. The defect of the bill implies its nullity in the end.
Features of the bill
Among the features of the bill are the following:
- the unconditional nature of a monetary obligation means that no circumstances will interfere with its fulfillment;
- independence means that the project is not legally linked to a specific contract, it arises as a result of a certain transaction or deal, but is separate from it and exists as a separate document;
- strictly defined filling form. The bill must contain all the necessary details, the absence of at least one of them makes it invalid.
Types
Types of bills is one of the key concepts. The bill can be:
- Simple - means the obligation of the debtor to pay the holder the agreed amount, which is nothing additionalconditioned. There are only 2 parties in a relationship.
- A transferable is a debt paper on which the payer receives a written notice from the drawer without any conditions for payment of the above amount.
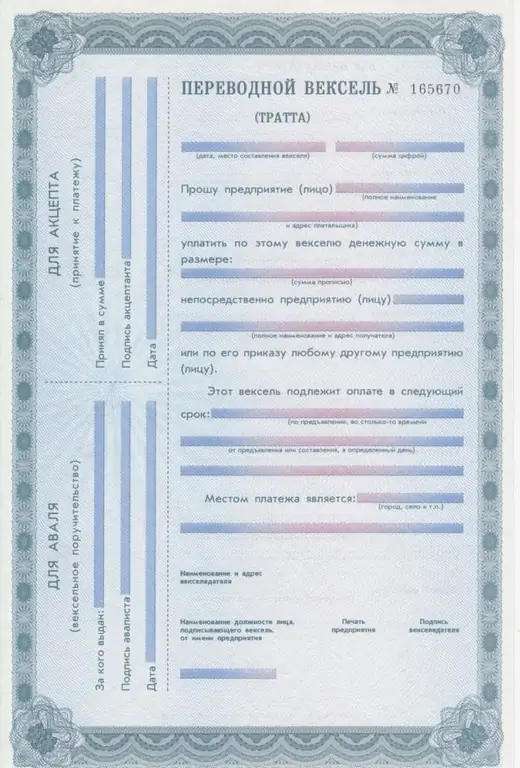
Three parties are already involved here: the one who issues the bill, the recipient of funds, the payer.
In this case, this is necessarily accompanied by a procedure (acceptance) confirming the ability of the payer to pay the recipient the amount of money.
It's actually a special case of a solo promissory note. Initially, all papers of this type are simple: with their help, the debtor is obliged to pay the specified amount to the creditor.
Procedure for accounting for own bills
Accounts in accounting are reflected differently depending on several factors related to their nature. Consider their impact on the reflection of accounts in accounting.
Own bill of exchange is usually issued by the buyer to the supplier in a situation where he cannot pay the delivery in cash. Such a document in bilateral relations has the property of receiving a debt and is not a security until it is transferred to a third party.
Its issuance - receipt are reflected in the buyer and supplier on the same settlement accounts as the main debt. Only the analytics changes. Accounting for bills of exchange looks like the photo below.
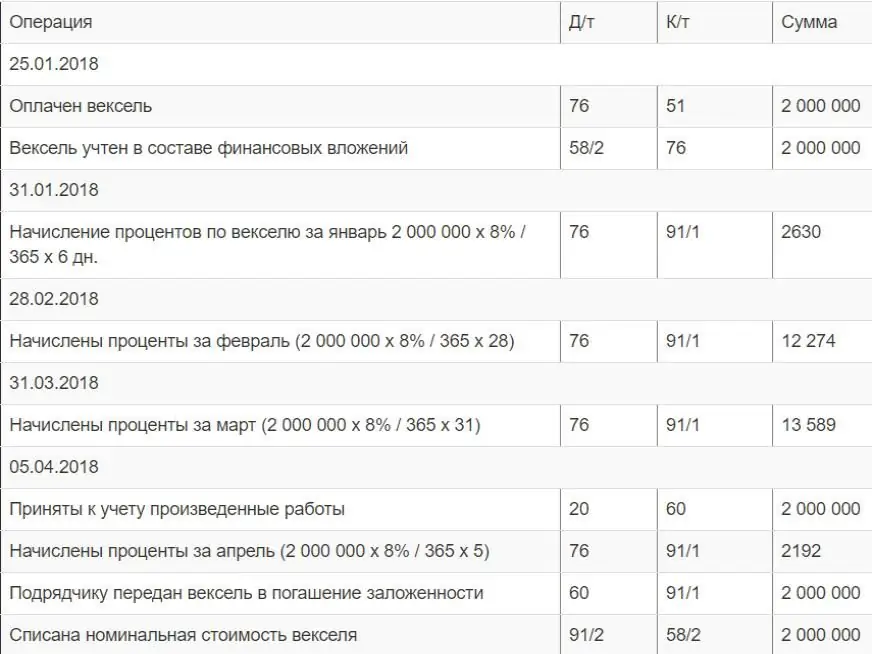
At the same time, both parties demonstrate the appearance of such a document on the balance sheet. Posting a bill inaccounting and postings are presented below:
- buyer - as security issued by: D/t 009;
- supplier - to receive security in the form of collateral: D/t 008.
If the bill is interest-bearing, then it will have monthly income, increasing the amount of the buyer's debt on the bill:
from the buyer: D / t 91 - K / t 60 veks., where 60 veks. - accounting for bills issued;
at the supplier: D / t 62 veks. - K / t 91, where 62 veks. is a sub-account of the debt on the buyer's own bill that was received
Payment on it will be reflected as debt closure:
from the buyer: D / t 60 vex.-K / t 51, where 60 vex. - sub-account of debt on own bill, which is issued;
at the supplier: D / t 51-K / t 62 vex., where 62 vex. - debt on the buyer's own bill, which was received
At the same time bills will be debited from off-balance accounts:
- from buyer: C/t 009;
- from the supplier: C/t 008.

Accounting for other people's bills as part of financial investments
Based on the signs of financial investments, papers bought at a price tag that was below par, or interest-bearing bills that can generate income.
They are accounted for in a separate sub-account 58-2 in the valuation corresponding to the acquisition amount at the expense or the agreed market settlement value. It is possible to use several methods, which will determine the placement of the accounting posting of bills in accounting. Examples are given below:
- whenpurchasing this guarantee - D/t 58-2-K/t 76;
- payment by the buyer for the delivery of a bill to a third party - D/t 58-2-K/t 62;
- receiving it as a contribution to the Criminal Code - D/t 58-2-K/t75;
- real estate exchange transactions - D/t 58-2-K/t 91; D/t 91-C/t 10 (01, 04, 41, 43, 58);
- free receipt - D/t 58-2-C/t 91.
Because the debt document is individual, the bills of exchange in accounting reflect the processes for each, and the valuation at disposal is made for each unit. The process of disposal (disposal) is carried out through account 91, making up the financial result from this operation. In this case, D / t 91 includes the accounting value of the account:
D/t 91-C/t 58-2.
On credit account 91 funds are formed depending on the method of issuance of the bill. For example, via:
- redemption or sale - D/t 76-K/t 91;
- payment on a bill of supply - D/t 60-K/t 91;
- contribution to the authorized capital - D/t 58-1-K/t 91;
- issuing a loan - D/t 58-3-K/t 91;
- property exchange - D/t 10(01, 04, 41, 43, 58) - C/t 91.
Promissory notes are not subject to VAT.
It is possible to take into account the income received from the purchase of a bill in two ways, which are reflected in the financial policy of the company:
- the value of the bill of exchange does not change and will be taken into account at the time of its disposal, reflected in the financial result;
- growth in value to face value will be made in equal shares in the time interval that corresponds to the maturity of the bill (D/t 58-2-K/t 91).
Interest on thispaper can be accrued monthly. They do not increase the book value of financial investments and therefore are reflected in the current account accounts: D/t 76-K/t 91.
When withdrawing, the amount of interest is added to the value of the bill itself in the accounting for the transaction: D/t 91-K/t 76.
Accounting for third-party bills that are not financial investments
Interest-free bills purchased at or above par value do not meet the conditions of return established for their accounting as financial investments. When accounting for promissory notes for this reason, they are not subject to fixation on account 58. But they are taken into account in settlements using account 76 of the account.
Methods of accounting for promissory notes (received) and their disposal can be the same as for income ones, but in addition to account 58, account 76 will be involved in the transaction, then the cost of the bill will be debited from the latter when debited to account 91.

Transactions if the bill is a security
The main requirements for recognizing a promissory note as a security are as follows:
- unconditional obligations;
- certainty - that is, the impossibility of deferred payment or changing payment terms;
- exclusively monetary form of liabilities;
- the possibility of existence only in paper form.
In fact, a bill is another way to settle settlements between individuals (companies).

Both promissory notes and bills of exchange can becommodity, that is, issued to confirm the amount of debt under an agreement on mutual obligations for the purchase and sale of stocks, or financial, when the document itself acts as the subject of the transaction. This feature affects which account will be used to write bills.
Often own account in the relationship of purchase and sale is in the nature of receiving a receipt (debt), as it appears when the buyer cannot pay for the goods with free funds, and the seller agrees to accept the bill. This promissory note is not a security until it is transferred to a third party. For accounting of a promissory note, use account 60 and open a subaccount 60.3 "Issued bills" (from the buyer), and the seller - a subaccount 62.3 "Received bills".
Transactions with it are recorded on both sides of the settlement accounts for items. Accounting bills and postings are reflected in the table below.
| Characteristics of the operation | Dt | CT |
| Promissory notes issued | ||
| Debt on delivery recorded | 60.1 | 60.3 |
| There is future payment security | 009 | - |
| In a situation where we are dealing with an interest-bearing bill, the debt will increase by the value of interest | 91 | 60.3 |
| Debt paid off | 60.3 | 51 |
| Disposal and write-off of a bill | 009 | |
| Promissory notes received | ||
| Debt for goods shipped reflected | 62.3 | 62.1 |
| Proof of payment received | 008 | |
| Interest on a bill | 62.3 | 62.1 |
| Payment for goods passed and received, secured by promissory note | 51 | 62.3 |
| Write-off of a bill | 008 |
Transactions if the bill is a liability
Accounting for a promissory note and an entry, provided that it is a financial liability, implies the fact that they are issued by banks. Promissory notes that have been purchased are reflected in account 58.2 “Debt securities”.

If an enterprise with free money invests it in the purchase of bills issued by banks and capable of generating income, then we are talking about financial investments. Such securities are the object of sale, they are accounted for on sub-account 58.2 "Debt securities". Accounting bills and postings are reflected in the table below.
| Characteristics of the operation | Dt | CT |
| Purchasedpromissory note | 76 (60) | 51 |
| A bill accepted for accounting | 58.2 | 76 (60) |
| The difference between the purchase of a bill and its face value | 58.2 | 91.1 |
Accounting for income from promissory notes
Discount accounting for promissory notes recognized as financial investments or cash equivalents is the same.
To simplify the preparation of financial statements, it is better to take interest in accounting separately from the cost of the bill itself on a subaccount to accounts 58 or 76.

To find out the discount, you can apply one of the possible options.
1 option
The discount amount on the bill appears evenly throughout the entire period that remains until the end of the document's maturity date. Under the discount in this case we will understand the difference between the face value and the amount of money that was given when buying paper. For calculations, they take the entire discount on this bill and divide it by the number of those days that remain until the date the document is presented for redemption.
The formula is:
Discount for one month=the total value of the discount value / the number of those days left until the date the document is presented for redemptionthe number of days that this paper is owned.
The number of days of possession per month is determined as follows:
- in the month of receipt of the paper - from the day following the onewhen the bill is received, before the last day of the month;
- in the month of departure of the bill - from the 1st day to the date of repayment or transfer;
- in other months - as the calendar number of days in them.
When taking into account the discount accrued for the month, we recognize as income monthly the posting on D / t 58, sub-account "Discount / interest" and the loan on account 91, sub-account "Other income".
In the balance sheet, the value of the account in the group "Financial investments" must be indicated taking into account the recognized discount amount.
Sometimes the discount is reflected not on account 76, but in the balance sheet in line 1230, which concerns debtor organizations.
If we take the financial results statements, then here the discount amount is reflected for the term 2320, which indicates the interest intended for the company.
2 option
The entire amount of the discount is taken as a single amount for the entire period. For example, in a situation where the term of the bill is small or the amount itself is insignificant.

Interest accounting
The procedure for calculating interest on a promissory note is not regulated by accounting rules, therefore, in each company, such operations are discussed separately in its financial policy.
From an economic point of view, bonus bills are not much different from discount bills, so the amount of interest on them is also taken into account, as in the case of interest, discussed above.
Promissory note bonuses are calculated when accounting for promissory notes at a discount rate based on the annual interest rate, face value and number of termsownership in days:
Amount of interest=face valuerate / 365number of days held.
Profit on bills is collected monthly on the last day of the month by placing debit account 76 and credit account 91.

Tax accounting
When using promissory notes in settlements for purchased products, the taxpayer must keep records separately for VAT amounts that are subject and non-deductible. In this case, we are talking about promissory notes for third parties, due to the fact that when transferring own debt securities, the sale does not occur.
Find out whether you need to pay VAT, allows you to study paragraph 2 of Article 146 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
In the event that a transaction is subject to VAT, the procedure for calculating and paying tax will be the same as for an ordinary sale: the VAT tax base will be determined as the price of products sold by their volume, which determines the value of the sale.
The VAT calculation date is also determined in a general manner - at the time of shipment or receipt of an advance payment, as well as in the form of a third party promissory note purchased in the tax period that precedes the purchase.
After calculating the "added" burden, an invoice is issued. In the VAT declaration, the sale of products for which a promissory note was received as payment will be reflected in the same way as an ordinary sale.
Separate accounting can be omitted in this case, when the expenses of the organization, which are associated with VAT-free work, do not exceed the materiality threshold of fivepercent of her total costs.
If bills are used occasionally in settlements, then it will not be necessary to keep records separately on this basis in accordance with paragraph 4 of Article 170 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
If you still need to keep bills of exchange in accounting separately, then you can single out the costs associated with their circulation and justify the calculation procedure in the accounting policy for taxation purposes.
With all this, a promissory note can only pay the price of purchased products or services, excluding VAT.
With regard to income tax, we note that the base for transactions with bills must also be calculated separately.
Often, using debt securities as a means of settlement, companies make transactions at their face value.
This means that all additional expenses for their acquisition and sale are losses of the company, which are not taken into account when taxing the income of the reporting period, but can be transferred to future indicators of similar work.
As a result, when organizing separate tax accounting in the company's accounting policy, one should strive to reduce the amount of additional costs that are included in the expenditure side of the special tax base.
Accounting for bills in accounting in 1s
In 1C (version 3.0), the sale of the necessary goods is executed using the document "Sales of goods and services". The type of operation applied is called "Goods".
In addition, in the above document, you must specify the type of agreement, composition and counterparty and, of course, the name of the product, its quantity.
Today there are no specialized tools for accounting bills in 1s.
Of course, it is possible to complete all or part of the necessary accounting and tax records manually, but at the same time, these operations will not be reflected in the operational accounting registers. This does not allow the use of a register-based user service and will make it problematic to get the full picture of customer settlements. A promissory note in accounting and postings to it can also be reflected in the program, but not in full.
As one of the possible ways out of the situation, to reflect the passage of bills through accounting registers, you can use the document "Adjustment of debt". This view reflects the accounting of received bills and their disposal.
To do this, the operation corresponding to the case must be selected in the “Debt Adjustment” document.
To separately reflect the receipt of a bill or its expense, you need to select the “debt write-off” procedure.
To register income-expense, it is possible to perform the operation "Settlements", and uncheck the box "Use auxiliary account" in the title of the document.
In the first case, on the tab of the document "Accounts", a bill of exchange account and the necessary analytics (security document, counterparty - issuer of the security) are selected, in the second - on the tab "Auxiliary account". In this case, in both options, accounts of settlements with counterparties (60, 62, 76) are selected as accounts in the document table.
Everyone elsetransactions: settlements with counterparties, income, expenses, VAT on accounting of a bill in accounting and postings to it are compiled using documents specially designed for this purpose in typical configurations.
Recommended:
Accounting documents are The concept, rules for registration and storage of accounting documents. 402-FZ "On Accounting". Article 9. Primary accounting documents

Proper execution of accounting documentation is very important for the process of generating accounting information and determining tax liabilities. Therefore, it is necessary to treat documents with special care. Specialists of accounting services, representatives of small businesses who keep independent records should know the main requirements for the creation, design, movement, storage of papers
Exchange rate differences. Accounting for exchange rate differences. Exchange differences: postings

The legislation that exists today in the Russian Federation, within the framework of Federal Law No. 402 "On Accounting" dated December 06, 2011, provides for the accounting of business transactions, liabilities and property strictly in rubles. Tax accounting, or rather its maintenance, is also carried out in the specified currency. But some receipts are not made in rubles. Foreign currency, in accordance with the law, must be converted
Promissory note surety. Types and rules for issuing bills of exchange

Security, the issue and circulation of which is regulated by bill of exchange law, is called a bill. Its purpose is to satisfy in cash the debt of one person (that is, the debtor) to another person (that is, the creditor). The rights to this type of securities may be transferred to a third party without the consent of the issuer, but by order of the owner
Accounting for working hours in the summary accounting. Summarized accounting of the working time of drivers with a shift schedule. Overtime hours with summarized accounting of wor

The Labor Code provides for work with a summarized accounting of working hours. In practice, not all enterprises use this assumption. As a rule, this is due to certain difficulties in the calculation
Where can I exchange change for paper bills? Terminals for exchanging small change for paper banknotes

Money, no matter what material it is made from, is a universal product that can be exchanged for any product or service. But money made of metal has a small nominal value, and therefore is less valuable. People try to avoid paying with coins, which is why they accumulate over time. And then the question arises, where you can change a trifle for paper bills

