2026 Author: Howard Calhoun | calhoun@techconfronts.com. Last modified: 2025-06-01 07:12:56
Calculation of cutting conditions is the most important step in the manufacture of any part. It is very important that it be rational. This is due to the fact that for various mechanical operations it is necessary to individually select the cutting speed, spindle speed, feed rate, as well as the thickness of the layer to be removed. A rational mode is one during which production costs will be minimal, and the quality of the resulting product will be as accurate as possible.
Basic calculation principles
In order to produce a part with the required dimensions and accuracy class, first of all, its drawing is made and the routing technology is painted. In addition, it is very important to choose the right workpiece (forging, stamping, rolling) and the necessary material from which the product will be made. The choice of cutting tool is also quite an important task. For every single operationthe necessary tool is selected (cutter, cutter, drill, countersink).

In addition, a separate process is performed for each item written in the route technology, even if it is applied to the same worksurface. For example, you need to make a hole D \u003d 80 mm and cut an internal metric thread with a pitch of P \u003d 2 mm. For each of the operations, you need to separately select such values as the depth of cut, cutting speed, number of revolutions, and in addition, select the cutting tool.
Required surface quality
It is also important to take into account the type of processing (finishing, roughing and semi-finishing), because the choice of coefficients in the calculations depends on these parameters. As a rule, during roughing, the cutting speed is much higher than during finishing. This is explained as follows: the better the quality of the surface to be treated, the lower its speed should be. Interestingly, when turning titanium alloys, the roughness value increases at high rates, since strong fluctuations occur in the machining zone, but it does not affect the Ra and Rz parameters at all.

Factors affecting cutting speed in milling and other operations
The choice of calculations is influenced by a huge number of factors. All of them differ from each other depending on the type of processing of the part. For example, for reaming holes, you can choose to feed twice as much as for drilling. In addition, this figure when processed without limiting factorschoose the maximum allowable, according to the strength of the tool used. When planing and cutting grooves, a factor is added to the main cutting mode formula that takes into account the impact load - Kv.
When threading, it is very important to pay attention to the choice of the cutting tool, since when using the cutter at close range, manual retraction is required, which means that the speed should be minimal.
Cutting speed during milling depends on the diameter of the working tool (D) and the width of the surface (B). Moreover, when machining steel surfaces with end mills, it is imperative to position the workpiece asymmetrically relative to the cutting tool. If this rule is neglected, then its durability can be significantly reduced.

This is a very important indicator that affects the calculation of cutting speed. It denotes the period of operation of the cutting tool until it becomes blunt. The tool life is increased with multi-tool processing.
Basic formulas
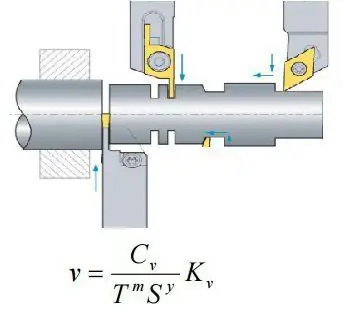
Cutting speed in any operation primarily depends on the selected cutting tool, on the material of the workpiece, on the depth and feed rate. Its formula is also affected by the method of mechanical processing. The cutting speed can be determined both by the tabular method and by calculation. So, when boring, as well as external, transverse and longitudinal turning, use the formula below.

How is this calculation different from the rest? Atshaped turning, slotting and parting off, the depth of cut is not taken into account. But in some cases, such a value as the width of the slot can also be taken. For example, when machining a shaft, its diameter will be considered the width, and when turning a groove, its depth. Due to the fact that it is rather difficult to retract the cutter during cutting, the feed is chosen no more than 0.2 mm / rev, and the cutting speed is 10-30 mm / min. You can also calculate using a different formula.
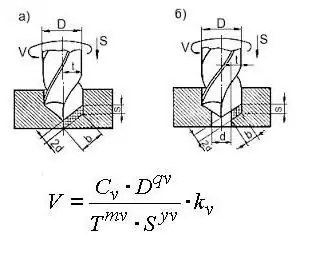
When drilling, countersinking, reaming and reaming, it is very important to correctly determine the cutting speed and feed. If the value is too high, the cutting tool may "burn out" or break. Drilling calculations use the formula below.
Cutting speed during milling depends on the diameter of the cutter, the number of teeth and the width of the surface to be machined. The selected depth is determined by the rigidity and power of the machine, as well as allowances per side. The tool life value depends on its diameter. So, if D=40-50 mm, then T=120 min. And when D is in the range of 55-125 mm, the T value is 180 min. The cutting speed in milling has the formula shown in the photo.
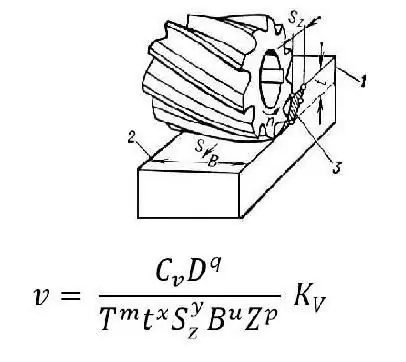
Symbols:
Cv is a coefficient that depends on the mechanical properties of the surface to be machined.
T - tool life.
S - feed amount.
t is the depth of cut.
B- milling width
z is the number of cutter teeth.
D - diameter of the hole to be machined (in some cases, a cutting tool, such as a drill)
m, x, y - exponents (selected from tables), which are determined for specific cutting conditions and, as a rule, have the values m=0, 2; x=0.1; y=0, 4.
Kv - correction factor. It is necessary, since the calculations are carried out using the coefficients taken from the tables. Its use allows you to get the actual value of the cutting speed, taking into account certain values of the factors mentioned above.
Tabular and programmatic method
Since performing calculations is a rather laborious process, there are special tables in the specialized literature and on various Internet resources that already indicate the necessary parameters. In addition, there are programs that themselves perform the calculation of cutting conditions. To do this, the required type of machining is selected and such indicators as the material of the workpiece and cutting tool, the required dimensions, depth, accuracy qualifications are entered. The program itself calculates the cutting speed when turning, feed and speed.
Recommended:
High-speed trains. high speed train speed

Today there are express trains in almost every country. Let's see which is the fastest train in Russia and the world. Here is a rating of express trains that can reach speeds of over 300 kilometers per hour
Automatic lathe and its characteristics. Automatic lathe multi-spindle longitudinal turning with CNC. Manufacturing and processing of parts on automatic lathes

Automatic lathe is a modern equipment used mainly in mass production of parts. There are many varieties of such machines. One of the most popular types are longitudinal turning lathes
Meat: processing. Equipment for meat and poultry processing. Production, storage and processing of meat

Information of state statistics show that the volume of meat, milk and poultry consumed by the population has significantly decreased in recent years. This is caused not only by the pricing policy of manufacturers, but also by the banal shortage of these products, the required volumes of which simply do not have time to produce. But meat, the processing of which is an extremely profitable business, is very important for human he alth
Cutting mode for milling. Types of cutters, calculation of cutting speed

One of the ways to finish materials is milling. It is used for processing metal and non-metal workpieces. The workflow is controlled by cutting data
Chrome plating parts. Chrome parts in Moscow. Chrome parts in St. Petersburg

Chrome plating of parts is an opportunity to give them a new life and make them more reliable and of high quality in operation

