2026 Author: Howard Calhoun | calhoun@techconfronts.com. Last modified: 2025-01-24 13:10:36
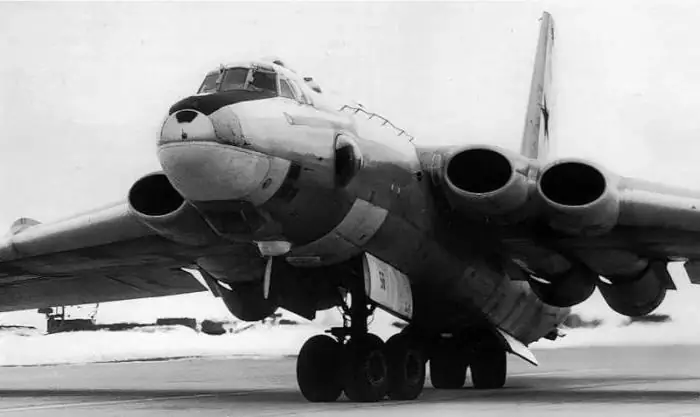
The 3M aircraft is a Soviet strategic bomber that has been in service for about four decades. There were many different events in the history of this aircraft. It ended up gaining a mixed reputation. Someone calls this aircraft an emergency model, and someone considers it a great achievement. One way or another, the 3M aircraft, the history of which was the subject of our conversation, deserves attention as the most serious project of Soviet aircraft designers.
Prerequisites for creation
In the late 1940s, when nuclear weapons appeared, there was a need for their transportation and mobile delivery to the right place. The military complex needed bombers, which, in terms of characteristics, could exceed the models produced at that time by 1.5-2 times. This is how the concept of a strategic bomber was formed. America began to develop such aircraft earlier. In 1946, two American aviation companies at once - Boeing and Convair - began developing a strategic bomber. So, in 1952, the B-52 and B-60 aircraft made their first flight. Both models differed from their predecessors in a high ceiling, as well as impressive speed and flight range.

Begin development
In the USSR, similar developments started with a significant delay. It all started with the fact that the designer V. Myasishchev, who worked as a professor at the Moscow Aviation Institute, proposed to the government the creation of a strategic bomber capable of flying up to 12 thousand kilometers. As a result, after consulting with experts, I. Stalin decided, on his own responsibility, to entrust Myasishchev with the development of the aircraft he proposed, but set tight deadlines. Development was to be completed on May 24, 1951. The Council of Ministries of the USSR commissioned the construction of the aircraft to be recreated after the closure of OKB-23 MAP. Myasishchev became the chief designer. Soon, the Air Force Commander-in-Chief approved the tactical and technical requirements for the machine. The maximum flight range was to be at least 12 thousand kilometers with a bomb load of 5 tons. The plane was supposed to fly at a speed of 900 km/h at an altitude of 9 kilometers.
The time allotted for the design and construction of the bomber under the "project 25" (as it was called during the development process) required the design bureau to cooperate with a number of other industry organizations: other design bureaus, research institutes and factories.
First developments
The first sketches of the aircraft were made by L. Selyakov - he had the role of a designer, aerodynamicist and strongman at the same time. V. Myasishchev at that time was engaged in the formation of divisions, departments and brigades. The team was created in parallel with the bomber. In a short time, the sketch of the project was prepared and approved. Together with thatproduction technology was being developed, because the USSR had not produced such large and heavy aircraft before. The machine needed new sizes of profiles and materials, as well as a nomenclature.
The bomber had to have good aerodynamic performance, develop high speed and be as light as possible. Designers paid much attention to the shape of the wing. During the first six months of development in the TsAGI wind tunnel, many models were tested until the optimal one was found. The created wing was relatively light, had flexible end parts and was carried out according to the caisson design. It resisted the influence of flutter well. At the root of the wing housed the motors, each of which had an air intake. With its help, it was possible to exclude the mutual influence of engines when operating in different modes. The nozzles were deployed in the horizontal and vertical planes by 4 degrees. This measure was necessary to remove the hot gas jet from the fuselage and tail.

Equipment
The power plant of the bomber included four powerful turbojet engines designed by Mikulin. Their thrust was 8700 kgf. When designing the power plant, the stake was placed on maximum reliability. By the way, according to the original project, the aircraft was to be equipped with three engines with a thrust of 13,000 kgf. However, the Dobrynin Design Bureau did not have time to prepare prototypes of these engines in such a short time.
It is worth noting the chassis option chosen by the designersbomber. To study the dynamics of the movement of such a heavy aircraft along the runway, a special expert group was organized. Initially, several chassis schemes were considered: standard with three legs, multi-pin and bicycle. During the tests, the chassis, built according to a bicycle scheme with a front “rearing” cart and side racks located at the ends of the wings, showed itself best. The aircraft drove steadily along the runway and took off with maintaining the required takeoff run.
The head pair of wheels mounted on the front bogie was oriented in a small range of angles (+ 150). When the pair turned, the direction of movement of the cart changed, and after it the direction of the entire aircraft changed. In the "rearing" mode, the front pair of wheels became uncontrollable. At the final stage of the run, the nose of the aircraft rose, and the angle of attack increased. The participation of the pilot in takeoff was minimal. This scheme was tested on the Tu-4 flying laboratory, the tricycle landing gear of which was specially replaced with a bicycle one. A model of a separate electrically controlled trolley was also built. Prototypes of the chassis passed a full range of tests and confirmed their suitability for use on a bomber.
The aircraft's bomb load was 24 tons, and the largest bomb caliber was 9,000 kg. Thanks to the RPB-4 radar sight, targeted bombing was provided. The bomber was satisfied with powerful weapons for defense. It consisted of six automatic guns with a caliber of 23 mm. They areplaced in pairs on three rotary installations in the upper, lower and rear fuselage. The crew, consisting of eight people, was housed in two pressurized cabins. The seats catapulted down through the hatches.

Tests
By December 1952, a prototype bomber was built. And on January 20 of the following year, the car was first lifted into the air. The flight was led by test pilot F. Opadchy. From that day, factory testing of the sample began in full swing. They lasted until April 15, 1954. The delay was due to the volume and complexity of the tests.
The maximum flight weight of the aircraft was 181.5 tons. Its speed at an altitude of 6700 meters was equal to 947 kilometers per hour. The practical ceiling (maximum flight range) with a weight of 138 tons was 12,500 meters. The designers managed to place on board a huge amount of fuel tanks. They contained 132,390 liters of fuel. However, the maximum filling was limited to 123600 liters.
In 1954, the second prototype was connected to the tests, which had a nose shortened by 1 m, an increased wing area and a number of other, less significant improvements. Engineers began to prepare for serial production of the bomber. By this time, in honor of the designer Myasishchev, the car was called "Aircraft M". "3M" - an index that was assigned to the model later. And at first it was called M-4.
Tests went far from the best. For most characteristics, the aircraft was fully consistent with the task, but the main requirement- the maximum flight range with 5 tons of bombs on board - he could not satisfy. After a number of improvements, the bomber was nevertheless accepted into service. But the question of insufficient flight range remained open.

Revisions
To solve the above problem, more powerful and at the same time economical RD-3M engines, developed by P. Zubets, were installed on the bomber. The bomber with a new power plant received the index "3M". In fact, the motors were modified versions of the AM-3A engine. Thrust in maximum mode was increased to 9500 kgf. Moreover, the RD-3M installation had an emergency mode, which, in the event of a failure of one motor, increases the power of the others to 10,500 kgf. With such power equipment, the 3M aircraft was able to reach speeds of 930 km / h and fly non-stop for distances up to 8100 km.
The search for opportunities to increase the flight range did not end there. The second experimental version was equipped with a refueling system developed at the Alekseev Design Bureau. A “bar” appeared above the cockpit for receiving fuel. Well, the tanker was equipped with an additional tank, pumping equipment and a winch.
While Myasishchev's 3M aircraft was being created, parallel work was underway to develop its high- altitude version, which received the working title 2M. The designers intended to install four VD-5 turbojet engines on it at once - on pylons spaced under the wing. However, the design of the "high-rise" was stopped, since the 3M version was able to achieve its design characteristics.
3M aircraft: development
Despite good performance, the model continued to develop. On March 27, 1956, the first flight took place on a 3M machine. The aircraft received new VD-7 engines, which had a thrust of 11,000 kgf. At the same time, they weighed less and consumed less fuel. First, the aircraft was equipped with two new engines, and by 1957 - all four. Thanks to the installation of wings of a new configuration and the improvement of the characteristics of the horizontal tail unit, the aerodynamic qualities of the aircraft have increased markedly. In addition, the volume of fuel tanks was increased. This was achieved, among other things, thanks to hanging tanks. Two of them were hung in the bomb bay (if the bomb load allowed it), and two more - under the wings, between the engines.
The 3M aircraft, the characteristics of which we are discussing today, received a lightweight design. However, its weight still rose to 193 tons, and even more with hanging tanks - up to 202 tons. Over time, the front of the fuselage acquired a new layout. It became possible to move the antenna station from under the fuselage to the nose, which was lengthened by 1 meter. Thanks to the new navigation equipment, the 3M aircraft could carry out effective bombing from high altitude at any time of the day and under any conditions.
As a result, all the improvements led to the fact that the maximum flight range, compared with previous versions, increased by 40%. With one refueling, hanging tanks and a maximum bomb load, this figure exceeded 15,000 km. To conquer such a distance, the plane needed about 20 hours. SoThus, there was a prospect to use it as an intercontinental strategic bomber. The 3M aircraft was exactly the machine that Myasishchev originally wanted to create, taking on great responsibility and enlisting the support of Stalin.

Another interesting quality of 3M is the fact that it can be used as a long-range naval torpedo bomber. Torpedoes were included in the regular armament, but they were used extremely rarely. The first tests of the naval version of the bomber were carried out on the M-4 prototype.
Merit of 3M aircraft
After the latest modifications, the aircraft was put into service and put into mass production. In 1959, pilots N. Goryainov and B. Stepanov, together with their crews, set 12 world records on it. Among them was a lift with a 10-ton load to a height of more than 15 kilometers and a lift with a 55-ton load to a height of 2 kilometers. In the tables of world records, the aircraft was named 201M. In the same year, test pilot A. Lipko and his team set seven speed records on a closed route, with varying degrees of loading. With a load of 25 tons, he developed a speed of 1028 km / h. In official documents, the 3M Myasishchev aircraft was again called differently - 103M.
When the new strategic bomber entered service, some of the earlier versions of the M-4, which differed only in a weak power plant, were converted into tankers.
Problems in operation and a new motor
Despite the highest performance, the aircraft had a number of problems. The most important of them was that the overhaul life of the VD-7 engines was much lower than that of the RD-3M-500A engines. Therefore, in order to carry out routine repairs, the motors were often changed. While the problems with the VD-7 were being solved, the same RD-3M, with which the success of the model began, was installed on the aircraft. With this power plant, it was called 3MS. Of course, compared to 3M, the aircraft showed worse results, but it was much better than its prototype, the M-4 version. In particular, without refueling, the ZMS aircraft could fly 9400 kilometers.
The problem with the motors was solved by the development of the VD-7B modification. To extend the life of the engine, the designers had to reduce its thrust to the level of RD-3M. It amounted to 9500 kGs. It is worth recognizing that, despite the fact that the engine resource was increased and increased several more times, it never reached the level of the RD-3M. Nevertheless, with a general deterioration in performance, the flight range, due to the efficiency of the power plant, was 15% higher than the range of the 3MS version.
Modification with VD-7B engines was named 3MN. Outwardly, it differed from the 3MS version only in engine hoods. On top of the hoods of the VD-7B there were barred hatches designed to release hot air into the atmosphere from under the bypass tapes. In flight, the aircraft also differed: the VD-7B engine left a clearly visible smoke trail.

Last modifications
In 1960, another modification of the aircraft was released, which was called 3MD. She isfeatured better equipment and improved aerodynamics. The motor remains the same.
In the 60s, the production of the aircraft began to be systematically reduced, and soon stopped altogether. The country's leadership has shifted priorities towards rocket technology. Therefore, another of the modifications of the bomber, which received the VD-7P engine and the name 3ME, remained a prototype. The takeoff thrust of the engines increased to 11300 kG. Tests were carried out in 1963. However, society will still remember the 3M aircraft - the history of the model does not end there.
With the reduction in the number of strategic bombers, some of them (versions 3MS and 3MN) were converted into tankers for refueling. They refueled in the air both the Tu-95 and the 3M strike aircraft that remained in service. The 3M tanker thus changed the M-4-2 version. But, in fact, it was all one car, only with different motors and communications associated with them.
Transport tasks
At the end of the 70s, it became necessary to transport the units of a new rocket complex from factories to the Baikonur cosmodrome. Due to the large dimensions, weight and a decent range of transportation, none of the types of conveyor could not solve this problem. For example, the central tank of the launch vehicle was 40 meters long and 8 meters wide. V. Myasishchev reminded of himself and offered to carry cargo on the fuselage of his bomber. The 3M aircraft had already been taken out of production at that time, and Myasishchev himself was the general designer of the design bureau recreated in 1967. In 1978, his proposal was accepted. When Vladimir Mikhailovich died (14October 1978), his work was continued by V. Fedotov.
In order not to delay the development, construction and testing of the carrier aircraft, three tankers were selected. They were immediately sent for testing to identify weaknesses. As a result, the aircraft received an updated frame and new fuselage panels. The tail section was reconfigured and lengthened by 7 meters. The plumage became two-keeled. A number of systems and components have been improved or replaced. More powerful VD-7M engines with the afterburner removed were installed on the aircraft, the thrust of which reached 11,000 kgf. The same engines, but with an afterburner, were installed on the Tu-22, but by that time they were no longer produced.

As a result, five configurations of the carrier aircraft were developed, each of which, due to specific dynamic and flight characteristics, was intended for cargo of a certain weight. The model was called 3M-T. One of the three built aircraft was transferred to TsAGI for static tests. And another one was additionally equipped with a refueling bar.
In 1980, the 3M-T transport aircraft took to the skies for the first time. And on January 6 next year, test pilot A. Kucherenko transported cargo on it for the first time. Subsequently, the aircraft was renamed ZM-T Atlant. More than 150 cargoes were transported to Baikonur on the carriers of this series. They transported all the bulky parts of the Energia and Butan complexes. The 3M cargo plane, the photo of which was recognized by everyone at one time, was regularly shown at all kinds of aviation festivals, including the Mosaeroshowin 1992.
Finally, it is worth noting that the Tu-134A-3M aircraft, which are sometimes confused with the hero of our story because of the “3M” index in the title, have nothing to do with it. All Tu-134s are passenger. And the Tu-134A-3M aircraft are a VIP modification of the agricultural version of the 134CX.
Conclusion
2003 marked the 50th anniversary of the first flight of the 4-M aircraft, which became the first-born in the family of Soviet bombers. Surprisingly, the 3M aircraft model is still found in combat units of the Air Force. We can only admire the talent of designers who managed to build equipment with such strong potential in the difficult post-war years.
Recommended:
Real estate development and its role in economic development. The concept, types, principles and foundations of development

In the framework of this article, we will consider the organization of the real estate development system and its role in economic development. The basic concepts, types and principles of organization of the development system are considered. The characteristic features of the system in Russian conditions are considered
"Renault": manufacturer, history and date of creation, management, country, technical focus, development stages, introduction of modern technologies and car quality
The Renault manufacturer produces high-quality cars that are in demand in many countries of the world. The products were to the taste of Russian motorists. In 2015, the French concern produced the millionth car from the lines of the Russian plant
"Boeing-707" - a passenger aircraft: overview, description, characteristics, history of creation and cabin layout

Today, Boeing Corporation is a trendsetter in the US aviation industry and one of the world's leading aircraft manufacturers. At one time, it was this company that invented the famous Boeing 707 aircraft, thanks to which international air travel gained wide popularity
Flying aircraft carrier: description, characteristics and history of creation

A flying aircraft carrier is an aircraft capable of carrying several smaller aircraft designed for air combat
Aircraft attack aircraft SU-25: specifications, dimensions, description. History of creation

In Soviet and Russian aviation there are many legendary aircraft, the names of which are known to every person who is more or less interested in military equipment. These include the Grach, the SU-25 attack aircraft. The technical characteristics of this machine are so good that it is not only actively used in armed conflicts around the world to this day, but is also constantly being upgraded

