2026 Author: Howard Calhoun | calhoun@techconfronts.com. Last modified: 2025-01-24 13:10:37
Many industries and construction use technological methods involving gas mixtures. This can be, for example, the processing of parts under propane burners or the formation of protective environments during welding to isolate the workpiece from oxygen. Under certain conditions, such processes can provoke gas corrosion - in particular, at elevated temperature or pressure. Chemical activity increases, which negatively affects the structure of metals and alloys. Therefore, special means are being developed to prevent such phenomena and combat the resulting traces of corrosion of this kind.
Determination of gas corrosion

This type of corrosion damage is a chemical deformation of the surface of metals at high temperature. Typically, such phenomena are found in the metallurgical, petrochemical and chemical industries. ToFor example, corrosion can occur during the production of sulfuric acid, during the synthesis of ammonia and the formation of hydrogen chloride. Also, gas corrosion of metals is an oxidative reaction process that occurs under conditions with a certain humidity coefficient in the surrounding air. At the same time, not every gas can provoke corrosion. The most active mixtures in this respect are nitrogen oxides, sulfur dioxide, oxygen, hydrogen, and halogens. As for the objects of destruction, reinforcing bars of furnaces and boilers, pipeline networks, surfaces of gas turbines, elements of internal combustion engines and alloys that are subjected to heat treatment in metallurgy.
Process Features

At the first stage of the reaction, oxygen atoms are chemisorbed on the metal surface. It is in the specifics of the interaction of oxygen with the metal that the main feature of this corrosion lies. The fact is that the reaction has the character of ionic interaction and this distinguishes it from typical chemical processes in dioxide. The bond is stronger because the oxygen atoms are affected by the field of the underlying metal atoms. Further, oxygen adsorption processes take place, and under conditions of thermodynamic stability, the chemisorption layer is rapidly transformed into an oxide film. Ultimately, gas corrosion can form s alts, sulfides and oxides on the metal surface. The intensity of the processes of corrosion damage is influenced by the properties of the oxidizing agent (gaseous medium),microclimatic parameters (temperature, pressure and humidity), as well as the current state of the chemical reaction object itself.
Protection against gas corrosion by alloying

One of the most common methods of protecting metal from all sorts of corrosive processes. This method is based on changing the properties of the structure of a corroding metal. Alloying itself involves the modification of the alloy by introducing components that cause the passivation of its structure. In particular, tungsten, nickel, chromium, etc. can be used. Especially for gas anti-corrosion protection, elements are used that increase the heat resistance and heat resistance of the metal. The alloying process can be carried out both by applying special coatings and by immersing the workpiece in the gas phase of modifying components. In both cases, the resistance of the metal to oxidative processes increases. For example, in order to halve the rate of oxidation of an iron part at 900 °C, it is necessary to alloy it with an A1 grade alloy of 3.5%, and for a fourfold reduction, with an A1 modifier of 5.5%.
Protective atmosphere as a means of combating corrosion

Another technique for protecting metal blanks and alloys from corrosion damage as a result of gas oxidation. Protective atmospheres can be formed by argon, nitrogen, and carbon media. For each metal, specific gas mixtures are used. For example, cast iron is protected by argon orcarbon dioxide compounds, and steel interacts well with hydrogen and nitrogen. In the maintenance of main pipelines, this kind of protection is mainly used when performing assembly welding activities. In a constant mode of operation, electrical protection of gas networks against corrosion is more often used, which is technically performed by semiconductors with cable circuits. This is a kind of electrochemical anti-corrosion shell, which includes elements of anode-protective galvanic protection in the structure.
Use of anti-corrosion heat-resistant coatings
This method also consists in reducing the rate of the corrosion process, but at the expense of special heat-resistant coatings. A commonly used technique for applying iron-aluminum thermal diffusion layers is known as thermochromizing. Ceramic-metal processing of metal parts and structures also provides effective protection. The advantages of such protection against gas corrosion include not only a reliable thermal and mechanical coating, but also the possibility of flexible modification of the physicochemical properties of the shell. Both refractory oxides and metal components like molybdenum and tungsten can be used as part of the functional layer.
Conclusion
Specialists are involved in the organization of control of anti-corrosion protection, developing and approving projects for specific objects. In Russia, one of the largest departments for the protection of gas networks from corrosion is Mosgaz JSC. Employeesof this structure are engaged in servicing gas facilities, maintaining the optimal condition of the working infrastructure. In particular, the organization performs such work as the installation of electrochemical protection installations, the assessment of the danger of underground gas pipelines, the analysis of the intensity of corrosiveness of materials, etc. For most of the work, modern metrological equipment is used to accurately and comprehensively examine target objects for corrosion from her.
Recommended:
Tread protection against corrosion. The main ways to protect pipelines from corrosion
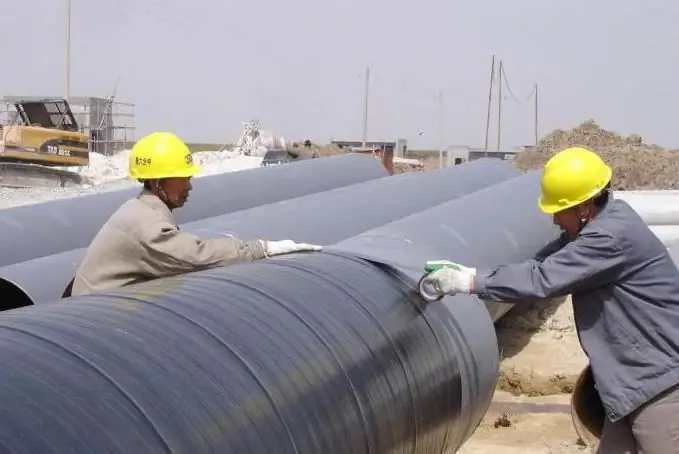

Protective corrosion protection is a universal solution when it is required to increase the resistance of metal surfaces to moisture and other external factors
Corrosion of aluminum and its alloys. Methods for combating and protecting aluminum from corrosion

Aluminium, unlike iron and steel, is quite resistant to corrosion. This metal is protected from rust by a dense oxide film formed on its surface. However, in the case of destruction of the latter, the chemical activity of aluminum greatly increases
Cash withdrawal limit: reasons, maximum withdrawal amount and ways to solve the problem

Some customers of banking institutions may have encountered a situation in which they could not get the desired amount of cash from an ATM. This situation may cause misunderstanding on the part of customers. However, there is nothing unusual about it. This is a restriction on cash withdrawals from ATMs. It is curious that not all bank card holders know about it
The energy problem of mankind and ways to solve it

Energy problem of mankind every year becomes more and more widespread. This is due to the growth of the world's population and the intensive development of technology, which leads to a constantly growing level of energy consumption. Despite the use of nuclear, alternative and hydropower, people continue to extract the lion's share of fuel from the bowels of the Earth
Need a cash loan? Trust Bank will help solve this problem

The most popular form of loan in any banking organization has been and remains an express loan. The reduced requirements of banks make it a tasty morsel for any person, and a high percentage eliminates the risks of a financial organization associated with fraud. Now, at the slightest need, you can get a cash loan. Trust-Bank allows you to get one at interest rates from 19 to 72% per annum

