2026 Author: Howard Calhoun | calhoun@techconfronts.com. Last modified: 2025-01-24 13:10:26
Any metal products are easily destroyed under the influence of certain external factors, most often humidity. To prevent such phenomena, sacrificial corrosion protection is used. Its task is to reduce the potential of the base material and thereby protect it from corrosion.
The essence of the procedure
Protective protection is based on a substance such as an inhibitor. It is a metal with high electronegative qualities. When exposed to air, the tread dissolves. As a result, the base material is preserved even if it is heavily affected by corrosion.

Various types of corrosion are easily defeated using cathodic electrochemical methods, which include cathodic protection. Such a procedure is an ideal solution when a company does not have the financial or technological capacity to provide full protection against corrosive processes.
Key Benefits
Protective protection of metals against corrosion is a good way to protect any metal surfaces. It is useful in several cases:
- When a business lacks the capacity to use more energy-intensive practices.
- When small structures need to be protected.
- When the protection of metal products and objects whose surfaces are covered with insulating materials is required.
To achieve maximum efficiency, it is advisable to use sacrificial protection in an electrolytic environment.
When is protection required?
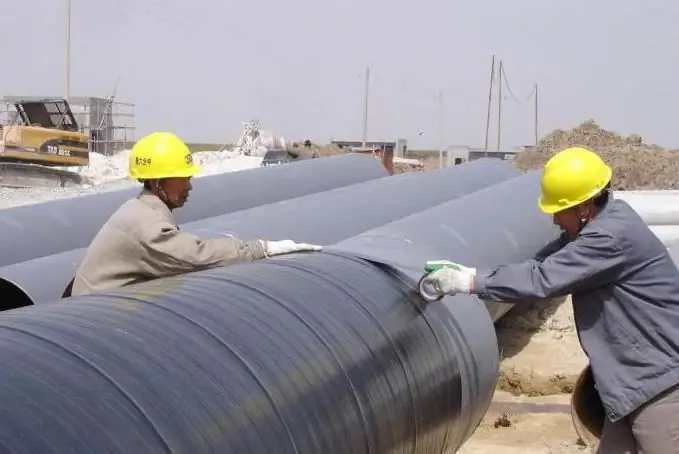
Corrosion occurs on any metal surface in a variety of areas - from the oil and gas industry to shipbuilding. Protective corrosion protection is widely used in the painting of tanker hulls. These boats are constantly exposed to water, and the special paint does not always do the job of preventing moisture from reacting with the metal surface. The use of protectors is a simple and effective solution to the problem, especially if the boats will be in operation for a long time.
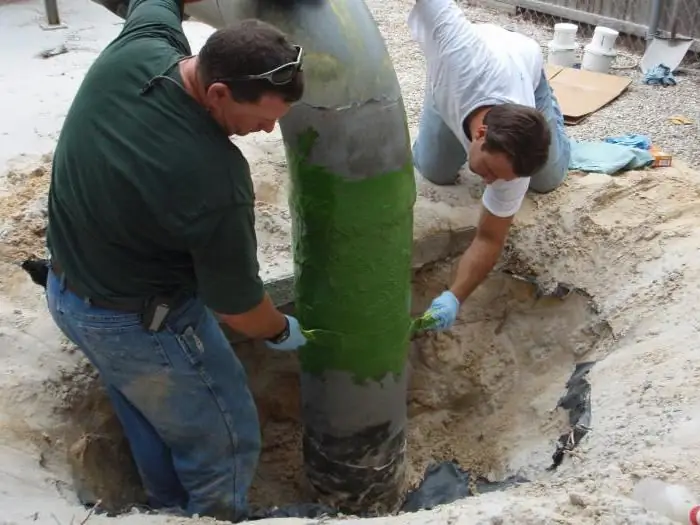

Most metal structures are made from steel, so it is advisable to use protectors with a negative electrode potential. Three metals are the main ones for the production of protectors - zinc, magnesium, aluminum. Due to the large potential difference between these metals and steel, the protective radius becomes wider, and any kind of corrosion is easily eliminated.
What metals are used?

Protection systemis built on the basis of various alloys, depending on the specific use of protectors, for example, the environment in which it will be used. Protective corrosion protection is most often required for iron and steel products, but zinc, aluminium, cadmium or magnesium surfaces also require it. A feature of the tread protection is the use of galvanic anodes, which protect pipes from soil corrosion. The calculation of such installations is carried out taking into account a number of parameters:
- current in the protector;
- indicators of its resistance;
- degree of protection required for 1 km of pipe;
- number of protectors for the same segment;
- the distance that exists between the elements of the protective system.
Pros and cons of different protectors
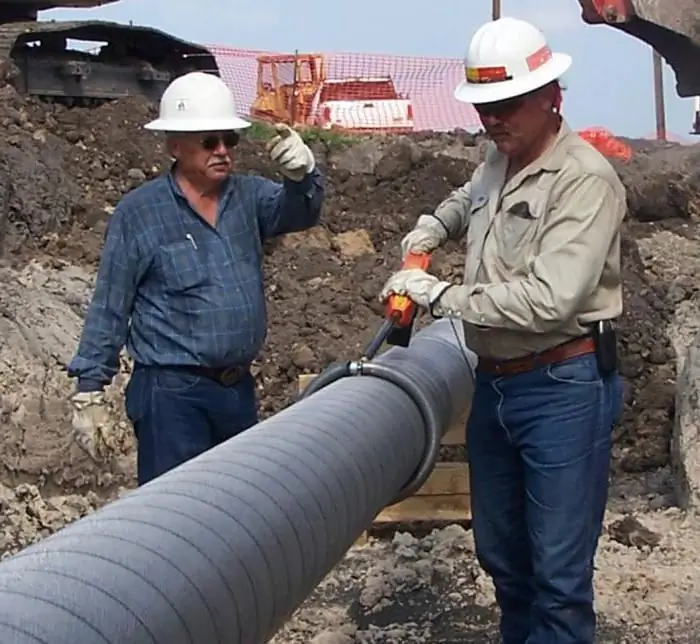

On the basis of protectors, protection of building structures against corrosion, pipelines of various types (distribution, main, field) is built. At the same time, you need to use them wisely:
- the use of aluminum protectors is advisable in order to protect structures and structures in sea water and coastal shelf;
- Magnesium is suitable for use in a slightly electrically conductive environment where aluminum and zinc protectors show poor performance. But they cannot be used if it is required to protect the internal surfaces of tankers, tanks, oil sumps, since magnesium protectors are characterized by increased explosion and fire hazard. Ideally, projectorsthe basis of this element must be used for external protection of structures that are used in a fresh environment;
- zinc protectors are completely safe, so they can be used on any objects, even if they have a high level of fire danger.
If the coating is paintwork

Very often it is required to protect the oil or gas pipeline from corrosion, taking into account the paintwork. Combining it with a protector is a passive way to protect structures from corrosion. At the same time, the effectiveness of such an event is not so high, but the following is achieved:
- defects are leveled on the coatings of metal structures, pipelines, for example, peeling, cracking;
- the consumption of tread materials is reduced, while the protection itself is more durable;
- protective current is evenly distributed over the metal surface of the product or object.
Protective corrosion protection in combination with paint coatings - this is the ability to distribute the protective current precisely on those surfaces that require maximum attention.
On Pipeline Protection

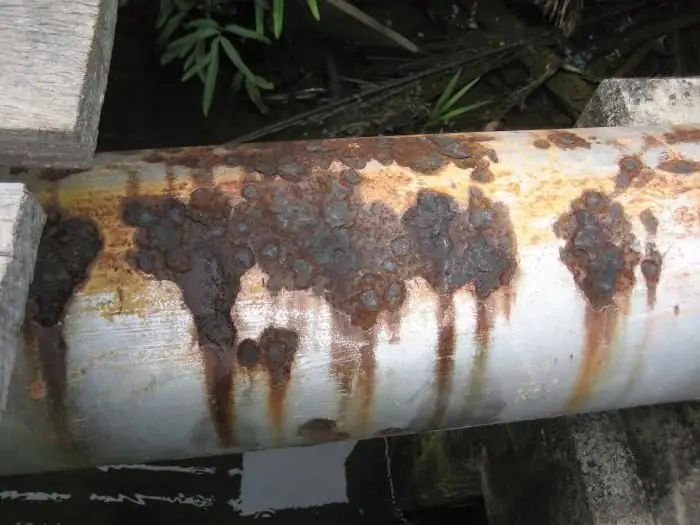
As metal pipes are used, they corrode inside and out. Plaque appears due to the fact that aggressive substances flow through the pipes, which react with materials. The internal state of metal products is affected by a high levelsoil moisture. If high-quality protection of building structures against corrosion is not thought out, the following will happen:
- the pipeline will begin to collapse from the inside;
- required more frequent preventive inspections of highways;
- more frequent repairs will be required, which will affect additional expenses;
- it will be necessary to completely or partially shut down the oil refinery or other industrial complex.
There are several ways to protect pipelines - passive, active. Also, reducing the aggressiveness of the environment can act as a means of protection. In order for protection to be comprehensive, the type of pipeline, the method of its installation and interaction with the environment are taken into account.
Passive and active protection methods
All the main ways to protect pipelines from corrosion come down to performing a number of works. If we talk about passive methods, they are expressed as follows:
- a special way of laying, when corrosion resistance is thought out even at the stage of pipeline installation. To do this, an air gap is left between the ground and the pipe, thanks to which neither groundwater, nor s alt, nor alkali will get inside the pipeline;
- applying special coatings on pipes that will protect the surface from soil influences;
- treated with special chemicals such as phosphates that form a protective film on the surface.
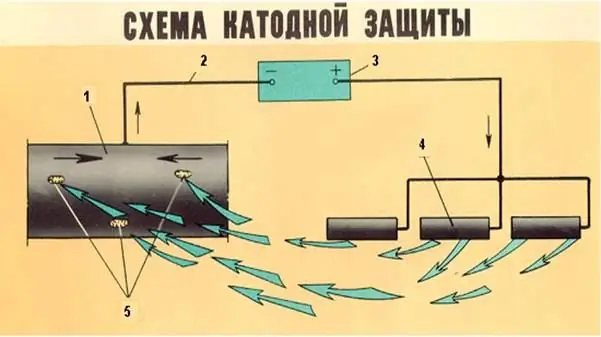
Active method protection scheme uses electric current and electrochemical ion exchange reactions:
- electric drainage protection to combat stray currents;
- anodic protection, which slows down the process of metal destruction;
- cathodic protection, when direct current increases the resistance of metals.
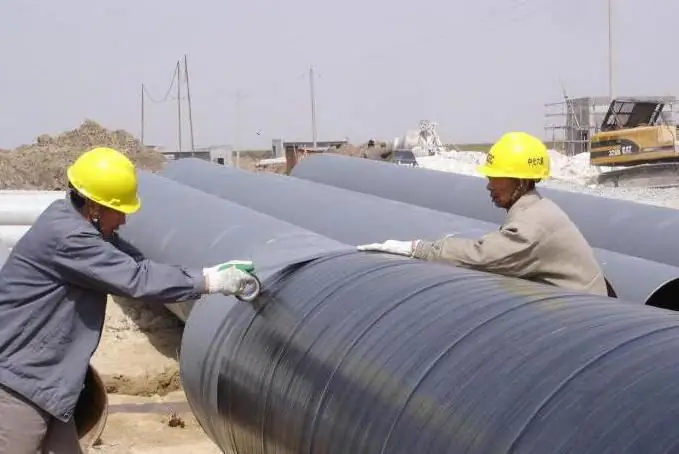

The case for tread protection
As you can see, there are many ways to improve the protective characteristics of pipelines and other metal products. But they all require the expenditure of electricity. Protective protection against corrosion of pipelines is a more profitable solution, since all oxide processes are stopped simply by applying alloys of other materials to the surface of pipes made of metals. The following factors speak in favor of this method:
- economy and simplicity of process due to the absence of a DC source and the use of magnesium, zinc or aluminum alloys;
- the possibility of using single or group installations, while the tread protection scheme is thought out taking into account the features of the designed or already built facility;
- possibility of application on any soils and in conditions of seas/oceans, where it is expensive or impossible to use external current sources.
Protective protection can be used to improve the corrosion resistance of various tanks, ship hulls, tanks that are used in extreme conditions.
Recommended:
Corrosion inhibitors. Corrosion protection methods

Each year, about a quarter of all the metal produced in the world is lost due to the development and occurrence of corrosion processes. The costs associated with the repair and replacement of equipment and communications of chemical industries are often many times higher than the cost of materials required for their manufacture
Categories of pipelines. Determining the pipeline category. Classification of pipelines by categories and groups

Modern industry cannot do without quality pipelines. There are many types of them. What are the categories of pipelines, how to determine them, is described in the article
Cathodic corrosion protection of pipelines: equipment, principle of operation
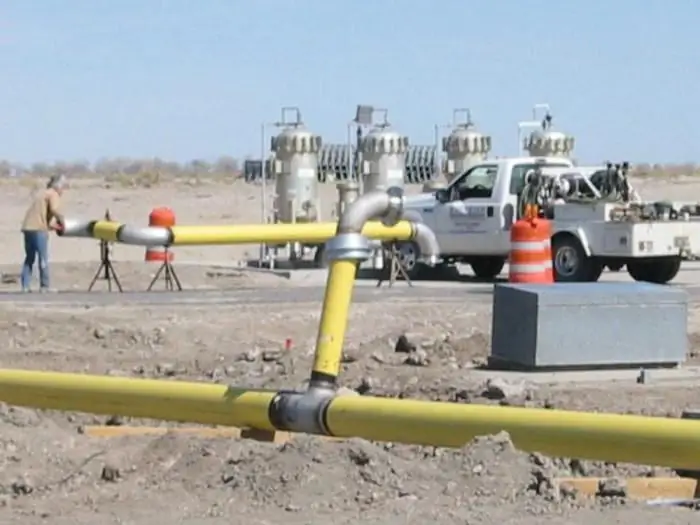

The article is devoted to the cathodic protection of pipelines from corrosion. The types of stations that implement such protection and the principle of operation of the technique are considered
Effective methods to protect the gas pipeline from corrosion
Protection of gas pipelines from corrosion: effective methods, features, special compositions, photos. Active and passive protection of gas pipelines from corrosion: types, processing technique, duration of action. How to protect underground gas pipelines from corrosion?
Passivation is The process of passivation of metals means the creation of thin films on the surface in order to protect against corrosion

Traditional methods of protecting metals from corrosion are less and less likely to meet the technical requirements that apply to the performance properties of critical structures and materials. Bearing beams in house frames, pipeline lines and metal claddings cannot do without mechanical rust protection alone when it comes to long-term use of the product. A more effective approach to corrosion protection is the electrochemical method and in particular passivation

