2026 Author: Howard Calhoun | calhoun@techconfronts.com. Last modified: 2025-01-24 13:10:37
Machining is carried out by cutting a groove, plane, flat (butt). In this case, a cutting tool called a milling cutter is used. Hence the name - milling. The cutter moves rotationally, while the workpiece moves forward.
The English industrialist Eli Whitney is considered the inventor of the milling machine. He received a patent for a milling machine in 1818.
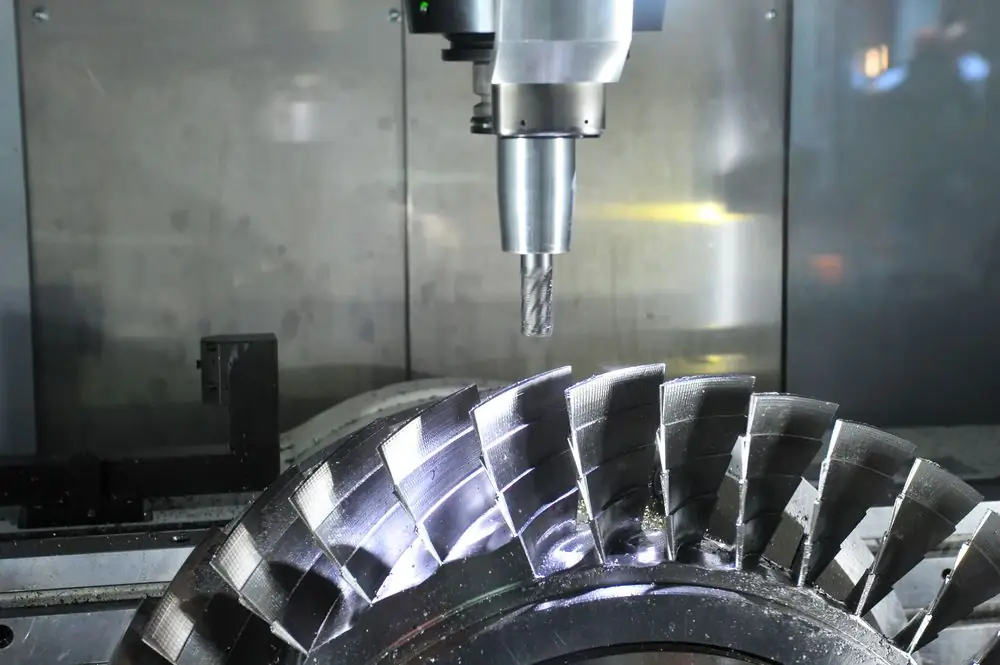

What is the instrument made of?
Before proceeding to the description of cutters, classification and purpose, it is worth understanding what each tool is. It consists of blades, rotation body and teeth.
The cutting part is made of carbide, cermet, mineral ceramic, diamond, solid carded wire or high speed steel. The structure can be made of one material (solid), or it can be prefabricated (different elements are connected to each other using standard fasteners, such as screws, wedges, nuts, bolts).
Also allocate cutters with brazed elements for cutting. Such tools are called soldered. Welded milling cutters include tail and cutting parts of various materials, which are connected by welding.
In addition, there are milling heads, which are also called mechanical. This is a special kind of cutter. The classification of cutters implies a large number of tools that are used depending on the properties of the workpiece. These include tools that consist of high speed steel and replaceable inserts (hard alloys). Separately, the head (without blades) is called the body.
Classification
There are a large number of types of cutting tools. The classification of cutters depends on various properties.
Main types:
1. Corner. This type of cutting tool is most often used in groove milling. They are:
- asymmetrical biangular (straight and helical grooves);
- symmetric two-angle (grooves at a shaped cutter);
- single angle (straight flutes).
2. With a flat end. I use this variety in the classification of cutters for cutting, roughing and sampling. At the end, the tool has the shape of the letter "P", and the shank in diameter is at least 0.2 mm. Coils designed to evacuate chips can have different directions:
- hybrid;
- left;
- straight;
- right.
The area of use varies depending on the number of teeth.
- 1 tooth - cutting, black finish;
- 2 teeth - semi-finished and cut;
- 3 and more - sampling, finishingprocessing of various types of steel, soft metals.
3. With a spherical end. Such tools are used in metalworking in the manufacture of parts of complex shape: molds, turbine blades, dies. They are mainly produced in one piece, although there are also cutters with interchangeable inserts. When processing wood, it is used to create a 3D product. Although this area is dominated by the use of conical cutters with a spherical end.
4. End. It is applied to industrial milling machines. Unlike a drill, a product can work in all directions, not just in an axial direction. End mills are mounted in the machine spindle with a tail in the form of a cone or cylinder. There are several types of end mills depending on the components:
- tungsten carbide crowns and screw blades;
- tungsten carbide;
- keyway with cylinder or cone shank;
- for segment keys.
5. Disk. In the classification of cutters, disk tools are used for cutting, cutting and other actions that are associated with rough processing of metals or non-metals. Divided into 3 groups:
- Spline (keyway) - have teeth only on a cylindrical surface.
- Three-sided - teeth on both ends.
- Double-sided - teeth on the end.
If your disc cutters have carbide inserts, they can be adjusted based on the position of the cartridge. This changes the width of the grooves. Most often, they profile wooden parts for furniture facades, wooden euro-windows,euro plinth, door glazing bead, panel, door frame, etc.
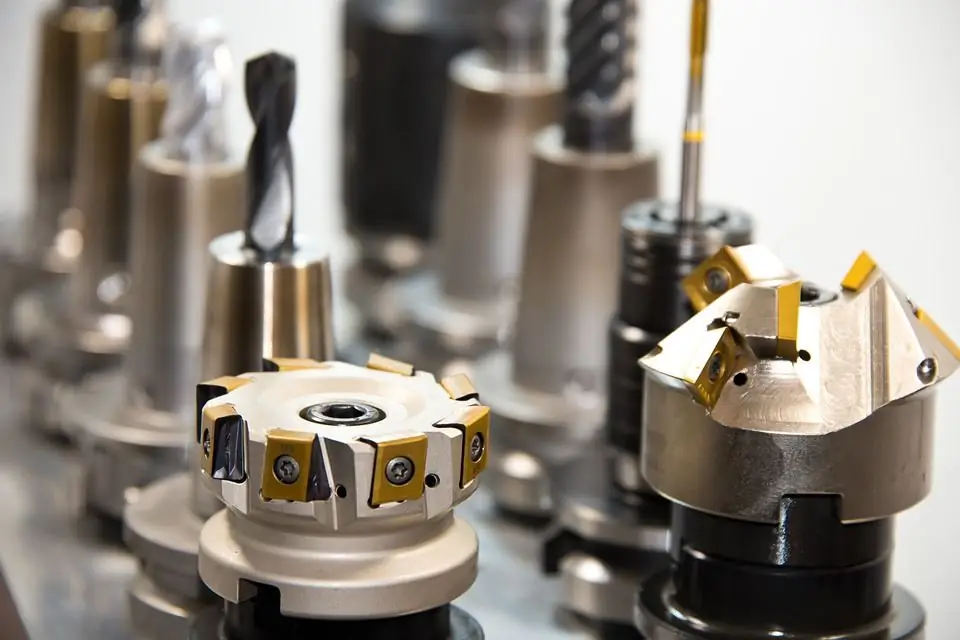

Assignment of cutters according to the material being processed
The classification of these tools and their purpose depends on the material to be processed. For example:
- Cast iron.
- Copper.
- Graphite.
- Tree.
- Hardened and stainless steel.
- Aluminum.
Technological features
In addition, tools are distinguished by properties that allow processing various materials:
- Splines and grooves;
- Body of rotation;
- For cutting material;
- Threads and gears.
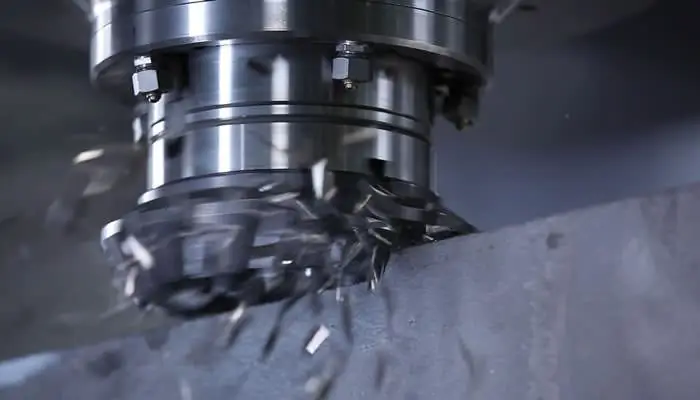

Design features
1. Tooth direction:
- straight;
- screw;
- oblique;
- multidirectional cutters.
2. Classification of cutters by design:
- solid;
- with collapsible and collapsible head;
- compound;
- Insert tool.
3. Tooth design:
- cutters with backed teeth (profile cutting edge is provided with consistency when repeating sharpening on the front surface);
- pointed.
4. Classification of cutters according to the method of installation on the machine:
- overhanging (milling cutter with holes);
- tool with cone or cylinder shank;
- end (tail).
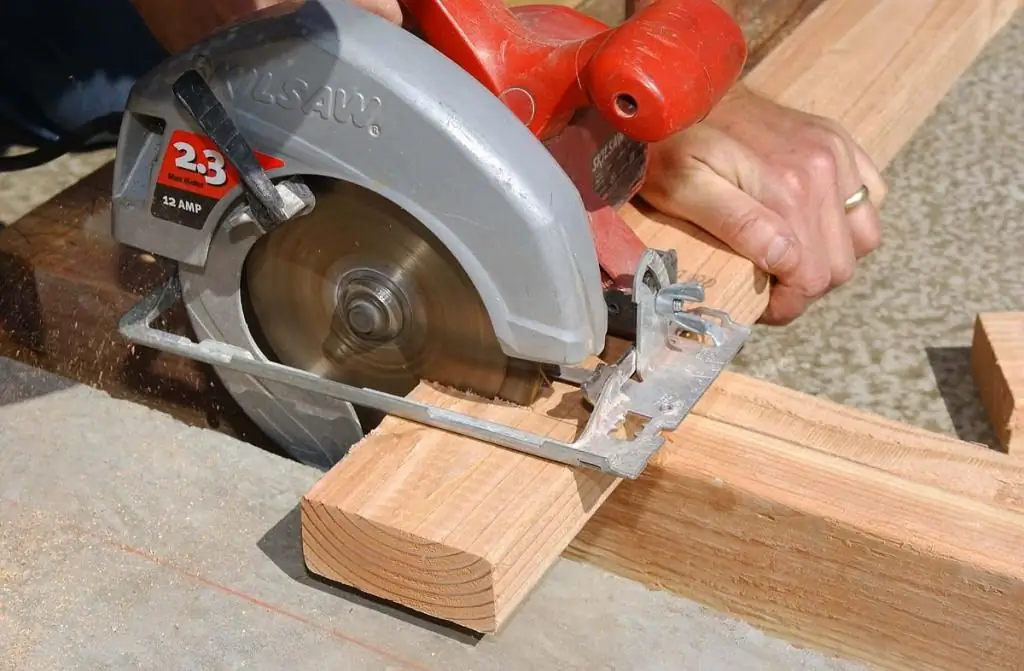

Tree
The choice of a specific tool from the classification of wood cutters depends on the surface to be machined.
Wood cutters can be used for:
- joining blanks by splicing grooves;
- making a recess for installing hanging loops and any other accessory;
- decoration, which is carried out using a pattern cutter.
The most commonly used tools are 6-12 mm in diameter. In this case, an inch collet and a millimeter tail should not be used in work. This can lead to breakage of cutters, and in the worst case, lead to injury to the worker.
Equipment manufacturers provide for some modifications. It is possible to use a manual cutter. Its tooling is designed to process plastic and metal, as well as wood.
Main types of woodworking
- Grooves are made, recesses are formed using end cutters.
- Cylindrical tool grooving.
- The use of shaped snaps for curly recesses, which makes the product unique and inimitable.
- Manufacture of products according to templates occurs using the construction of edge and bearing.
Also, do not forget that the bearing in a hand mill requires maintenance of the entire tool. The rotating element is lubricated with a thin layer throughout the life of the item.
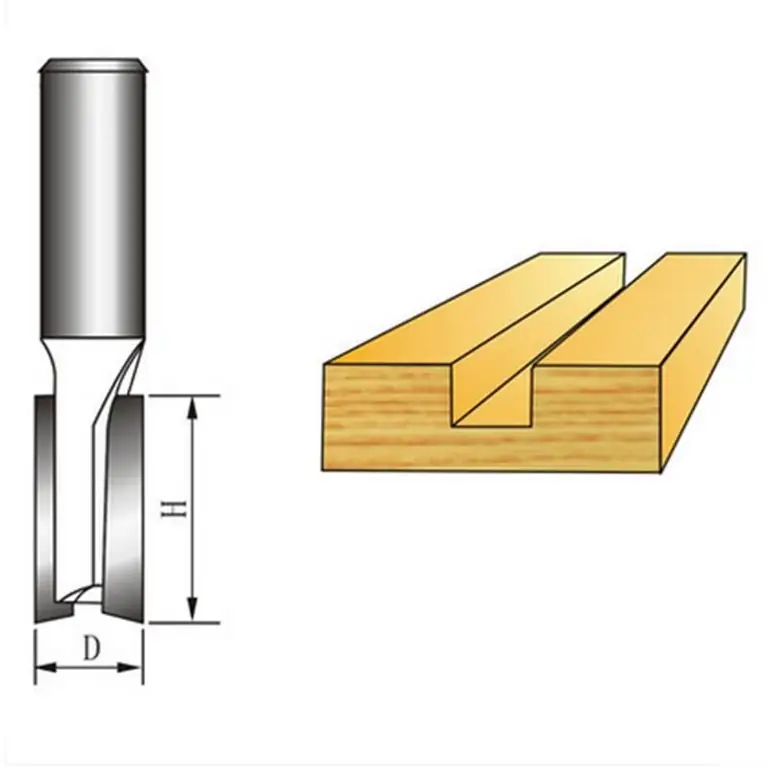
Metal
Classification of cutters for metal:
1. End. They are most often used for processing a plane on a vertical milling device. This type of cutter has the working tops of the sharp edges of the teeth. The main activity is carried out with the help of lateral pointed edges located outside the part. And the end edges are additional equipment. This tool ensures smooth operation, as the contact angle depends on the diameter of the cutting object. The end mill is very rigid and massive, which allows you to conveniently and securely position and secure the cutting elements, as well as equip them with hard alloys. This milling is more productive than other tools.
2. Disk. This is the most important modern equipment. It is used for milling grooves and grooves, there are three types. Disc cutters have high productivity, despite the fact that they often have sheared teeth. Thin disc cutters, also called saws, are used to cut slots and narrow grooves on parts. To do this, sharpen chamfers from the ends of the equipment. It can cut off half of the cutting edge. Because of this, the teeth cut off chips of the required width, which will be narrower than the width of the slot being cut. Thus, chip removal in the tooth cavity is improved, since it is placed as spacious as possible. If the dimensions of the cut and the groove are exactly the same, the ends of the chips will begin to touch the side of the groove. As a result, there will be difficulty in the free placement of chips, then the diskcutter may break.
3. Angle and end mills. Angle tools are used for milling an inclined plane and a corner slot. The single-angle cutter has cutting edges. They are located on the end and conical surface. The cutting edges of a double-angle cutter are on two conical surfaces. The end mill is used when processing a deep groove in the body parts of ledges and contour recesses. In this case, a conical or cylindrical shank is fixed in the machine spindle. With this tool, most of the cutting work is done by the main edges on a cylindrical surface. In this case, the auxiliary edges are used to clean the bottom of the groove. These cutters are most often equipped with helical or inclined teeth.
4. Keyway cutters. As noted above, this is a type of end mill. It is a drill-like tool. It can go deep into the workpiece during the axial feed process, drilling a hole, and then guided along the groove. In the first part of the work, cutting occurs with the help of end edges, one of which must certainly fit the axis of the cutter. This will directly drill the hole.

OKPD: classification of cutters
This is an abbreviation, which is usually deciphered as "All-Russian classifier of products by type of activity." It is part of the standardization system in the Russian Federation.
Used to determine the subjects of public procurement (in accordance with the Federal Law "On the contract system"). Applicable since 2008.

Conclusion
Milling cutters are the most commonly used cutting tool for machining. It can have several types of teeth, cutting edges and blades at once. A distinctive feature of this type of equipment is a wide variety in sizes, types, profiles and applications.
Cutters, their types and classification are very different in their configuration, properties and functions. To determine the specifics, you need to study the workpiece.
Recommended:
Thermal imaging control of electrical equipment: concept, principle of operation, types and classification of thermal imagers, features of application and verification
Thermal imaging control of electrical equipment is an effective way to identify defects in power equipment that are detected without shutting down the electrical installation. In places of poor contact, the temperature rises, which is the basis of the methodology
Types of cast iron, classification, composition, properties, marking and application

The types of cast iron that exist today allow a person to create many products. Therefore, we will talk about this material in more detail in this article
Main types and types of business plans, their classification, structure and application in practice

Each business plan is unique, because it is developed for certain specific conditions. But you need to familiarize yourself with the features of various types of business plans in order to understand their key features. Experts recommend doing this before compiling your own similar document
Cutting mode for milling. Types of cutters, calculation of cutting speed

One of the ways to finish materials is milling. It is used for processing metal and non-metal workpieces. The workflow is controlled by cutting data
Elbor cutters: overview, features, GOST and reviews

The article is devoted to elbor cutters. The features of this tool, characteristics, user reviews, etc. are considered

