2026 Author: Howard Calhoun | calhoun@techconfronts.com. Last modified: 2025-01-24 13:10:26
Today, water transportation has become popular. In this review, we will talk about what Incoterms rules are, FOB conditions, and will also consider the main points of the relationship between the seller and the buyer during the supply of goods. By simulating various situations, the most important features of international contracts will be revealed, as well as recommendations are given that allow beginners to avoid the most common mistakes.
What are FOB terms?

Let's take a closer look at this. So where do you start looking at FOB? Incoterms delivery conditions are certain rules for conducting trading activities that allow you to streamline supply chains. They stipulate the distribution of transport costs, as well as the moment of transfer of risks from the seller to the buyer. FOB is used only when it comes to shipping. Domestic transportation of cargo is rarely used, so it would be advisable to immediately consider internationaloption. This basis can also be applied to river transport within the country.
How does FOB stand for? Translated from English free on board means "free on board". This wording may not be too clear, so it is worth doing a little linguistic analysis. The word "board" in this case means "a place on the ship." "Free" means that the supplier is released from his obligations after the cargo has entered the vessel. The last moment is given increased attention also because the loading service is not cheap. On average, it is about 400 US dollars. Thus, if the supplier specifies the FOB price in the contract, he must load the goods at his own expense. Export clearance costs are also the responsibility of the seller.
Delivery place

Like any other Incoterms delivery basis, FOB terms also include a specific place of transportation. For the format under discussion, this is usually a port terminal. The supplier handles all export formalities and loads the goods on board the ship. After that, the responsibility for it passes to the buyer.
In addition to the cost of loading on board and export clearance fees, the supplier still has to bear the costs associated with the delivery of cargo to the port. To do this, the buyer's agent contacts the seller's representative to agree on a loading date. An empty container ordered by the buyer is transferred to the customer's warehouse for loading. Deliverycontainer is transported by the seller's agent.
Delivery by transport
Another popular scheme is used if there are several suppliers of goods or one delivers from different addresses. In this case, the seller transports the goods by his own transport to the consolidation warehouse/terminal. Subsequently, a container is fed into it for loading. In this case, the seller will also pay for the container stuffing service - loading the goods by the agent.
Costs

This item should be given special attention. FOB delivery terms also include the following items:
- transportation of goods to the port of export (paid by the seller);
- forwarding and loading (supplier bears costs);
- sea freight (paid by buyer);
- unloading and port forwarding at the port of import (calculated by the customer);
- delivery and forwarding to the point of customs clearance and unloading (paid by the customer).
The above is a classic cost sharing scheme. However, there are several ports in the world where the FOB terms stipulate that loading on board is at the expense of the buyer. All terminals in the United States operate under this scheme.
In the next edition of Incoterms, these conditions may be displayed separately, however, at present it is better to check with the shipping agent at whose expense the loading is carried out.
Now that you have read the main features of the FOB delivery terms, you shouldthink over the mechanism of interaction with partners. The main obligation of the buyer is to make payment for the goods on time. The main obligation of the seller is to place the goods at the disposal of the customer and attach all accompanying documents.
Design
What do you need to know about this? The terms of the FOB contract provide for the preparation of a number of permits and licenses. If you are the buyer of the goods, then you are responsible for all costs associated with the clearance of goods in the country of import and transit. If you are the seller, then you must provide at your own expense the export clearance provided for by the delivery time. Other formalities necessary for the export of the goods are also the responsibility of the seller. If a third party or a third-party organization is engaged in registration, then relations with him should in no way affect the fulfillment of obligations to the buyer.
Conclusion of contracts for transportation and insurance

So, how does this procedure work? The contract on FOB terms implies the removal of responsibility from the supplier for the goods after the cargo has been delivered on board the ship. Therefore, the customer will need to pay for the services of further transportation. At the same time, there is no obligation for the seller to choose an agent or a shipping line. Also, no one can oblige to carry out additional cargo insurance. At customs clearance in the country of import, you will need to provide a document that indicates the cost of transportation to the border. Usually, a reference-invoice from the shipping company is sufficient.agent. When unloading in the customs territory of the Russian Federation under FOB conditions, it will be enough only to provide proof of freight payment. Manipulations such as unloading and port forwarding have nothing to do with the customs value of the goods and do not affect the calculation of payments.
The seller is also not required to insure the cargo, and may choose a shipping agent at his discretion. As a rule, suppliers use the services of the same agents with whom the customer arranges transportation. This scheme is acceptable if the amount of payments and remuneration of agents is acceptable for all participants in the transaction. Otherwise, you can use the services of any other transport company.
Delivery of goods and acceptance of delivery

What is the peculiarity of this process? FOB and CIF stipulate that the buyer must take delivery. The process itself is nominal and is a simple exchange of documents between the agents of the seller and the buyer. The supplier is obliged to deliver the goods on board the ship at the agreed time and place them at the disposal of the carrier with whom the contract has been concluded with the buyer. In this situation, a shipping line, a logistics company or a shipping agent can act as a carrier, which buys from the line and resells delivery services to its customers, in our case, the buyer. The assumption that it is much cheaper to tow a container through a shipping line than through an agent is often erroneous. The fact is thatshipping companies usually give agents decent discounts. Such conditions are rarely offered for individual customers of container transportation. In addition, it should also be taken into account that shipping companies are not engaged in the provision of port services and further freight forwarding. Working with an agent, you can immediately order all the procedures related to the delivery, from the delivery of the container on board to the final destination.
Bill of lading
Let's look at what it is and why it is needed. To collect cargo at the port of destination, the buyer will need a document such as a bill of lading. The data that should be indicated in this paper must be agreed with the buyer. Separately, this should be stipulated in an international treaty. Usually the agent issues the bill of lading and hands it over to the seller after all shipping and handling charges have been paid. The supplier then forwards the bills of lading to the customer. If the procedure is delayed, the buyer, together with the seller, may order a telex release. This will save on courier costs and make it much faster.
Risk sharing

This question should be read very first. How do CIF and FOB delivery terms distribute risks? Until the goods are transferred on board the ship, the responsibility for them lies with the seller. Then she goes to the buyer. If something happens in the port area during the loading of a container with goods, the ship has the right not to take it on board. For marriage in this case will be responsiblesalesman. If the damage occurred while the goods were already on board, the responsibility to the buyer lies with the agent.
Notifications
If you are a customer, then the agent representing you must notify the seller in a timely manner about the completion of the shipment by one or another vessel. This will allow the supplier to prepare the goods and clear them for export. The seller, in turn, is obliged to notify the buyer that the goods have been handed over to the company specified in the contract. The supplier can notify the customer in any form convenient for him, unless otherwise stipulated in the concluded contract.
Conclusion

In this review, we have examined in detail what the FOB conditions are, their features and characteristics. They are used only when it comes to the transportation of goods by water, and strictly stipulate the process of transferring goods. The seller's obligations are removed after the goods get on board the ship. At the same time, it bears all the costs of export clearance. The seller also bears all costs associated with the delivery of goods to the port. The buyer bears all costs for clearance of goods in the country of import.
Recommended:
Contract Specialist: job description, admission requirements and working conditions

The job description of a contract work specialist allows an employee to understand their duties and their rights when applying for a job. This document is also predetermining regarding future wage payments. What items the job description may contain, you will learn from the article proposed for reading
Payment for fuel and lubricants: contract execution, calculation procedure, rules and features of registration, accrual and payment
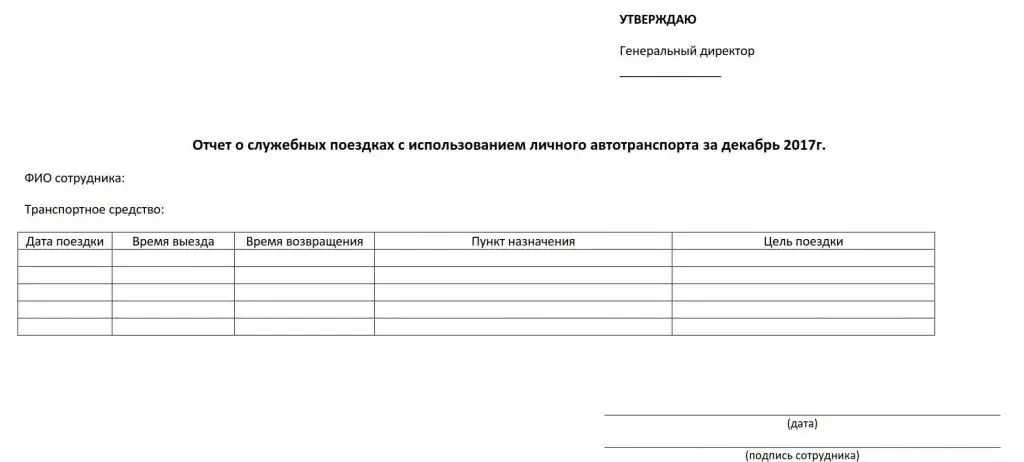
Situations often arise when, due to production needs, an employee is forced to use personal property. Most often we are talking about the use of personal vehicles for official purposes. Moreover, the employer is obliged to compensate for the related costs: fuel and lubricants (POL), depreciation and other costs
Delivery Club food delivery service: feedback from employees and customers

The Delivery Club service is used by millions of Russians every day, because it allows you to save on the delivery of food and drinks and receive bonuses for purchases. An order at the "Delivery Club" is possible through a mobile application, on the website or by calling the delivery service. According to reviews, "Delivery Club" is the leader in the list of Russian delivery services and is one of the most famous companies
What you need to work in a taxi: necessary documents and requirements, regulations and legal aspects. Feedback and advice from taxi drivers, customers and dispatchers

According to many passengers, the job of a taxi driver is the easiest. You sit, listen to pleasant music and drive back and forth. And they give you money for it. But this is only the outer side of the coin. The reverse is much less rosy. We will talk about it in this article. And we will also highlight what you need to work in a taxi
Cash on delivery: what is it? Advantages and disadvantages of cash on delivery

When ordering various goods in online stores, you most likely saw the item "cash on delivery" in the list of delivery and payment options for the purchase. What it is?

