2026 Author: Howard Calhoun | calhoun@techconfronts.com. Last modified: 2025-01-24 13:10:38
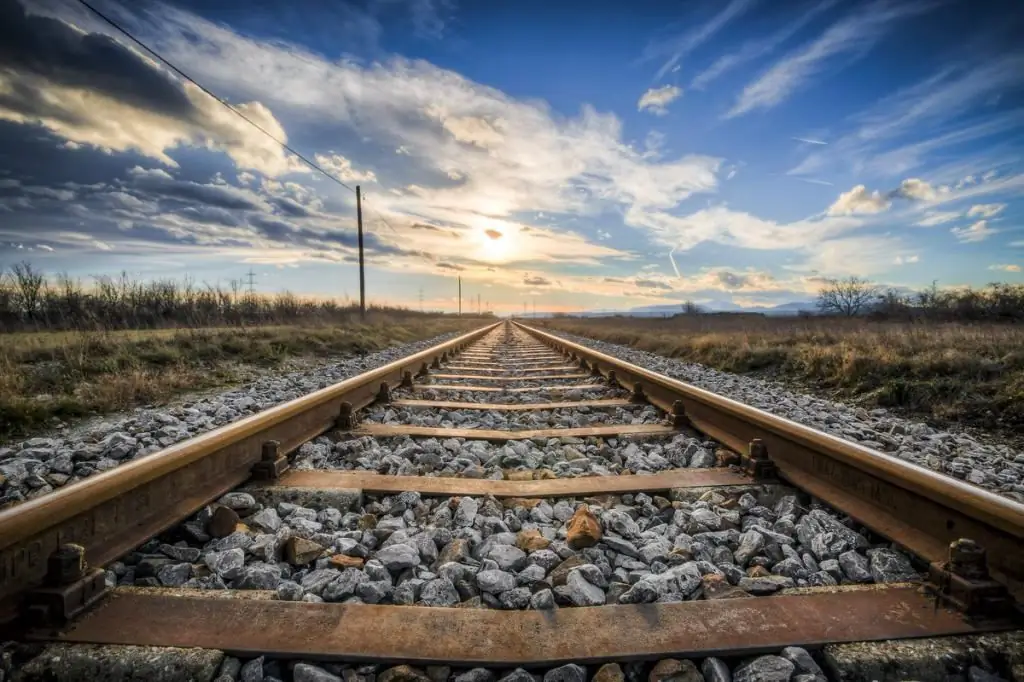
Riding trains around cities and towns, you can learn a lot of interesting and amusing things about the world of the railway.
More than once travelers have asked themselves questions about where this or that railway line leads. It's interesting. And what does the engineer who manages the train feel when the train is just starting off or arriving at the station? How and where do metal cars move and what are the railway transport routes?
What good is the railway
Every person was at least once on the station platform, and maybe even rode in a compartment car one on one with a cheerful company, singing songs until the morning and not letting other passengers fall asleep. And for some reason, during such trips along the endless railway, special feelings arise in the soul: freedom, mystery, and lightness. There are also friends with whom lies a long, in the same direction, path. The path, which is good in all respects, because it is not boring, runs through Russia, is built with high quality and works properly.

What is a rail track
A railway track is the construction of a whole complex of engineering facilities that perform a single function of passing trains through a certain section at a designated speed.
Railways are characterized by the presence of a pair of long metal strips arranged in parallel along the entire length of the track. The smooth and durable surface created with low running resistance, especially horizontal, makes it possible to transport huge masses without the use of significant traction forces.
Mandatory satellites of railway tracks are always stations, signaling and other equipment requiring careful maintenance.
The operation of the rolling stock depends on the technical condition of the tracks:
- safety and continuity of train movement;
- efficiency of operation of general technical facilities of railway lines.

Main components of the railway track
Among the main components of the railway track are two buildings: lower and upper.
The structure of the lower structure includes the following elements: subgrade; ditches designed to drain water; all kinds of artificial structures.
All unnatural structures in this case are a series of man-made objects on the way of laying the railway track:
- bridges are needed to overcome water obstacles - straits, streams, rivers;
- pipes are designed to pass medium-sized streams under the tracks;
- air overpasses - overpasses and viaducts - replace huge embankments in places where solid ravines and dry valleys are forced, contribute to safe multi-level traffic at the intersections of railways and roads, as well as pedestrian crossings;
- tunnels open up the possibility of laying paths through mountain ranges, hills and hillocks;
- retaining walls are needed to support earth slopes;
- mudflow slopes and special galleries are installed in places disadvantaged by mudflows and rockfalls.

Path superstructure includes:
- rails;
- under-rail foundations: reinforced concrete blocks, frames, slabs, sleepers;
- rail fasteners and anti-theft elements;
- ballast layer;
- bars: bridge and transfer (reinforced concrete base for the turnout);
- deaf arrowless intersections and elements of turnouts.
Ballast track
The rail and sleeper grating consists of rails and a base: slabs, blocks, sleepers. The base is laid on a layer of ballast, consisting of two or one layer.
As a rule, a ballast prism is installed, consisting of a couple of layers. The main layer is hard crushed stone, and under it another one is in the form of a pillow of sandor sand and gravel. In a single-layer construction, in addition to the above, the use of slag, shell rock or industrial asbestos waste is allowed.
The ballast layer is needed for the transverse and longitudinal stability of the rail-sleeper grid, the elasticity of the transfer of pressure from the rolling stock to the subgrade and the drainage of water from the upper structures.
Rails and rail fasteners
Rails are of different types. It all depends on which railroad track. In both straight and curved sections of the main track, the rails must guide the progress of the wheels and directly take the weight from passing trains, transmitted through sleepers and a layer of ballast to the soil below them.
The size range of rails, weight characteristics, metal chemical composition and other parameters are set by the State Standard. The nominal length of the rails is 25 m.
The design of the railway track involves the connection of the rails to each other and to the sleepers by means of butt and intermediate rail fastenings. Bolts, linings and linings are used for connection. Thus, a single continuous structure with butt gaps between the rails is formed from individual rail links. The gaps left are needed during temperature changes, since the metal tends to shrink and decompress under the influence of them. Rail junctions are places where railroads are often stressed. A seamless path is considered more progressive when rail lashes of 800 m are welded, and three or four butt rail links are laid between them.

Turouts
In the process of using railway tracks, turnouts are used to connect them to each other. Cross and ordinary arrows are used to connect rails or their branches. Thanks to the switch design, the rolling stock has the ability to move along different tracks. Blind intersections are operated at conventional rail intersections, where the train does not need to switch to another track.
Today, centralized control of turnouts has been established from a special EC console. Previously, there was no electrical centralization, the transfer was carried out manually by the switchmen on duty according to the instructions of higher responsible officials.

Track facilities
For the smooth and safe rail traffic, it is necessary to maintain not only the rolling stock, but also the railway tracks in good condition. The work to keep the highways in good condition in all weather conditions, in the smooth movement of both passenger and freight trains is a very important direction of the railway transport operation services.
More than 50% of the main funds from the operation of the entire railway system are brought to the share of the track facilities. The number of travel workers exceeds 20% of the total workforce.

Profession - Traveler
The field of activity of track facilities workers includes:
- railway tracks in combination with their devices andfacilities;
- a number of industries and business units operating to maintain the state of the railway track at the proper level, including the organization of scheduled repairs.
Traveler professions exist for rail safety.
The structural links of the track facilities include: track distances, roadside machine stations and sections of forest shelterbelts.
Classification of railway lines
To move people and goods, there are water, air and land routes of communication. These include railroad tracks. These, in turn, are the following path types:
- Main - serve to connect separate points and stations.
- Station.
- Special purpose - branching off main non-public paths, safety branches and catching dead ends.

Station tracks are divided into types:
- handling;
- receiving-departure - serve to receive, park and send trains to the stage;
- connecting;
- exhaust;
- sorting;
- running and others.
Those near-station tracks that continue the main branch of the haul adjacent to the station and do not deviate at turnouts are called main station tracks. At large stations, tracks with similar functions are grouped into parks.

Railwaysnon-public use are intended for the approach or departure of trains to industrial enterprises or other users of railway services on a contractual basis, as well as for the implementation of railway workers' own work. Such tracks adjoin the public highway directly or through other railway sidings.
Length of paths
The technical documentation of the station indicates two characteristics of the length of the station track - full and useful.
The total length of the section of the railway track is the interval between the joints of the frame elements of the arrows that limit this area of the track. For a dead-end section, the full length is the gap from the junction of the frame rail of the arrow to the stop.
The useful length of a railway track is a segment of the full length within which rolling stock can be delivered, if it is possible to safely move other trains along adjacent tracks.

Useable rail track length is limited as follows:
- If a section of the track is equipped with traffic lights and electrical insulation, then on the one hand they are guided by the shunting (exit) traffic light, on the other - by the insulating joint of the rail section.
- When equipping the canvas with only traffic lights, one side is limited by a traffic light, the other by a column indicating the limit.
- In the absence of special equipment, the restriction is made by limit posts on both sides.
Railway gauges
A track is two parallelrail threads. The track width is the distance between the rails. Wheelset size and track width must match.

In Russia, this size is 1520 mm, in Europe - 85 mm less. A wider gauge makes it possible to increase both freight traffic and transport more people by rail. The passenger railway track in Russia cannot be imagined as small-sized. Passenger stations and station platforms receive many trains and suburban electric trains along the access and departure tracks. For them, special ways of settling passenger rolling stock are provided. Such sections of the railway are equipped with signaling devices, warning banners, pedestrian bridges, tunnels, crossings, waiting areas.
There is another type of railway track - a narrow gauge railway, familiar to many from children's railways. Narrow roads are simpler and less expensive, but still more suitable for mine, peat production, as well as logging sites and mines. Their width can be from 0.6 to 1.2 m.
Rail gauges
Compliance with the specified center distance between adjacent railway tracks is a necessary condition for the safe traffic of trains, as well as guaranteeing the life and he alth of people caught between two main lines. In this case, it is necessary to take into account both the dimensions of the railway transport and the presence of nearby buildings. Operating rules do not allow to exceed the followingdistance between tracks:
- for double-track traffic - 4.1 m;
- if there are three or more paths, then between the second and third - 5 m;
- on station tracks - 4.8 m;
- in places of secondary routes and cargo areas - 4.5 m.
To date, the threads of railways have enveloped the entire Earth. Trains move along railway tracks in one direction and along multi-track highways in different directions.

If the railway does not have at least one thing, even a wheel set from a train or reliable track facilities, it will cease to be a faithful companion for everyone on travel and business trips.
Good luck everyone!
Recommended:
Electric locomotive 2ES6: history of creation, description with photo, main characteristics, principle of operation, features of operation and repair

Today, communication between different cities, passenger transportation, delivery of goods is carried out in a variety of ways. One of these ways was the railroad. Electric locomotive 2ES6 is one of the types of transport that is currently actively used
Vacuum train: principle of operation, testing. Train of the future

To increase the speed of any vehicle, it is necessary to suppress the friction force as much as possible. This is how spaceships fly into space, which can travel in space for a very long time without resistance. This same feature is at the heart of the project known as the "vacuum train"
Thermal conductivity of sandwich panels: concept, main characteristics, dimensions, thickness, thermal conductivity coefficient, installation rules, pros and cons of operation
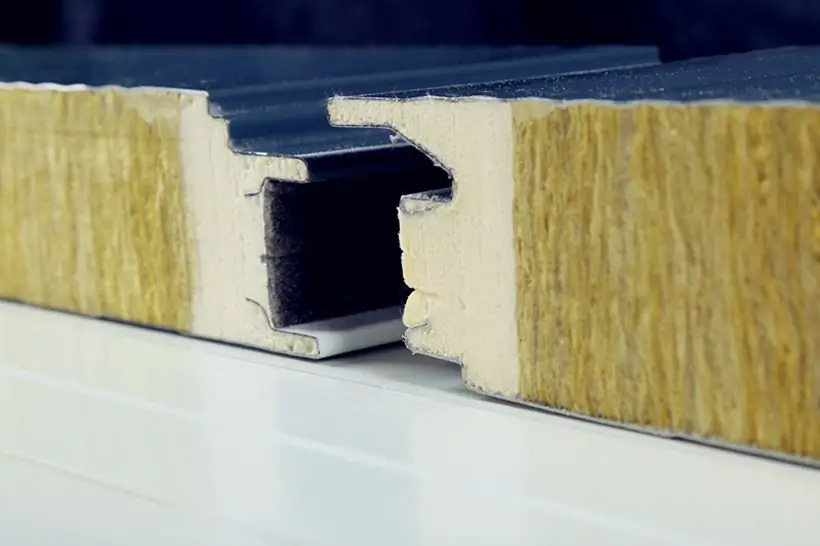
Thermal conductivity of sandwich panels will be the lowest if polyurethane foam is the basis. The parameter under consideration here varies from 0.019 to 0.25. The material is strong, dense and light. It is chemically resistant and does not absorb moisture. Rodents are indifferent to polyurethane foam, fungi and mold do not develop inside it. Working temperature reaches +160 ˚С
Low pressure heaters: definition, principle of operation, technical characteristics, classification, design, operation features, application in industry

Low pressure heaters (LPH) are currently used quite actively. There are two main types that are produced by different assembly plants. Naturally, they also differ in their performance characteristics
Dimensions of wooden railway sleepers. Reinforced concrete sleeper: dimensions

The production of railway sleepers in the Russian Federation is regulated by strict state standards. This applies to both wooden and reinforced concrete structures. What are the specifics of the standards governing the dimensions of both types of sleepers?

