2026 Author: Howard Calhoun | calhoun@techconfronts.com. Last modified: 2025-01-24 13:10:39
Steel normalization refers to the hardening process by a cycle of heating to a certain temperature and cooling. Heat treatment has different modes for each type of metal. As a result of the application of technology, the material becomes stronger due to the elimination of defects. The latter inevitably appear as a result of previous stages in the manufacture of steel products.
Purpose of technology
Normalization of steel can be carried out in garage conditions with the appropriate equipment. The advantage of the technology is the production of a thin eutectoid. The structure of this layer directly affects the strength and rigidity of the metal.

Since the normalization of steel is carried out to improve the quality of the product, the cost of its manufacture increases accordingly. Technology is used only when necessary. For lightly loaded parts, it is not required. Often it is applicable to the production of sectional metal.
Technology can be a replacement for such procedures as hardening with high tempering, classic annealing. Normalization of medium carbon steel does not give high strength comparable to the structure after hardening. But it doesn't lead tostrong deformation and helps to get rid of internal cracks.
The essence of technology
Steel normalization refers to the thermal processing method. There are several metal heating technologies that differ in conditions:
- The heating temperature of metals and alloys is different.
- Hold holding time.
- The type of cooling is more often prolonged due to heat exchange with the environment.
It is slow cooling that makes it possible to obtain a uniform steel composition. The purpose of annealing is a homogeneous metal structure, the desire to remove shells and voids, small cracks.

The following types of annealing are commonly used to reduce local thickening after hot and cold rolling:
- Diffusion - changes the chemical composition.
- Full - affects the entire structure, helps to achieve uniformity.
- Recrystallization - removes hardening of steels.
- Incomplete - makes the steel more malleable for metalworking.
- Isothermal - the best way to reduce the strength of steel.
- Spheroidizing - transforms flat perlite grains into spherical ones.
Steel normalization temperature was selected empirically for each type of alloy. After casting or cold rolling, no workpiece has an ideal structure. Additional heat treatment - annealing - helps to correct the situation.
Correction of the chemical composition
Normalization and hardeningsteel is needed to correct internal inhomogeneities after casting. Shaped castings and ingots are subjected to heat treatment. This is most often required for alloy steel products.

To fix defects in steel, you need to heat to a very high temperature. In this state, the atoms of the alloying elements begin to move. There is a uniform redistribution of the internal volume.
At 1100 degrees is the optimal heat treatment of steel. Diffusion normalization lasts about 10-20 hours when heated, followed by very slow cooling.
Full annealing
Normalization and hardening of hypoeutectoid steel is necessary to correct the structure disturbed by heating in the process of manufacturing castings and forgings processed by pressure. The processing temperature must exceed the critical point when pearlite begins to transform into austenite.

The temperature rise should be strictly 30-50 degrees above the critical point Ac3. This value for alloy steels is taken from the tables, and for carbon steels it is determined from the state diagram. Normalization process:
- The initial stage is heating by 30-50 degrees above the critical temperature of Ac3. Austenitic grains are formed.
- Holding at high temperature is accompanied by the growth of austenite grains.
- Long-term uniform cooling - small austenite crystals break up into several pearlite grains. going onuniform filling of the ferritic pearlite layer structure.
Incomplete annealing is required to reduce the hardness of metals. More often it is necessary under the conditions of metal cutting. As a result of normalization, the excess tension of the steel is eliminated. Unlike full annealing, the entire process takes place at lower temperatures. Accordingly, less time is spent.
Processing of complex alloy steels
During the process of isothermal normalization, hard metals become more malleable for cutting. Heating occurs at the following temperatures:
- Structural steels - not higher than 30-50 degrees of the critical point Ac3.
- Tool steels - 5-100 degrees higher than point Ac1.
Unlike the considered methods, during isothermal annealing cooling of steel immersed in molten s alt is carried out. Natural cooling is carried out after the temperature drops to 700 degrees. At this point, austenite completely transforms into pearlite grains.
Correction of broken structure of metals and alloys
Two-stage cooling of steels makes it possible to transform perlite plates into grains. Heating occurs to a temperature above the Ac1 point. Then it is reduced to 700 and maintained up to 500 degrees. Further, the metal cools for a long time in air. This normalization is called spheroidizing. As a result, the product can be easily cut. This is how metals containing 0.65% carbon are treated.

Klep is education morestrong areas of metal after cold stamping or drawing. Recrystallization annealing removes this defect - the brittleness of steels is eliminated by heating up to 700 degrees (below Ac1). At this moment, the crystallization lattice of metals is restored. The structure becomes fine-grained and homogeneous. Bright annealing can also be carried out, restoring the properties of steels after sheet rolling, in order to maintain a shiny surface.
Recommended:
Arc steel furnace: device, operating principle, power, control system
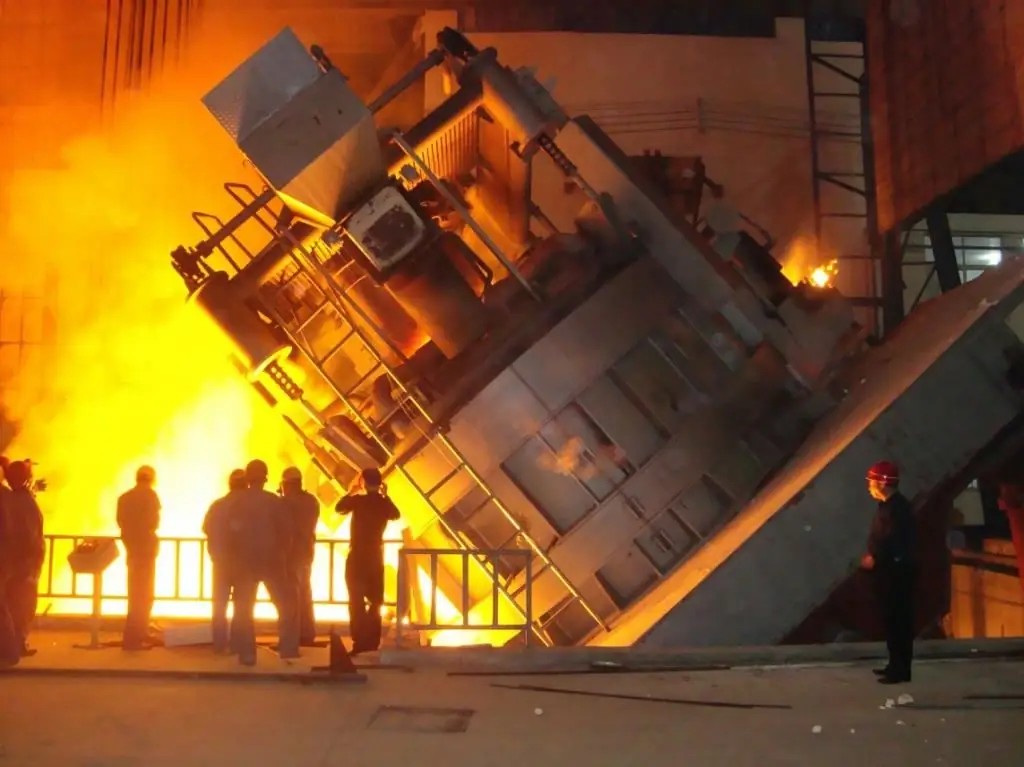

Arc steel-smelting furnaces (EAFs) differ from induction furnaces in that the loaded material is directly subjected to electrical bending, and the current at the terminals passes through the charged material
Food stainless steel: GOST. How to identify food grade stainless steel? What is the difference between food stainless steel and technical stainless steel?

The article talks about grades of food grade stainless steel. Read how to distinguish food stainless steel from technical
Continuous casting of steel: principle of operation, necessary equipment, advantages and disadvantages of the method
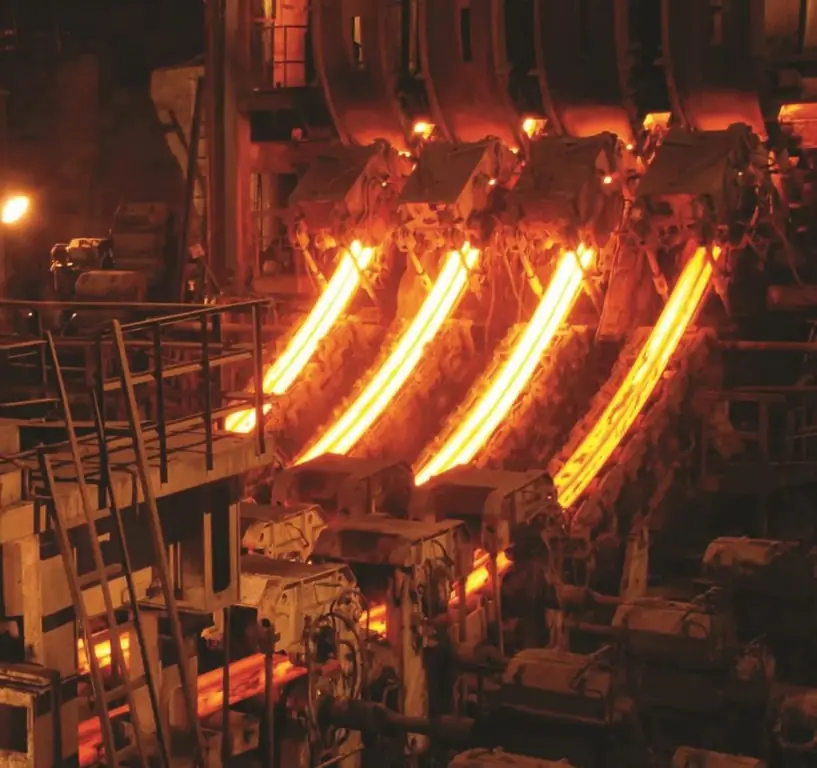
Today, a huge number of various things, parts, etc. are made of steel. Naturally, this requires a large amount of source material. Therefore, the plants have long been using the method of continuous casting of steel, characterized by the most important feature - high productivity
Corrosion resistant steel. Steel grades: GOST. Stainless steel - price

Why metal materials break down. What are corrosion-resistant steels and alloys. Chemical composition and classification according to the type of stainless steel microstructure. Factors affecting pricing. Steel grade designation system (GOST requirements). Application area
440 steel - stainless steel. Steel 440: characteristics
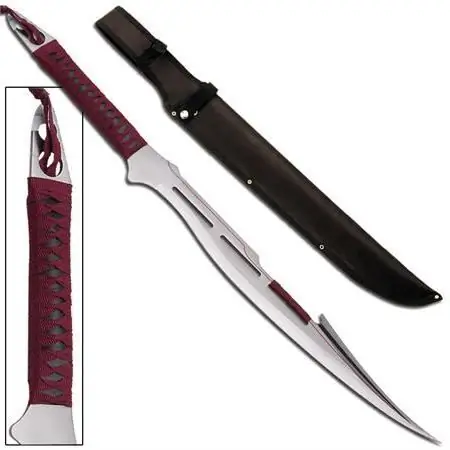

Many people know 440 steel. It has established itself as a reliable, anti-corrosion, time-tested hard material, which is most often used for the manufacture of knives for various purposes. What is the secret of this alloy? What are its chemical, physical characteristics and applications?

