2026 Author: Howard Calhoun | calhoun@techconfronts.com. Last modified: 2025-01-24 13:10:43
Protection of gas pipelines from corrosion is carried out in several ways. This is due to the different nature of the origin of the deformation itself, which depends on the type of location of the highway and the surrounding conditions. Corrosion of metal wires means spontaneous deformation of these elements due to chemical or electrochemical processes. The main types of deformations are liquid, atmospheric, underground.

Reasons
The following are brief definitions of damage that is leveled by corrosion protection of gas pipelines:
- Chemical action - spontaneous oxidation of metal parts, due to its transformation into a stable ionic region, under the influence of non-conductive compounds.
- Electrochemical corrosion - the metal is destroyed at a rate depending on the electrode penetrations. This is due to the fact that the atoms are ionized separately, with the renewal of the oxidizing agent in the electrolyte.
- The most dangerous corrosion is stray current attack. This problem is observed nearelectrically conductive systems, for example, in the area of \u200b\u200brailways with a contact network.
General information
The main types of protection of gas pipelines against corrosion include three types: tread, cathode and drainage methods. In order to maximize the safety of serviced objects, complex measures are used, including cathodic, tread, and drainage protection. Cathode stations are being built with several drainage compartments and scattered anodes to avoid the shielding effect of underground communications.
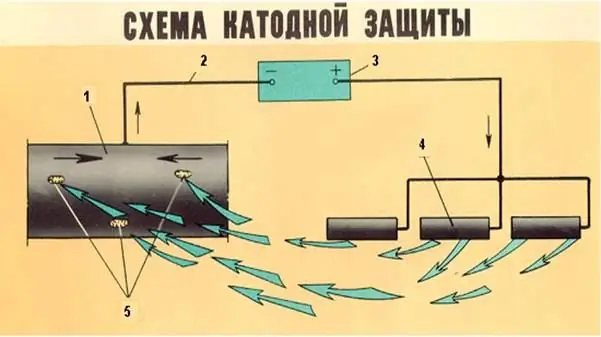
Cathodic corrosion protection of gas pipelines
This method is to connect the positive pole of the DC generator to the conductor of the anode-grounding. From it, currents enter the soil, flowing through damaged sections of insulation into the pipeline. They go through the pipe to the place where the conductor is connected, then to the negative boundary of the source.
If there is a sufficient voltage level, the entire working part of the gas pipeline becomes negative-cathode. This makes it possible to prevent the formation of active corrosion. In this case, grounding (waste metal) becomes the anode section. As a result, the pipe is potentiated negatively with respect to the ground.

Protective countermeasures
Protective protection of a gas pipeline against corrosion provides for the creation of a blocking potential by connecting metal protectors to pipes with a more negative indicator than the parameter of the pipeline itself. UsingThis method does not provide for an external current source, the required characteristics are created by means of a galvanic anode cell. Under the influence of the protector, cathodic polarization acts on the gas pipeline, which helps to stop corrosion processes.
The working material can be zinc, aluminum, magnesium in the form of special alloys (ML, TsO, Ts1 and the like). This type of protection is as simple as possible, does not require additional maintenance. This method, in combination with other methods, is relevant to apply to protect individual compartments that are not intersected by adjacent sections of cathodic safety. Protector protection of the gas pipeline against corrosion is appropriate for special casings at railway and highway crossings, at facilities with developed underground structures.
Protectors are mounted in bundles of several elements, connected directly to the pipe or cathode outlet. Between themselves, they are connected using a special cable, wire made of steel or copper. To increase the effectiveness of protection, the protectors are located in the filler, which reduces the contact resistance. The composition is magnesium sulfate or sodium with clay. The installation distance of protectors from the pipeline is about 3-6 meters.

Drainage
Very often, tram and railway rails on electrified tracks do not have proper conductivity, which causes part of the electric current to enter the ground. It is from this that it is necessary to protect pipelines running near railways. On theat the point of entry of stray currents into the pipe, the cathode potential is formed, and at the exit, the anode zone. It is in the last places that the metal is actively damaged.
Drainage corrosion protection of steel gas pipelines is an effective way to combat stray currents. This is very important, because under the influence of this effect, the pipes are deformed through and through in a very short period. The specified type of protection involves the removal of currents from the pipeline to the primary source using a conductor. At the same time, the potential of the pipes with respect to the ground decreases, which contributes to the elimination of alternating and anode sections with the simultaneous suspension of current leakage into the soil.
Drainage features
The placement of electrical drainage lines depends on the location of the potential threat. Protection of the main gas pipeline against corrosion is being built on the negative bus of the traction substation or on railway rails. In the first case, the connection can be direct or polarized.
Direct drainage is appropriate if the potential of the pipeline is higher than that of the stray current removal system. When arranging electrical drainage on rails, the connection must be exclusively polarized. It differs from the direct version in that the circuit provides for special settings to prevent the return of electric currents to the pipes. The drainage line is available in a cable or atmospheric version, and instrumentation is mounted on it.

Corrosion of underground pipelines
The indicated type of pipe damage is one of the main factors of their destruction due to the formation of cracks and ruptures. Corrosion as a result of the reaction of the metal with the environment causes changes in its structure, which leads to corresponding deformations. Electrochemical protection of the gas pipeline against corrosion makes it possible to prevent such malfunctions, since most reactions are caused in a similar way. That is, cathode and anode zones are formed in different parts of the pipe.
Under the influence of the electromotive flow of a galvanic pair, electrons through metal elements enter the cathode compartment, flowing into the ground and creating a reaction with an oxidizing electrolyte, provoking the formation of oxygen and hydrogen ions. The electrolytic balance is disturbed, at the anode site, positive iron particles go into the soil, which causes galvanic damage due to the loss of metal mass.

Protection of underground gas pipelines from corrosion
There are two ways of protection in this direction: active and passive. In the second case, it is supposed to create an airtight barrier between the metal of the pipe and the soil surrounding it. To do this, use various coatings such as polymer tapes, bitumen, resins.
All insulating coatings for passive corrosion protection of gas pipelines must meet certain standards and requirements. Among them:
- chemical resistance;
- high electrical resistance;
- acceptable rateadhesion to metal surface;
- high mechanical strength;
- not exposed to climatic factors;
- preservation of its properties when exposed to high and low temperatures;
- no mechanical or factory defects;
- the composition should not contain components that have a corrosive effect on the metal;
- resistance to the attack of various kinds of bacteria.

Efficiency
As practice shows, it is almost impossible to achieve an optimal continuous layer by applying an insulating coating. Different types of materials have different diffuse permeability, which causes different quality of pipeline processing from the environment. In addition, during the construction and laying process, dents, cracks and other defects form on the coating. Through damage to passive protection is the most dangerous, since in these places the process of ground corrosion is actively going on.
Since this method is ineffective for the complete safety of pipes, active protection of the gas pipeline against corrosion is additionally used. It is based on the control of electrochemical processes taking place at the boundary between pipe metal and ground electrolyte. This approach is called comprehensive protection. In the active phase, cathodic polarization is provided, which contributes to a decrease in the rate of dissolution of the metal as the corrosion potential moves to a negative indicator, upwards from the natural parameter.
Principle of cathodic polarization
Cathodic protection of underground pipelines is carried out using sacrificial anodes or through polarization from a direct current source. In the first case, the calculation is taken on the fact that different metals in the electrolyte have different potentials. Therefore, when creating a galvanic pair of two materials and immersing them in an electrolyte, the metal, the potential of which has a large negative indicator, will be the anode. As a result, the opposite material is subject to less destruction.
In practical terms, sacrificial galvanic cells consist of magnesium, aluminum or zinc protectors. Such protection is effective in soils with low resistivity (up to 50 Ohm m).

External sources
Cathodic protection of gas pipelines from corrosive processes with the help of external sources is more complicated. Despite the complexity of organizing the process, such a system does not depend on the specific soil resistance and has an unlimited energy resource. The role of direct current sources is played by converters of various configurations and designs, which are powered by a variable electrical network.
Converting elements make it possible to adjust the current of the protective direction in a wide range. At the same time, the protection of the gas pipeline is guaranteed, regardless of the surrounding conditions. Main power sources:
- overhead transmission lines 0, 4/6, 0/10, 0 kW;
- diesel generators;
- thermal, gas and other analogues.
Protective current flows acting on the pipes create a potential difference from the metal to the ground and are distributed unevenly along the length of the gas pipeline.
Recommended:
Tread protection against corrosion. The main ways to protect pipelines from corrosion

Protective corrosion protection is a universal solution when it is required to increase the resistance of metal surfaces to moisture and other external factors
Gas pipeline to China. Project and scheme of a gas pipeline to China

Russia and China have signed a long-awaited gas contract. To whom is it beneficial? Will the fact of its signing affect the geopolitical situation?
Corrosion of aluminum and its alloys. Methods for combating and protecting aluminum from corrosion

Aluminium, unlike iron and steel, is quite resistant to corrosion. This metal is protected from rust by a dense oxide film formed on its surface. However, in the case of destruction of the latter, the chemical activity of aluminum greatly increases
Laying a gas pipeline: methods, equipment, requirements. Gas pipeline security zone

Laying of the gas pipeline can be done by underground and ground methods. When choosing equipment for such systems, safety standards should be followed. Actually, the laying of highways is carried out with strict observance of all the required technologies
Gas pipeline to Crimea. "Krasnodar Territory - Crimea" - the main gas pipeline with a length of 400 km

The gas pipeline to Crimea was commissioned in December 2016. Its construction took place at an accelerated pace in order to solve the main problem of the Crimean gas transportation system: the lack of own gas to fully supply the peninsula due to increased consumption