2026 Author: Howard Calhoun | calhoun@techconfronts.com. Last modified: 2025-01-24 13:10:26
The metalworking process is inherently associated with strong friction that occurs between the workpiece and the tool. This is especially evident in turning and milling operations, when the cutter is very hot, during cold extrusion, and high-speed multi-position heading. Intense friction contributes to premature wear of the tool, plastic deformation of the workpiece, changes in the properties of the metal due to overheating. A special cutting fluid (coolant) is required to reduce friction and temperature.
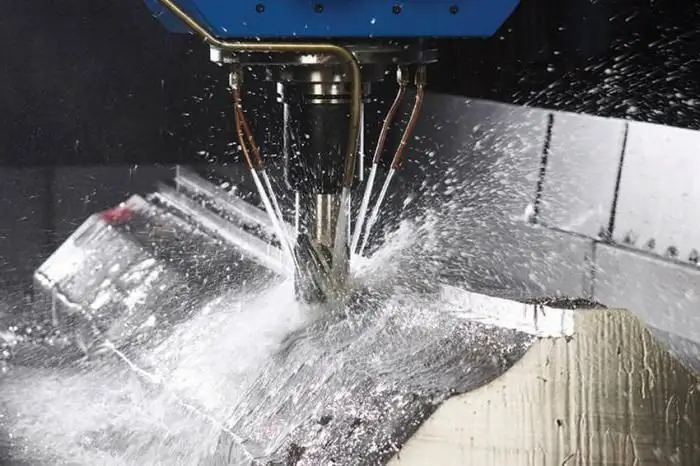

Classification parameters of cutting fluids
The general classification of cutting fluids is based on several basic parameters:
- According to the origin of the components. Oil coolants are produced, which are based on petroleum oils, animal or vegetable fats.
- According to the layout method. Emulsol is a finished product with a long shelf life or technical coolants prepared immediately before use from a concentrate in accordance with GOST.
- Poindustries of application. Various types of coolants are produced for different working conditions of application. Synthetic cutting fluid for plastic deformation operations, coolant for turning or milling machines.
- According to physical and mechanical parameters - viscosity, acid number, flash point. The latter characteristic determines the use of oil coolants for hot stamping.
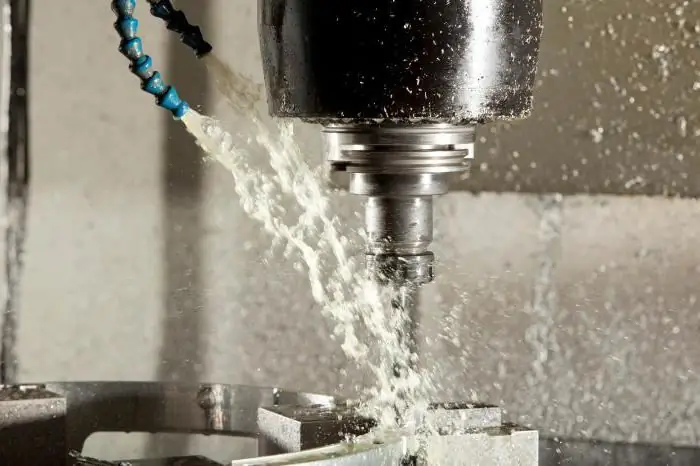

Classification of cutting fluids by composition
The following types of coolant are distinguished by composition:
- Oily - compositions of components that do not mix with water. The base of oil coolants are paraffin, mineral or petroleum oils (60-95%). To enhance the effectiveness against wear, friction, corrosion, various additives and inhibitors are included in the composition. Oil coolants have excellent lubricating properties. Used for soft metals in simple applications.
- Mineral - the base is made from oil by catalytic hydrogenation. To increase efficiency, additives from fats, chlorine, sulfur, phosphorus compounds are included in the composition. These compositions are used in such types of metalworking as: cutting steel, aluminum, brass, threading, milling work on alloy steels.
- Water miscible - mineral-based aqueous solution. These compounds have excellent cooling properties and low toxicity, but low lubricating properties. Scope of application - light and medium turning of copper and bronze, milling and drilling of all types of non-ferrousmetals, grinding and steel stamping.
- Synthetic and semi-synthetic - a mixture of water, surfactants, water-soluble polymers, anti-foam and antibacterial additives, corrosion inhibitors. Anti-wear additives are also added to synthetic formulations to increase lubricity.
- Emulsions are compositions with a high concentration of dispersed particles. Reduce tool and equipment wear in virtually all metalworking operations.
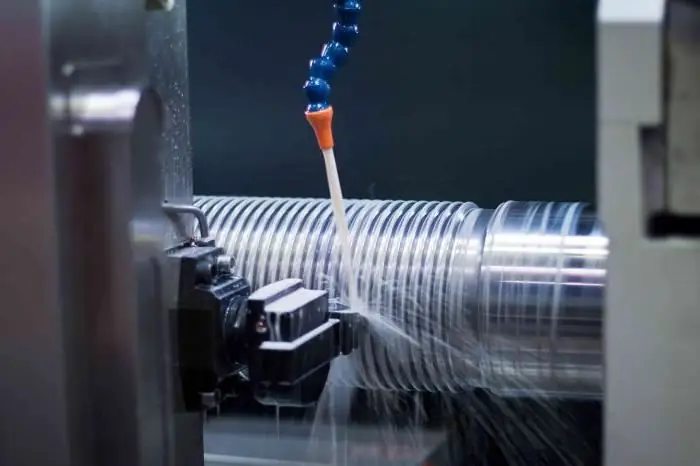

Structure and mechanism of coolant action
The widespread use of coolant in metalworking processes is due to the effective separation of the rubbing surfaces of the workpiece and tool and to reduce their temperature. The most effective cutting fluid may include the following components:
- Based on synthetic oils or animal fats.
- Additives that increase anti-friction and extreme pressure performance.
- Components that prevent the separation of the composition during storage.
- Additives that prevent corrosion and destruction.
- Components that reduce foaming and improve the wettability of surfaces in metalworking.
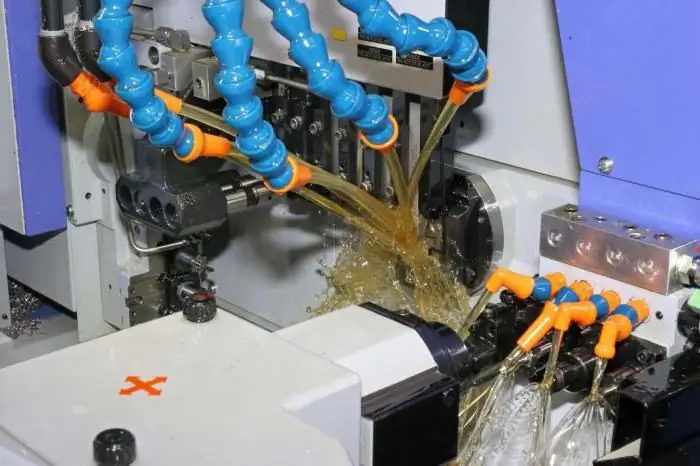

Application of coolant
Cooling fluids are used to lubricate and cool the working area in metalworking. Coolant properties make it possible to reduce friction in the processing zone, thereby reducing tool wear, increasing product quality, improving the intensity of technologicalprocess and, as a result, overall productivity.
Due to their lubricating properties, coolants well reduce the friction force between the surface of the workpiece and the edge of the cutting tool, internal friction in the cut metal layer. Separate technical lubricants have chemical properties that help to reduce not only the friction force, but also the cutting force. Most coolants are surfactants with high adsorption properties. They are able to form a stable film on the metal surface, which significantly reduces friction. Some special surface-active additives have a "wedging" effect on the metal. The elongated molecules of such additives fall into microcracks on the metal surface, like a wedge, thereby weakening the bond between the particles of the material. Thus, the coolant "helps" the working tool to cut off the layer from the base metal.
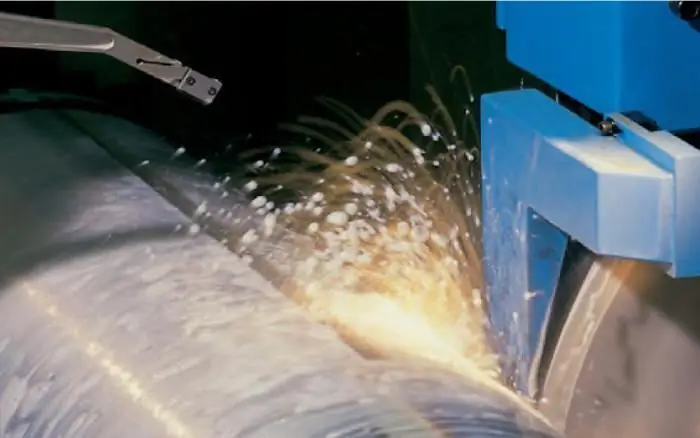

Most common machine tool coolants
The following types of fluids are produced for metalworking on turning and milling machines:
- Emulsols based on mineral and petroleum oils.
- Emulsifiers with synthetic fatty acids.
- Turning and milling operations involving high-speed machining of stainless and alloy steels are performed in accordance with GOST 38.01445-88. For these purposes, synthetic compounds are provided, which are based on tall oils, high-atomic alcohols, triethanolamine.
- Sulfofresols are mixtures of highly purified oil and sulfur-containing compounds. Notcontain water, alkalis, acids. Such coolants for machine tools effectively reduce friction and do not cause corrosion.
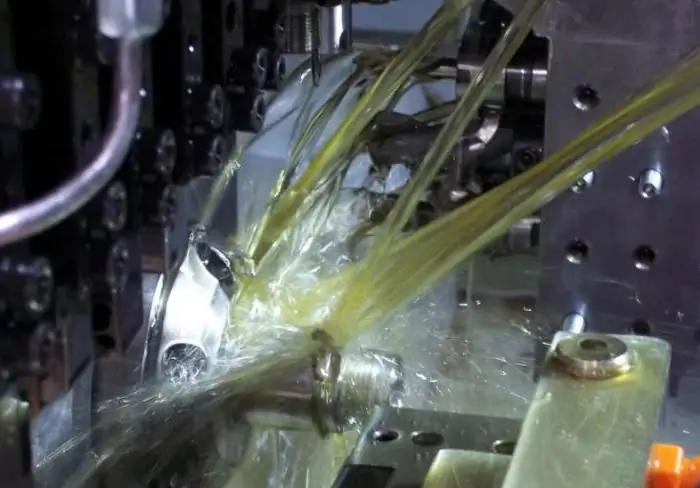
Use of coolant for metal forming
This method of metalworking is accompanied by significant specific forces and relative slippage between the workpiece and the tool. The coolants used in such technological processes must have a significantly higher viscosity. The salient features of metal forming compounds are:
- Sufficient viscosity.
- Resistant to fracture and delamination under high temperature conditions.
- Water graphite compositions are used with the inclusion of fine-flake graphite based on oil suspension.

Features of the use of cutting fluids
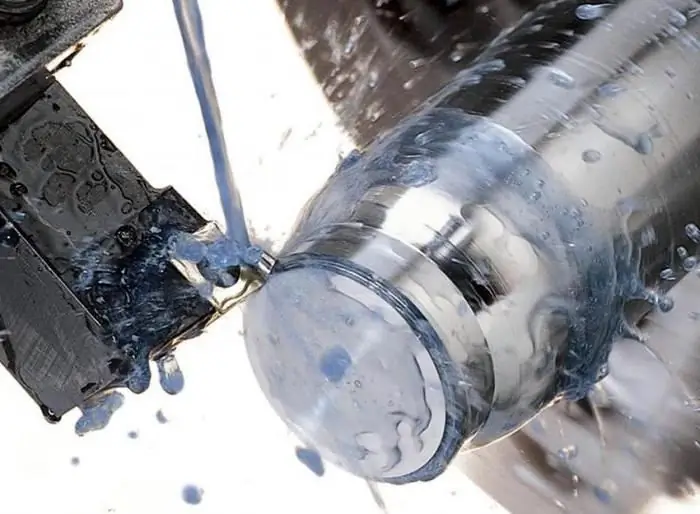
To use the coolant more efficiently, there are a few simple rules to keep in mind.
- The minimum flow rate, regardless of whether it is an aqueous solution or an emulsion, is 10-15 l/min.
- It is very important that the coolant supply is carried out in the place where the maximum amount of heat is generated. In turning, this is the area where the chips separate from the workpiece.
- Coolant must be supplied immediately. When coolant is applied after some time, a very hot cutter will cool rapidly, which will lead to the formation of cracks in it.
- Coolant is not suitable for turning brittle metals (bronze, cast iron, etc.). When turning such materials,small chips, which, mixed with coolant, can clog the working units of the machine (carriage, caliper, guide bed), which leads to premature wear and breakage of these units.

Production and storage of cutting fluids
In addition to ready-made compositions for long-term storage, concentrates and components for the preparation of liquids adapted to the conditions of a particular enterprise are produced. Coolant, coolant, the price of which mainly depends on the composition that meets a certain type of work, is sold on the modern market for 70-160 rubles / liter for finished formulations of domestic manufacturers and 105-290 rubles / liter of foreign production. The average cost of the concentrate is 240 rubles / liter. Before applying the liquid, the following procedures are carried out:
- Mixing of the components is carried out at the temperatures specified for the composition and brand (60-110 0С).
- Analysis of the composition for compliance with GOST.
- Prepared compositions are stored in specialized containers that allow periodic heating, mixing.
- When preparing the coolant, it is possible to introduce additives, which is carried out on fine emulsification vibrators.
- Refilling continuous feeders.
- In the process of use, the compositions become contaminated. Coolant cleaning systems from metal residues are provided. Waste products that cannot be effectively cleaned must be disposed of.
Recommended:
Pyrotechnic composition: classification, components, application

A pyrotechnic composition is a substance or mixture of components designed to produce an effect in the form of heat, light, sound, gas, smoke, or a combination thereof, as a result of self-sustaining exothermic chemical reactions that take place without detonation. A similar process does not depend on oxygen from external sources
Thermal imaging control of electrical equipment: concept, principle of operation, types and classification of thermal imagers, features of application and verification
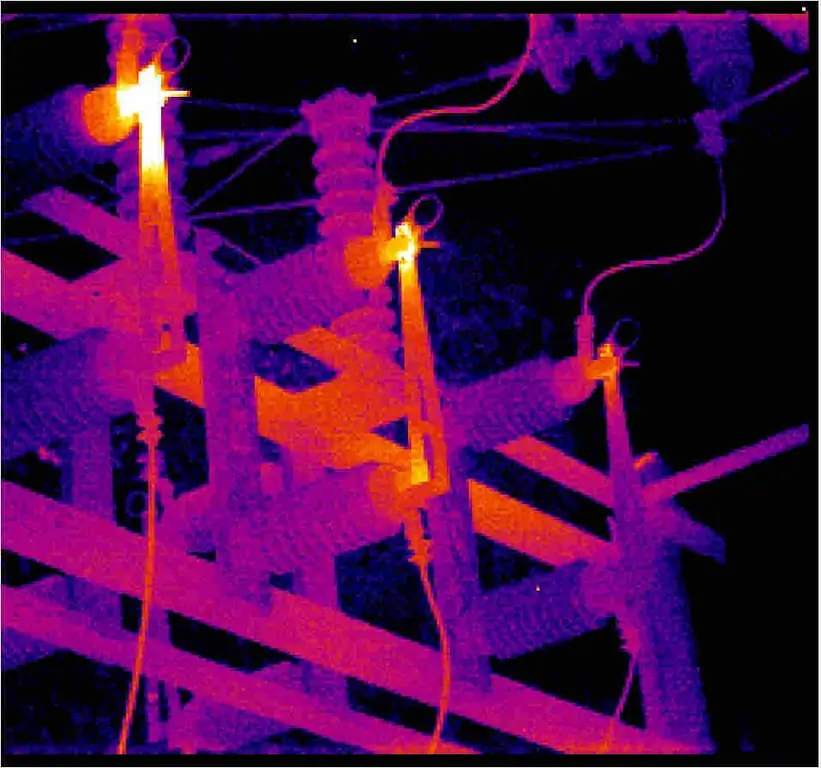
Thermal imaging control of electrical equipment is an effective way to identify defects in power equipment that are detected without shutting down the electrical installation. In places of poor contact, the temperature rises, which is the basis of the methodology
Classes of the Nice Classification: codes, list and classifier. What is the International Classification of Goods and Services?

For the registration of each mark of new products in business, the International Classification of Goods and Services is used. At the initial stage, the applicant determines under which category his activity falls. In the future, this will be the basis for the implementation of registration procedures and determining the amount of the fee paid by the entrepreneur
Classification of production and consumption waste. Classification of waste by hazard class

There is no general classification of consumption and production waste. Therefore, for convenience, the basic principles of such a separation are often used, which will be discussed in this article
How to find out the budget classification code? Budget classification codes for taxes

The problem of how to find out the budget classification code arises in front of almost every taxpayer when the deadline for paying taxes comes. No one can avoid it: neither the accountant of the organization responsible for the relevant transfers to the tax office, nor ordinary citizens who own housing, land, a car or a simple outboard motor

