2026 Author: Howard Calhoun | calhoun@techconfronts.com. Last modified: 2025-01-24 13:10:27
Cooperation is a type of social movement in which a certain organizational and economic system of people's activities is formed.
Essence of cooperation

As a special form of labor organization, cooperation is represented by the cooperation of different numbers of people jointly participating both in one and in different interrelated labor processes. All of these processes occur within some organizational and economic systems.
Types of cooperation
Considering this concept in the understanding indicated above, the following forms of cooperation are distinguished: simple and complex.
Thus, simple cooperation is formed in the process of performing homogeneous work. For example, this is the joint cultivation of land, trade or construction.
Complex cooperation is based on a clear division of labor of persons engaged in joint work. With such an organization of work, the means of production, as well as the knowledge, labor and qualifications of those employed in such joint work, can be used more efficiently.
Other forms of bringing people together
From the standpoint of relations arising from the merger of property, labor cooperation allows you to combineparticipants, based on the collective-share form, which is created through the formation and subsequent reproduction of capital on a share basis.

This association is based on voluntariness, democracy, equality, mutual economic interest and responsibility for the results of joint activities to meet the needs of each individual member of the team. It does this by increasing income and reducing some expenses.
Collective-share cooperation of labor has the main features that are determined by the economic entity itself and are manifested in the principles of its organization. These include: formation on a democratic basis, organization and effective management on the basis of equality of members of the cooperative.
Cooperation of production - the establishment of long-term ties between individual industries, business entities, as well as their divisions in order to participate in the manufacture or repair of specific products. With such a combination, enterprises can supply the parent enterprise (consumer) with finished products or semi-finished products (forgings or blanks) that it needs to produce final products.
Production cooperation is the activity of business entities in two main areas:
- establishing a close connection both between industries and between enterprises that are directly dependent on the technological process;
- organization of links between specializedenterprises to fully utilize all production capacities.
Cooperation of production: basic forms
The following forms of production cooperation are distinguished:

- aggregate (subject), in which business entities performing related work supply the main enterprise with some items (aggregates) that are necessary to complete an already finished product (electrical equipment or engines for tractors or cars can be used as an example);
- detailed, represented by the supply of related parts (these can be piston rings for automobile or tractor enterprises);
- technological, in which specialized enterprises supply others with some semi-finished products (for example, stamps) or perform certain technological operations for them.
Classification by location
Depending on the territorial location, cooperation is:
- intra-district (association of enterprises located in the same economic zone);
- interdistrict (when business entities are located in different economic zones).
Industry affiliation

Considering industry affiliation, the following forms of enterprises are distinguished: intra-industry and inter-industry cooperatives. So, when cooperating business entities working in the same industry, we get intra-industry associations. For example,sugar refinery industry. If business entities from several industries participate in cooperation, then in this case intersectoral cooperation is used (for example, pasta factory, electronic or engineering industry).
Cooperation and specialization
Such concepts as specialization and cooperation are closely interconnected. It is also safe to say that cooperation in its economic essence is derived from specialization. Thus, the second term leads to the formation of a list of highly specialized industries and enterprises within the framework of the law on the division of labor. Business entities with a narrow specialization produce only individual items, assemblies, parts. And the creation of a finished product often requires certain relationships with the unification of efforts that will allow it to be assembled into a common whole.
Thus, cooperation is the next stage of economic management, based on developed specialization, which contributes to the rational use of raw materials, materials and labor resources.
Cooperation indicators
The following performance figures are known in the industry:

- The share of cooperative supplies in the cost of manufactured products, represented by the ratio of the indicated indicators and expressed as a percentage.
- The number of enterprises cooperating with each other. In this case, the effectiveness of such associations is quite clearly seen. Thus, often the formsenterprises involve the manufacture of only one type of product, which is much more profitable for a large enterprise to purchase than to set up its own production for the production of one or another spare part. So, for example, various tools or hardware in cooperative deliveries are much cheaper than their manufacture at each individual enterprise. In this case, industrial relations arise. This is the interaction of individual business entities for the manufacture of specific parts (specialized production).
International cooperation
In this article, the association of enterprises within the framework of one state was considered. However, there is also international cooperation. Here is a good example.
On the territory of one state there is an enterprise that produces a suspension for drugs for cancer (chemical industry). However, this plant does not have a closed cycle of such production due to lack of funds for the purchase of special equipment. Therefore, the resulting suspension is sent to another state (in our case, to the UK), where appropriate production facilities are available, which already produce the medicine itself, ready for use.
Industries where cooperation is not used
Industries where such a combination of enterprises does not exist include the food industry.

This is due to a fairly simple process of manufacturing finished products. Howeverthere are also exceptions. For example, this is the production of wine, champagne, cognac and pasta. However, on an industrial scale, this is of no particular economic importance. Therefore, in the food industry, it is enough to establish simple relationships between independent enterprises.
To some extent, cooperation within the food industry is manifested in the joint use of some auxiliary production facilities, as well as service farms with a full load throughout the entire period of operation. The economic feasibility and effect of this form of cooperation is somewhat mitigated due to the seasonal nature of individual industries.

Thus, in the off-season, when the main production is idle, the available technological capacities and areas can be leased to other nearby enterprises. For example, these are repair shops, electrical installations or warehouses. And in the season, the service economy and auxiliary production can be used much more rationally thanks to such leasing. For example, it is much cheaper for a food company adjacent to a sugar beet factory to purchase steam or electricity from it than to produce it on its own. Such a centralization of the service economy and auxiliary production receives a kind of concentration effect and certain advantages of this production.
Summing up the above material, it should be noted that cooperation is a fairly effective form of associationenterprises in order to increase productivity and reduce the cost of finished products.
Recommended:
How to write business letters, or "We look forward to further cooperation"

Ethics (rules of conduct) in business is what will help you achieve your goals. The success of his company directly depends on the behavior of an entrepreneur and a businessman, because judge for yourself, if a person behaves adequately, politely and restrainedly, then we trust such a business representative more than someone who is pan-bratted and cannot connect a couple of words
A bank statement is The concept, necessary forms and forms, design examples
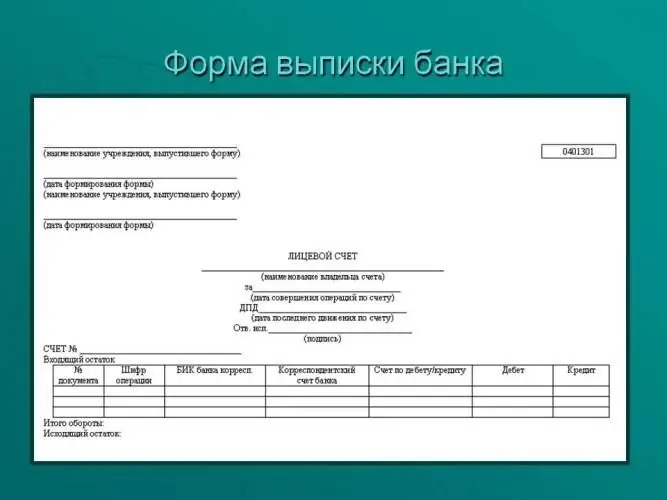
When purchasing any banking product, any client, sometimes without knowing it, becomes the owner of an account with which you can carry out income and debit transactions. At the same time, there must certainly be a certain tool that allows any client to exercise control over the movement of their own funds. This is a bank statement. This is a document that is usually issued upon request to the client. However, not everyone is aware of this possibility
Mutual settlements between organizations: drawing up an agreement, necessary documents, forms of forms and rules for filling out with examples

Settlement transactions (offsets and settlements) between business entities are quite common in business practice. The result of these operations is the termination of the mutual rights and obligations of participants in civil relations
Documents for property deduction: general information, required forms and forms

Registration of a property deduction is a procedure that many citizens of the Russian Federation are interested in. This article will show you how to get it. What needs to be prepared? Under what conditions and to what extent can one claim a property type deduction?
Sample letter of cooperation. Sample Letter of Proposal for Cooperation

The fate of the transaction often depends on the results of consideration of a proposal for cooperation. A sample letter of cooperation will help you make it effective

