2026 Author: Howard Calhoun | calhoun@techconfronts.com. Last modified: 2025-01-24 13:10:28
Consolidated balance sheet is a type of financial statements, which is filled in by almost every company. With the help of this document, it becomes possible to summarize information about the property of the organization, track changes in dynamics. Based on the information received, current and strategic decisions are made in the course of enterprise management. What is a balance sheet, as well as the basic principles of its preparation will be discussed further.
Assignment of balance
A consolidated balance sheet is a type of financial statements that an organization submits to the IFTS. The information collected in it allows you to analyze the current activities of the company, as well as make a forecast. The balance sheet is drawn up for a certain period (most often a year). This allows you to track changes in the property status of the organization duringtime.
The consolidated balance is as follows:
- Property condition of the company.
- Reflection of the result of activity.
- The state of the organization's finances.
- Property structure.
- Reflecting changes in the value of the organization.

It is worth understanding the balance as reporting that characterizes the activities of the organization as a whole. Therefore, this form is the main one, as well as universal. Other types of financial statements complement it. For this reason, the balance sheet is called Form No. 1. This is a kind of pivot around which data on the results of the enterprise are grouped.
The consolidated balance is made up on a certain date. Comparing the data over time, you can track the dynamics of the property status of the organization. The users of the information summarized in the balance sheet are:
- IFTS;
- organization owners;
- managers of different levels;
- employees of the financial and economic service;
- representatives of state statistics;
- lenders or investors;
- sponsors;
- counterparties, partners of the organization;
- representatives of the administration of the company's activities.
Based on the current balance, a forecast balance is created. In this case, a standard, statutory form is used. It is viewed by both internal and external users. But for an enterprise, it may be necessary to generate reports that are not in a standard form. In this casethe data is presented in a transformable form. This allows you to see in detail the results of current activities. Based on the information received, managers can take appropriate decisions and specific measures to improve the organization's performance. It is very important to know the procedure for the formation of the consolidated balance sheet.
Varieties of balance forms
A consolidated balance sheet is created according to the standard, generally accepted form. Accounting and reporting allow you to obtain the necessary information for both internal and external users. Official data is provided to the IFTS. To do this, information is summarized and provided in the prescribed form.

For internal use, an organization can create a modified type of report. But this does not mean that the information will be provided to the governing bodies in this form. The modified balance sheet is for internal use only. It varies depending on the purpose of reporting and may be as follows:
- Data are taken either on a certain date, which allows you to form a balance sheet, or on turnover for a certain period (turnover balance).
- Initial data can be inventory or accounting. The choice of aggregation methodology depends on the purpose of the report.
- Data can be decoded in the form of regulatory articles. These include depreciation, markup and reserves. The report can be made without these articles.
- You can draw up a balance for only one type of activityorganizations.
- The form can be full or abbreviated.
- Balance is an equality that can be drawn up between property and the amount of capital and liabilities. In some cases, only borrowed capital is taken into account. Own resources are not taken into account when compiling the report. The standard form takes into account both the capital and liabilities of the company.
- The report can be compiled for one enterprise or for several organizations. How to draw up a consolidated balance sheet for a group of companies, there is a certain methodology. In this case, the scale of generalization will be larger.
- Balance can be created for a specific event. This can be a liquidation or opening report, as well as a separation or unification balance sheet.
- In addition, a property reflection of the state of the company can be compiled for a preliminary assessment, development of a forecast. The balance may be interim or final.
The consolidated balance sheet is a summary report for several divisions of one company or group of organizations. Approaches to filling out this form are saved regardless of the approach to reflecting summary information.
Abbreviations and terms
When compiling the consolidated balance sheet of a group of companies, accountants take into account the recommendations presented in the order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated 02.07.10 No. 66n. Here the full form with selected articles is approved. It is recommended to allocate them if the enterprise has relevant data. For those sections for which information is missing, articles are not highlighted. If arequired, the balance sheet reflects additional data that increases the reliability of reporting.

In accounting, certain terms and abbreviations are often used. You need to know them in order to understand what information is being discussed. The most common abbreviations that are used when compiling the consolidated balance sheet of a bank or enterprise are:
| Abbreviation | Transcript |
| TZR | shipping and procurement costs |
| NMA | intangible assets |
| OS | fixed assets |
| R&D | research and development work |
| RBP | deferred expenses |
| DBP | deferred income |
| WIP | work in progress |
| TMC | inventory |
| FSS | social security fund |
One of the most important consolidated balance sheet terms that every accountant should know is minority interest. Reporting can be created for several enterprises.
In the consolidated balance sheet, minority interest representspart of the property of a subsidiary in the total capital of the organization. It is owned by minority shareholders. The group of these owners cannot influence the management of the company's activities, as it is in the minority.
It is worth noting that the minority share is the capital of those shareholders who have invested their resources in a subsidiary that is not directly related to the parent organization. Such funds are shown in the consolidated balance sheet as equity or liabilities with an indefinite term.
General reporting principles
The consolidated balance sheet of a group of enterprises or individual production units is compiled, first of all, in a standard form. It may have notes for each article. The company decides on its own whether this column is needed in the report. Most often, it is used when there are deviations from the standard form approved by the Ministry of Finance.

In some cases, the balance is drawn up in a simplified form. It is used by some legal entities that meet certain requirements. In this case, the information is presented in the appropriate form. The balance is divided into sections, and there is no notes column. At the same time, in a simplified form, some articles are combined to consolidate indicators.
There are certain rules for completing the balance sheet. They are presented in PBU 4/99. These rules were approved by the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation on July 6, 1999 No. 43n. The main ones in the preparation of the consolidated balance sheet are:
- Accounting data serves as a source of information for reporting.
- Information on the basis of which the balance sheet is formed must be formed on the basis of existing PBUs, as well as in accordance with the accounting policy of the enterprise.
- Data must be complete and correct.
- The consolidated balance sheet of a group of enterprises and branches is compiled in a generalized form for the entire organization.
- Information presented in the report should be comparable to previous periods.
- Articles are distinguished according to the principle of materiality.
- The reporting period is equal to the calendar year.
- Assets and liabilities are divided into short-term (up to 12 months) and long-term (there are more than 12 months).
- Offset between liability and asset items is not done, unless otherwise provided by PBU.
- Property is valued at net worth on the balance sheet date. At the same time, regulatory articles are deducted.
- In the annual report, the data must be confirmed by inventory.
General filling rules
The consolidated balance sheet is filled in based on the data on the balance on the accounting accounts as of the date of its compilation. It is important to determine the exact purpose of such work. In accordance with this, a consolidated balance sheet is drawn up.

Since accounts at enterprises are closed on a monthly basis, reporting is prepared with the inclusion of all months of the current year. Most often, the data is given in thousands of rubles. If the enterprise is large, the balance sheet can be drawn up inmillion rubles.
The structure provides for the division of the report into information about property and capital, through which it was financed. The asset has two main sections. These are non-current (long-term) and current (short-term) assets.
The liability is divided into three main sections. These are long-term and short-term liabilities, as well as the equity of the organization.
Recommendations for filling

When filling out the form, you need to be guided by certain transcripts:
- Data on the cost of intangible assets and fixed assets are indicated minus depreciation.
- Information on tangible and intangible prospecting assets, R&D is filled in only if they are available. If they are, then their amount is reflected minus depreciation deductions.
- If a company has financial investments, which can be represented by issued loans, deposits, contributions to the development of other organizations, securities are reflected in the balance sheet by their maturity. They should be presented in the long-term and short-term sections of the asset, respectively. At the same time, reserves created in case of depreciation of financial investments must be deducted from the amount.
- Data on deferred tax payments presented in the lines of non-current assets and long-term liabilities are filled in only subject to the application of PBU 18/02.
- Information on stocks, including the balance of materials with inventory, goods, work in progress, finished products, RBP is reduced by the amount of reserves created for the depreciation of goods and materials. You also need to subtract the value of the trade margin, if it is included in the price.
- Accounts payable and accounts receivable are reflected in detail. The amount of funds owed to the enterprise by counterparties, suppliers, employees, funds, etc. should be reflected net of reserves for doubtful debts. Financial investments are also taken into account separately.
- Reflect the amount of VAT on advance payments can be different. It depends on the accounting policy adopted at the enterprise.
- Cash is reflected in the total amount (currency, cash, non-cash). Deposits are deducted from it, which are reflected in the lines of financial investments.
- If there is an amount of additional capital in the account, it is divided into two lines. It is divided according to the principle of whether it is related to the revaluation of property.
- Retained earnings (or uncovered loss) in the consolidated balance sheet is the total of the total number of years after the reformation or the first balance sheet. If the report is interim, you need to add the result of previous years and the amount received for the current period. In this case, this line may reflect a negative result.
- In the consolidated balance sheet, data on borrowed funds are reflected in terms of the period remaining to maturity. On this basis, liabilities are reflected in different sections of liabilities. Accrued interest is shown as part of short-term debt.
- According to the same principle, estimated liabilities for reserves of future expenses.
- Include earmarked funding information in the DBP.
- In all sectionsthere is a line to reflect other assets or liabilities. Data that is not reflected in other articles is indicated here.
Simplified form
When drawing up a consolidated balance sheet, a simplified form may be used. However, some articles are merged. New names are provided for them:
- The article "Tangible non-current assets" shows the amount of fixed assets, capital investments in progress. In a standard report, it is divided into "Tangible exploration assets", "Intangible exploration assets", "Profitable investments in tangible assets", "Fixed assets".
- In the article "Intangible, financial and other non-current assets" combines the amount of R&D, intangible assets and ongoing investments in them, long-term financial investments, deferred tax payments.
- The amounts of short-term financial investments and VAT on purchased valuables, receivables are reflected in the item “Financial and other current assets.”
- The amount of authorized, reserve, additional capital, repurchased shares of your organization, revaluation and retained earnings are reflected in the article "Capital and reserves".
- In "Other long-term liabilities, data on deferred tax and long-term estimated liabilities are indicated.
- Information about DBP, short-term valuation circumstances are indicated in "Other short-term liabilities".
Asset Filling Guide
For the formation of the consolidated balance sheet, the balance of accounting accounts as of the reporting date is required. ForThis requires the following information:
- To fill in the item "Intangible Assets", you need to add up the balances of account 04, from which the amount of account 05 is subtracted. The line "Research and development results" is not taken into account.
- For the article "Research and Development Results", you need to take the data reflected in account 04.
- Data on tangible and intangible exploration assets are reflected on account 08. From this, depreciation must be deducted, which is taken into account respectively on account 05 and 02.
- To fill in the line "Fixed assets", you need to subtract the funds of account 02 from the amount of account 01. You will also need to add to the result the cost of capital investments on accounts 07, 08.
- The line "Profitable investments in material assets" is filled on the basis of data on accounts 03, 02.
- For the item “Financial investments”, information on non-current assets with a maturity of more than 12 months is selected. For this, data is taken from accounts 55 (for deposits), 58, 73 (loans to employees). This amount must be reduced by reserves for long-term investments, which are reflected in account 59.
- To fill in the line "Deferred tax assets" you need to take the data of the account balance 10, 11, 15, 16, 20, 21, 28, 29, 41, 43-46, 97.
- “Value added tax on acquired valuables” is filled in from account 19.
- To fill in the "Accounts Receivable" item, you need to take the sum of the balance of accounts 60, 62, 66-71, 73, 75, 76.
- “Financial investments (net of cash equivalents)” are filledafter sampling in current assets the amounts on the account 55, 58, 73.
- The amount of the item "Cash and equivalents" is reflected in accounts 50-52, 55 and 57.
Guidelines for filling liabilities
To fill in the liability of the consolidated balance, do the following:
- "Authorized capital" is reflected in account 80.
- The item "Own shares repurchased from shareholders" is formed from account 81.
- “Revaluation of non-current assets” is filled in after determining the balance on account 83. These balances relate to intangible assets and fixed assets.
- To fill in the item "Additional capital", you also need to take into account the balance of account 83 (except for the balances of intangible assets, fixed assets).
- The item "Reserve capital" is filled in from account 82.
- To fill in the "Retained earnings", you need to determine the balance of account 84. If interim reporting is formed, take the sum of the balance of accounts 84 and 99.
- To fill in the line "Borrowed funds" from the balance of account 67, you need to select data on long-term debt (more than 12 months). At the same time, the interest paid by the company is reflected in short-term liabilities.
- “Deferred tax liabilities” are filled in according to account 77.
- The article "Estimated liabilities" is indicated in accordance with the balance of account 96.
- To fill in the line "Borrowed funds" in the consolidated balance sheet, you need to get information about the balances of the account 66, 67.
- In "Accounts payable" the sum of the balance of accounts 60, 62, 68-71, 73, 75, 76.
- DBP indicated on accounts 86 and 98.
- "Estimatedliabilities "are formed from the balances of account 96, from which short-term reserve data is selected.
Filling the reduced balance
To fill in the articles of the simplified balance, you need to follow certain rules. For each article, data is also taken from accounting accounts.

To indicate the correct amount in the article “Tangible non-current assets”, you need to determine the data of accounts 01, 03. Subtract the amount of account 02 from them. Next, add the amount of accounts 07, 08 to the result obtained. They refer to non-current assets.
The article “Intangible, financial and other non-current assets” includes the amounts of accounts 04, 05, to which data on accounts 55, 58, 73 are added. Also, the amount of reserves on account 59, 09, 08 is subtracted from the result.
The article "Financial and other current assets" summarizes the data of accounts 19, 55, 58, 60, 62, 66-71, 73, 75, 76.
To correctly indicate the information in the article "Capital and reserves", you need to calculate the amount of balances on accounts 80-84.
The item "Other long-term liabilities" reflects the balances of accounts 77, 96. The line "Other short-term liabilities" summarizes the balances of accounts 86, 96, 98.
The rest of the articles are filled out according to the same rules as in the standard form.
When doing such work, not only beginners, but also experienced accountants have difficulties, especially when a difficult situation arises. There are special programs that fill out form 1 automaticallymode. Such a result requires verification by an experienced accountant. This is due to the peculiarities of the setting. The program must be applied in accordance with the peculiarities of the financial policy of the organization. It requires prior proper setup.
Recommended:
Net sales in the balance sheet: string. Sales volume in the balance sheet: how to calculate?

Annually, enterprises prepare financial statements. According to the data from the balance sheet and income statement, you can determine the effectiveness of the organization, as well as calculate the main planned indicators. Provided that the management and finance department understand the meaning of terms such as profit, revenue and sales in the balance sheet
General concepts of the balance sheet: assets, liabilities, balance sheet currency

The balance sheet contains important information for assessing the company's financial results. Each section of the asset, liability, as well as the balance sheet currency is necessary to calculate many financial indicators
Formula of net assets on the balance sheet. How to calculate net assets on a balance sheet: formula. Calculation of net assets of LLC: formula

Net assets are one of the key indicators of the financial and economic efficiency of a commercial firm. How is this calculation carried out?
Liquidation balance sheet is Definition of the concept, approval, form and sample of filling out the liquidation balance sheet
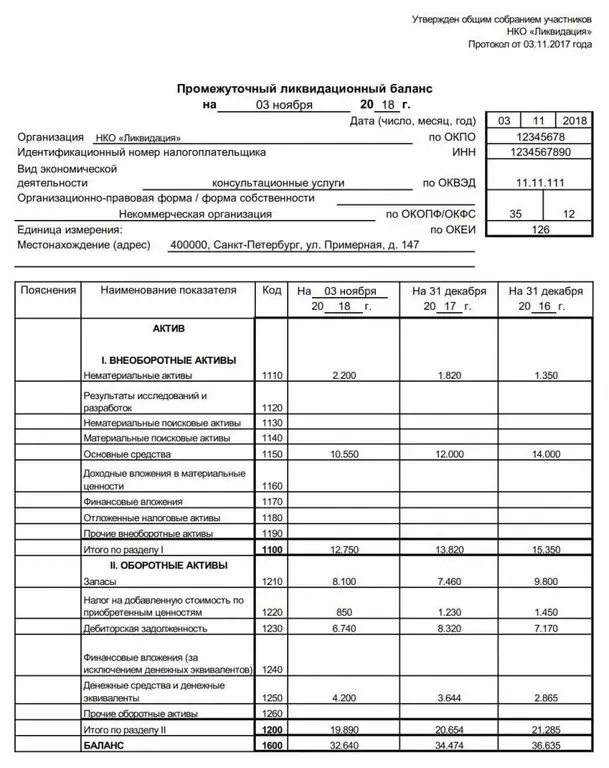
The liquidation balance sheet is an important financial act drawn up during the closing of an organization. It can be intermediate or final. The article tells what is the purpose of these documents, what information is entered into them, as well as how and when they are approved and submitted to the Federal Tax Service
Balance: types of balance. Types of balance sheet
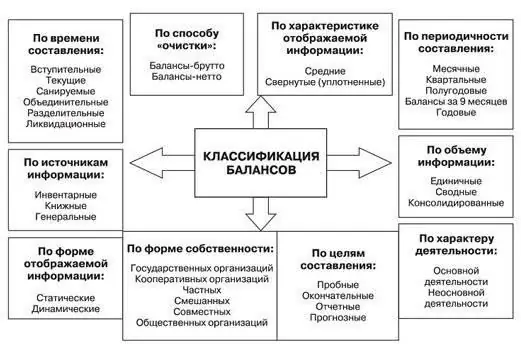
The balance sheet is the most important accounting document of an institution. What is it, what are the rules for filling it out, types and classification

