2026 Author: Howard Calhoun | calhoun@techconfronts.com. Last modified: 2025-01-24 13:10:29
Water use refers to the process of water consumption, its source is natural objects or water supply systems.
Water consumption is usually normalized, that is, to determine its measure established according to the plan. This is done taking into account the quality of the natural resource. As well as those standards that are approved for the release of a unit of industrial output.
Why do we need rationing?
Its main task is to guarantee the most efficient use of water resources in production and at home.
Rationing in the field of public utilities is carried out on the basis of the relevant SNiPs, at industrial enterprises, specially developed guidelines are used for this. What exactly is subject to it?
It is accepted to standardize the total amount of water consumed during the production of products (per unit), fresh drinking water, as well as technical water. In addition, take into account the water that is reused and recycled. As well as sewage, i.e. sewer water (as discharged fromconsumer and production).

What data does SNiP "Water Consumption Standards" use
The so-called specific value is taken as the basis for such rationing. What is the water consumption rate? This unit is equal to the maximum allowable volume of water accepted according to the plan (with appropriate quality), which is required for the production of a unit of production of a standard sample under certain production conditions or for consumption for drinking or economic purposes.
The formation of specific norms is carried out by using their element-by-element components. What is included in them? Basically, we are talking about the specific water consumption for production (for each unit) or for the volume (area) of the enterprise. The same rate of water consumption by the enterprise exists for each individual process, which includes both its drinking and household needs.
Another calculated value regulates those losses in the production cycle that are irretrievable. We are talking about leakage, evaporation, entrainment, filtration, etc. These are usually referred to as factory, industry and inter-sectoral. It is customary to measure standards in natural units (liters, cubic meters, etc.).
On the regulation of wastewater disposal
But specialists are interested not only in the rate of water consumption. It turns out that the exact opposite procedure is also subject to accounting. Drainage, that is, the discharge of water, is the process of removing wastewater outside the places where the primary use of the resource takes place (an enterprise, a populated area).paragraph). They are removed to natural sources or transferred to specialized organizations for cleaning.
Under the norms of water disposal is meant the planned maximum amount of wastewater, also taken per unit of output. In this case, water can refer to one of two degrees of pollution - conditionally (regulatory) clean and requiring purification.
Due to the constant improvement of technology, the norms of water consumption and sanitation are reviewed without fail every five years. They are calculated directly at the production site upon approval by management.

How water quality is taken into account
Requirements for the quality and composition of drinking water in centralized water supply systems are set out on the pages of SanPiN, published in 2001
Technical water is divided into 4 separate categories with their own requirements for each.
I - water-coolant at thermal power plants, nuclear power plants, etc. The presence of mechanical impurities, hardness and aggressiveness are excluded. The effluents of such water do not need to be treated, but can be hot.
II - water for washing products, containers, raw materials. Drains are heavily contaminated.
III - raw water (for food products, in the construction industry, etc.).
IV - water of complex use.
Given this separation, production technology is selected as rationally as possible with minimization of environmental damage.

What is a limitwater consumption
This is the result of the calculation, which is based on the rate of water consumption, the amount of drinking and technical water for each enterprise according to production conditions, planned losses, and a resource saving program.
The water disposal limit is the amount of wastewater sent to a natural object, taking into account its condition and standard standards.
Both of these limits, calculated and accepted directly at the enterprise, must be approved by the water use agency. They are accepted in the general case for a year, but in a difficult situation with water resources - monthly or even daily.
Water in public utilities
Providing the population with drinking water is the most important matter of the state scale, one of the first duties of the authorities of any locality. In the absence of clean water for drinking, diseases instantly arise - up to epidemics. There are still plenty of places in the world where access to acceptable quality water is an unaffordable luxury.
In our country, the Water Code proclaims the priority of public water supply. First of all, regardless of the conditions, the population must be provided with clean water. Its supply should not be below the mark of 97% (this means that only three days out of a hundred water interruptions are acceptable).
Of course, this area also has its own water consumption norm. The structure of domestic water supply is as follows.

Household and drinkingwater supply is allocated 56%, public buildings - 17%, industry - 16%. The rest goes to other needs (firefighters - 3%, city - fountains, watering, etc. - 1%, the same amount for all others).
Household water is consumed in the following percentage: for drinking and food purposes (cooking) - 30%, for washing - 10%, using bathtubs - 30%, flushing toilet bowls - 30%.
Water consumption standards - a day in a big city
Inhabitants of large cities are provided with up to 600 l/day of water for all domestic and communal needs. This is the rate of water consumption per person. The structure of her expenditure looks like this:
- for personal needs - 200 l;
- for public utilities - 100 l;
- to maintain city cleanliness - 100 l;
- local enterprises - 200 l.

The following is typical for domestic water supply.
Water quality must be exceptionally high in terms of both physical (color, transparency, taste, odor) and chemical (hardness, salinity, acidity, composition of impurities) properties.
This also includes the content of organic substances, the normalized radiation of radioactive particles, and the bacterial composition. Drinking water should be free of parasites, viruses, pathogenic microbes.
The best water
Quality standards (the first of them in our country dates back to 1937) tend to become tougher year by year.
What is the reason for this? Science is notstands still, every year there are more and more new facts about the impact on humans of certain substances. Accordingly, the quality requirements for the composition of water are subject to revision.
The best content is in interstratal underground artesian waters, which are considered as protected from pollution as possible. Somewhat worse - groundwater, which is not so deep, and the least suitable for water supply is surface water.
In order for water to meet quality standards, it is subjected to filtration, coagulation (precipitation of impurities), chlorination, removal of unwanted impurities and the introduction of the desired impurities.

On uneven consumption
Another property of water consumption in the housing and communal services sector is a combination of relative uniformity of water consumption throughout the year with uneven daily consumption. If the percentage of seasonal fluctuations is no more than 15-20, then the difference is much greater per day (we spend about 70% of water in the daytime). Therefore, a special coefficient of non-uniformity (hourly and daily) has been developed. Thanks to him, the fluctuation in the consumption of water resources by hours and months is taken into account, which is required when designing supply systems. After all, their task is to ensure a guaranteed supply even in the mode of maximum water consumption.
Recommended:
Shelf life of water meters: period of service and operation, verification periods, operating rules and time of use of hot and cold water meters

The shelf life of water meters varies. It depends on its quality, the condition of the pipes, the connection to cold or hot water, the manufacturer. On average, manufacturers claim about 8-10 years of operation of devices. In this case, the owner is obliged to carry out their verification within the time limits established by law. We will tell you more about this and some other points in the article
What is rationing: concept, definition, types, methods and formulas for calculations

What is rationing? This is a controlled distribution of limited resources, goods or services, or an artificial reduction in demand. Rationing revises the size of the ration, which is the allowed part of the resources allocated per day or some other period of time. There are many forms of this control, and in Western civilization people experience some of them in daily life without realizing it
"Royal Water": customer and employee reviews, addresses, order conditions, delivery and water quality

Royal Water is one of the largest companies in the bottled water market. The company was founded in 1994. An extensive dealer network and a large number of branches determined the presence of the organization in many regions of the country
UV water disinfection: principle of operation, installation. Drinking water - GOST valid
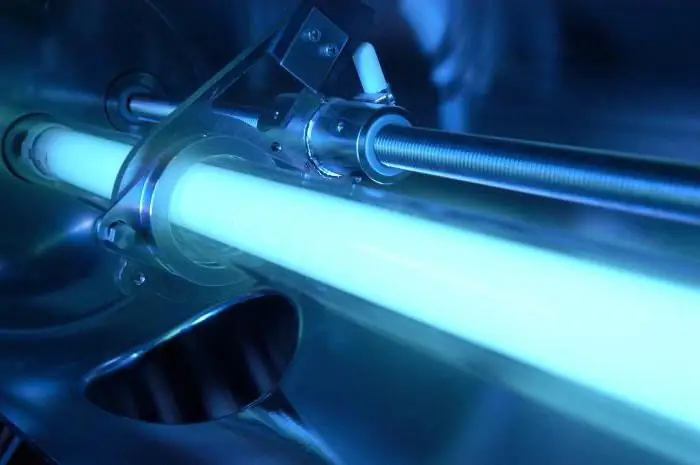
Technologies in the field of water treatment do not stand still. Today, many methods are used to ensure the required quality of drinking liquids that meets the requirements of GOST. One of them is ultraviolet disinfection of water. It will be discussed in the article
The balance of water consumption and sanitation is a necessary calculation in the design of any facilities and in water use

One of the documents required by an economic entity when issuing a license for the use of a surface water body or when issuing a license for the extraction of groundwater is the balance of water consumption and water disposal. This water management calculation is also mandatory when designing any object of the national economy or a residential building

