2026 Author: Howard Calhoun | calhoun@techconfronts.com. Last modified: 2025-01-24 13:10:37
In manufacturing and construction industry, non-destructive testing is one of the most popular methods for diagnosing materials. Using this method, builders evaluate the quality of welded joints, check the density in certain sections of structures, revealing deep defects and flaws. Diagnostic magnetic flaw detectors can detect both surface and subsurface damage with a high degree of accuracy.
Device device
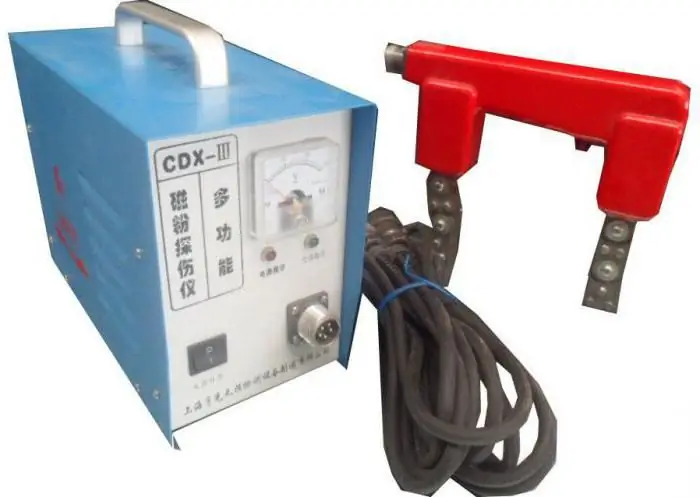

The basis of the segment of magnetic thickness gauges and flaw detectors are hand-held devices provided with magnetizable working bodies - usually in the form of pincers. Outwardly, these are small devices, the filling of which is an electromagnet that regulates the poles of the wave action. The middle class allows you to work with magnetic permeability, the coefficient of which is higher than 40. The body is provided with an ergonomic handle, thanks to which the device can be used in hard-to-reach places. To supply electrical current, the instruments are also provided with a cable connected either to a generator station (if work is carried out outdoors) or to a 220 V household electrical network. More sophisticated non-destructive testing equipmenthas a stationary base connected to a computer. Such diagnostic tools are more often used to check the quality of manufactured parts in production. They perform quality control, fixing the smallest deviations from the normative indicators.
Ferroprobe flaw detectors
A kind of magnetic devices designed to detect defects at a depth of up to 10 mm. In particular, they are used to fix discontinuities in the structure of structures and parts. These can be sunsets, shells, cracks and hairlines. The fluxgate method is also used to assess the quality of welds. After the end of the working session, magnetic flaw detectors of this type can also determine the level of demagnetization of the part as part of complex diagnostics. In terms of application to parts of different shapes and sizes, the devices have practically no restrictions. But, again, one should not forget about the maximum depth of structure analysis.

Magnitographic and eddy current flaw detectors
With the help of magnetographic devices, the operator can detect product flaws at a depth of 1 to 18 mm. And again, the target signs of deviations in the structure are discontinuities and defects in welded joints. The features of the eddy current testing technique include the analysis of the interaction of the electromagnetic field with the waves generated by eddy currents that are fed to the subject of control. Most often, an eddy current flaw detector is used to examine products made of electrically conductive materials. Devices of this typeshow a highly accurate result when analyzing parts with active electrophysical properties, but it is important to consider that they work at a shallow depth - no more than 2 mm. As for the nature of defects, the eddy current method makes it possible to detect discontinuities and cracks.
Magnetic Particle Flaw Detectors
Such devices are also focused mainly on surface defects that can be fixed at a depth of up to 1.5-2 mm. At the same time, the possibility of research is allowed to reveal a wide range of defects - from the parameters of the weld to the detection of signs of delamination and microcracks. The principle of operation of such non-destructive testing equipment is based on the activity of powder particles. Under the action of an electric current, they are directed towards the inhomogeneity of magnetic oscillations. This allows you to fix the imperfections of the surface of the target object of study.

The highest accuracy in determining defective areas by this method will be present if the plane of the defective area forms a 90-degree angle with the direction of the magnetic flux. As we deviate from this angle, the sensitivity of the instrument also decreases. In the process of working with such devices, additional tools are also used to fix the parameters of defects. For example, the magnetic flaw detector "Magest 01" in the basic configuration is provided with a double magnifier and an ultraviolet flashlight. That is, the direct determination of the flaw on the surface is performed by the operator by visual inspection.
Preparation for work
Preparatory activities can be divided into two groups. The first will include directly preparing the working surface, and the second - setting up the device. As for the first part, the part must be cleaned of rust, various kinds of grease, oil stains, dirt and dust. A high-quality result can only be obtained on a clean and dry surface. Next, the flaw detector is set up, in which the key step will be calibration with verification against standards. The latter are samples of materials with defects, which can be used to evaluate the correctness of the results of the analysis of the device. Also, depending on the model, you can fix the working depth range and sensitivity. These indicators depend on the tasks of detecting defects, the characteristics of the material being examined, and the capabilities of the device itself. Modern high-tech flaw detectors also allow automatic adjustment according to the specified parameters.
Magnetizing the part

The first stage of work operations, during which the magnetization of the object being examined is performed. Initially, it is important to correctly determine the direction of flow and the type of magnetization with sensitivity parameters. For example, the powder method allows you to perform pole, circular and combined impact on the part. In particular, circular magnetization is carried out by passing an electric current directly through the product, through the main conductor, through the winding or through a separate section of the element with the connection of electrical contactors. ATIn the pole action mode, magnetic flaw detectors provide magnetization using coils, in a solenoid medium, using a portable electromagnet or using permanent magnets. Accordingly, the combined method allows you to combine two methods by connecting additional equipment in the process of magnetizing the workpiece.
Application of magnetic indicator

Indicator material is applied to the pre-prepared and magnetized surface. It allows you to identify the flaws of the part under the influence of an electromagnetic field. It has already been said that powders can be used in this capacity, but some models also work with suspensions. In both cases, before working, it is important to consider the optimal conditions for using the device. For example, magnetic flaw detector "MD-6" is recommended to be used at temperatures ranging from -40 to 50 °C and at air humidity up to 98%. If the conditions meet the requirements for operation, then you can start applying the indicator. The powder is applied throughout the area - so that a small coverage of areas not intended for study is also provided. This will provide a more accurate picture of the defect. The suspension is applied by jet using a hose or aerosol. There are also methods for immersing the part in a container with a magnetic indicator mixture. Then you can proceed directly to the troubleshooting of the product.
Inspecting part
The operator must wait until the indicator activity ends,be it powder particles or suspension. The product is checked visually with the aforementioned devices in the form of optical devices. In this case, the magnifying power of these devices should not exceed x10. Also, depending on the requirements for the examination, the operator can take pictures already for more accurate computer analysis. Multifunctional magnetic flaw detectors-stations have in their basic equipment equipment for decoding replicas with powder deposits. The drawings obtained in the course of sorting are subsequently compared with standard samples, which allows us to make a conclusion about the quality of the product and its admissibility for the intended use.
Conclusion

Magnetic flaw detection instruments are widely used in various fields. But they also have disadvantages that limit their use. Depending on the operating conditions, these include the requirements for the temperature regime, and in some cases, insufficient accuracy. As a universal means of control, experts recommend using a multi-channel magnetic flaw detector, which is also capable of supporting the function of ultrasonic analysis. The number of channels can reach 32. This means that the device will be able to maintain optimal flaw detection parameters for the same number of diverse tasks. In essence, channels are understood as the number of operating modes focused on certain characteristics of the target material and environmental conditions. Such models are not cheap, but they providethe correctness of the results when detecting surface defects and internal structure of various kinds.
Recommended:
Glass furnace: types, device, specifications and practical application

Today, people actively use glass for a variety of purposes. The glassmaking process itself is the melting of raw materials or charge. Glass melting furnaces are used to melt the material. They come in different types and are classified according to several criteria
Thermal imaging control of electrical equipment: concept, principle of operation, types and classification of thermal imagers, features of application and verification
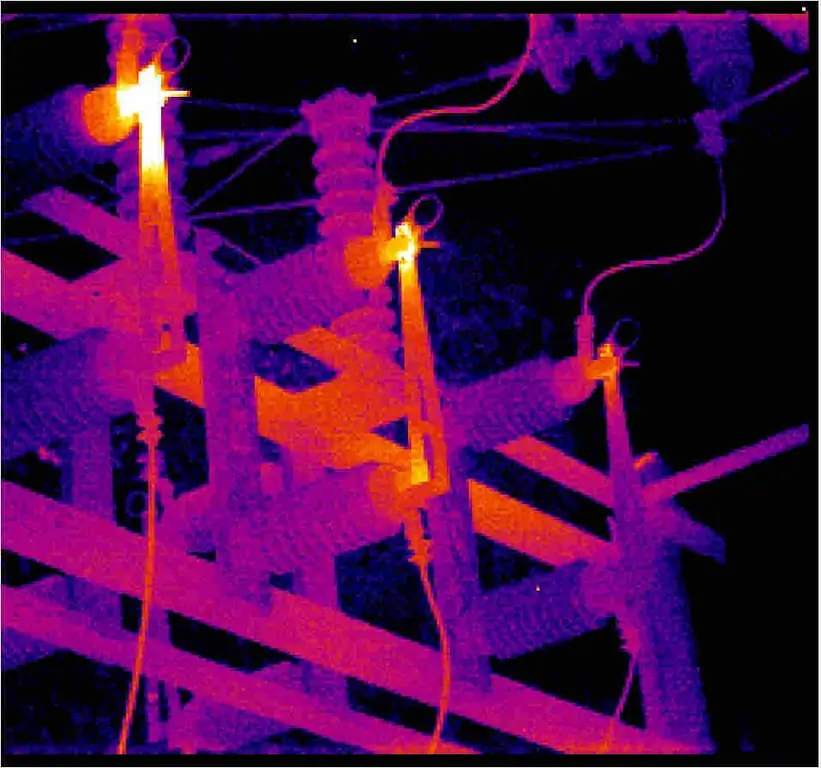
Thermal imaging control of electrical equipment is an effective way to identify defects in power equipment that are detected without shutting down the electrical installation. In places of poor contact, the temperature rises, which is the basis of the methodology
V-belt: device and application
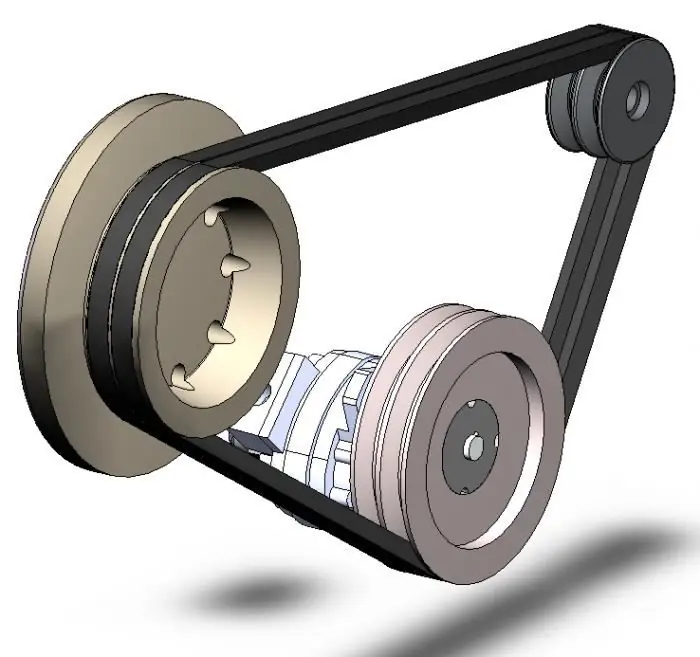
V-belt is the main connecting device used in the manufacture of various types of machine tools, mechanisms and machines with moving components. This tool transmits the inertial rotational movements of the engine (or any other mechanism) and brings them into final contact. At the same time, V-belts bypass the corresponding pulleys during operation and transmission of forces from one mechanism to another
Flame control sensors - features, device and principle of operation

Today, people actively use fire for their own purposes. However, it is very dangerous, and therefore, when working with it, it is necessary to put safety in the first place. On an industrial scale, this role is played by a flame control sensor
Color flaw detection of welds: features and description

The article is devoted to color flaw detection of welds. The features of the procedure, its description, technological stages, etc. are considered