2026 Author: Howard Calhoun | calhoun@techconfronts.com. Last modified: 2025-01-24 13:10:37
Saratovskaya HPP is one of the ten largest non-nuclear power plants in Russia and Europe. It is an integral part of the Volga-Kama cascade of hydroelectric power stations. 24 hydroelectric units installed at the station make it possible to generate up to 6 billion kWh annually. The average annual rate over the past decade was 5.4 billion kWh.

Green Energy
Russian hydroelectric power plants play an important role in the uninterrupted supply of electricity to domestic and foreign consumers. The vast territory of the country, through which the largest rivers of Europe and the world flow, conceals the unlimited potential of "green" energy based on renewable sources - water, wind, sun, geothermal energy, tidal wave power and others.
There are 102 hydroelectric power plants with a capacity of more than 100 MW in the Russian Federation. The Saratov HPP (1378 MW) occupies the 9th place in the list of giants, taking into account those being completed. At the beginning of 2015, the installed total electric capacity of all plants amounted to 47,712.39 MW - andthis is over 20% of all energy generated in Russia.
It is important that HPPs are the most mobile systems. This type of power plant allows you to increase or decrease energy production within minutes, which is incredibly important for solving the problem of peak loads in the global power grid. For comparison, it takes several hours to increase the efficiency of a CHP plant, while for a nuclear power plant this figure is even several days. No wonder the construction of hydroelectric power plants continues.
Description of the Saratov HPP
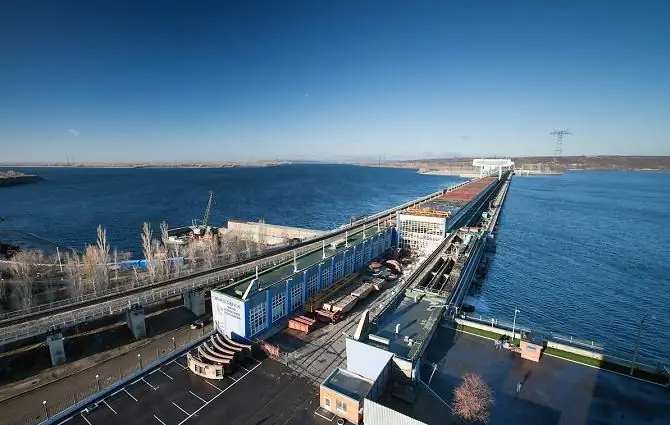
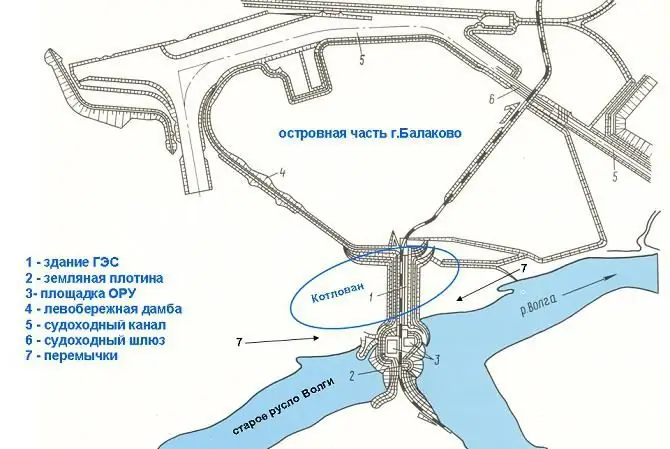
The hydroelectric power plant is the seventh in the Volga-Kama cascade and is located in the city of Balakovo, in the north of the Saratov region. 24 hydroelectric units with a capacity of 1378 MW allowed in 2014 to provide the country with 5504.6 kWh of electricity (useful supply). The spillway area is 1,280,000 km² with an average annual water discharge of 7959 m³/s.
The facility has become an important transport hub of the region - a road and a railway run along its dam, linking both banks of the mighty Volga. Also, related functions of the HPP include ensuring uninterrupted large-tonnage navigation, irrigation, and water supply.

History
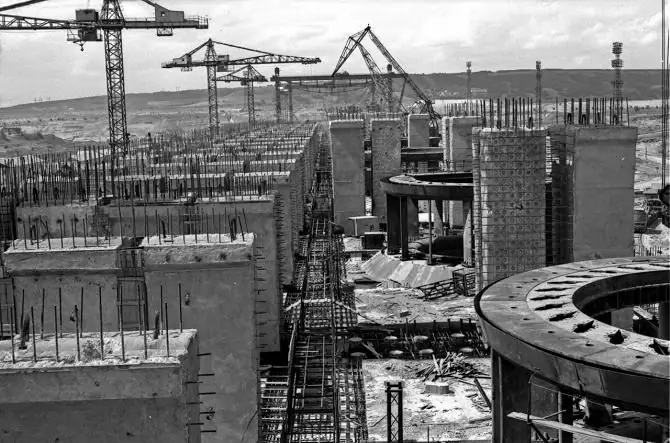
The city-forming enterprise "Saratovskaya HPP", whose photo impresses with the grandiose size of the structures, began construction on June 5, 1956 - this is the official date for the start of the All-Union Komsomol construction in the city of Balakovo. A few years later, the provincial town received a second birth, turning into a major industrial center of the country. More than 20,000 people from all regions took part inconstruction of a unique structure, many of the builders linked their fate with Balakovo.
The hydroelectric power plant has actually become a platform for experiments, the embodiment of the latest achievements and original ideas in the field of building large hydroelectric power plants, and it is not without reason that some of the characteristics of the structure are unique. On December 27, 1967, the first two hydroelectric units were launched, and in January 1968, the Saratovskaya HPP was connected to the country's general energy system. The station reached its design capacity at the end of 1970, since then it has been continuously supplying consumers with clean energy.
Saratovskaya is an integral part of the interconnected hydro complex of the European part of the Russian Federation. Other large hydroelectric power plants on the Volga and Kama: Rybinskaya, Nizhny Novgorod, Cheboksary, Kamskaya, Votkinskaya, Nizhnekamskaya, Zhigulevskaya, Volzhskaya and others.

Interesting facts
- Since its launch, the plant has generated over 250 billion kWh of electricity.
- Saratovskaya is one of the largest HPPs, photos of which can be seen in the media, encyclopedias, scientific papers, and Internet resources.
- The structure has a non-standard layout - the absence of a catchment platinum.
- The engine room is the longest in Russia, and is equipped with a collapsible roof.
- 24 units are available in 3 different sizes - some of which are the largest in Russia.
- HPP facilities are assigned the 1st class of capitalization, they include: embankment dams, earthen dam, main building,gateway, fish receiver, switchgears for 35, 220 and 500 kV.
- The dam has a length of 1260 m, the maximum height is 42 m, 6.6 million m³ of soil has been reclaimed for the dam. It consists of the main (360 m wide) and station sections.
- The total length of the dams of this large hydroelectric power plant in Russia is over 13 km. Height at the highest point - 23 m.
- The main body of the channel type - that is, it takes on the pressure of water, is located in the heart of the dam.
- The turbine hall of the HPP is the longest in the Russian Federation - 990 m. The diameter of the turbine wheel is also a record - 10.3 m.
JSC RusHydro
Saratovskaya HPP in January 2008 became part of the JSC RusHydro group - in Russia it is the largest generating company, and the second in the world among HPPs in terms of installed capacity (over 25 GW). At this stage, RusHydro has united 64 operating and 7 CHPPs under construction, 23 operating and 7 HPPs under construction, 3 GeoPPs, one tidal power plant, research centers, sales companies and design organizations. Among all this diversity, Saratovskaya is one of the ten largest suppliers of electricity among all types of stations. The association occupies a leading position in the "green" (renewable) energy.
The largest investment project
The construction of hydroelectric power plants continues, but we must not forget about the improvement of the old ones, as evidenced by the tragic accident at the Sayano-Shushenskaya hydroelectric power station. Taking into account the sad experience, the management company RusHydro is carrying out a phased renewal of worn-out equipment.
BAt present (and until 2030), the Saratov HPP is undergoing a phased modernization with the installation of the most advanced equipment. In particular, RusHydro agreed with the Austrian company Voith Hydro to replace 21 hydro turbines and hydro unit No. 24 with the commissioning of facilities by the end of 2025 on a turnkey basis. The current investment project, whose cost will exceed 1 billion euros, has become unprecedented for the Saratovskaya HPP and the largest for the region. It is planned that the turbines will be produced by the Russian-Austrian joint venture.
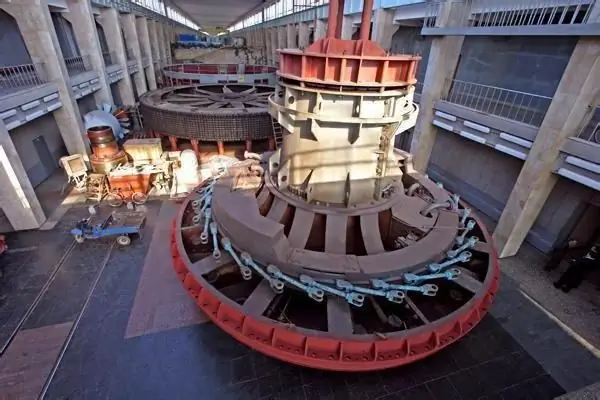

Turbine modernization
Reconstruction of the HPP involves the installation of water turbines of a fundamentally new generation. The preliminary developed project provides for a fundamental change in the design of the impeller, which will be equipped with S-type blades and a servomotor located below. This system, patented by Voith Hydro, makes the turbine fish friendly. The design is designed to reduce many times the injury and mortality of fish passing through the turbines, which is a serious problem for the entire Volga-Kama HPP cascade. It will also improve environmental safety by preventing turbine oil from entering the water.
Modernization of power units
At the Saratov HPP by the end of 2013, power engineers replaced all five power units. The reconstructed and put into operation equipment is more modern, reliable, safe and economical. Power units can do without overhaul for more than 30 years.
Together with the upgraded power units, hydroelectric units No. 13 and No. 14 were put into operation - the last of the verticalunits of the station, on which a modern automatic control system (ACS) is installed. Thus, the final stage of the five-year project for the reconstruction of the ACS of all vertical hydraulic units has been completed.
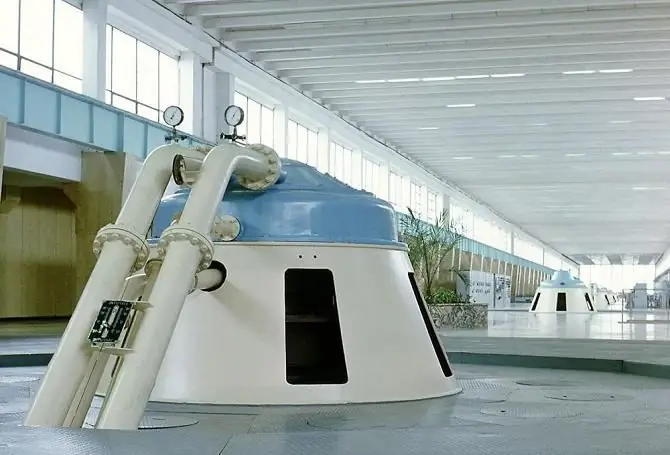

Cost and efficiency
Comprehensive modernization program involves updating the hydropower plant, taking into account the feasibility, cost-effectiveness and using the latest technological developments. It is necessary to ensure minimum downtime and reduction in hydropower generation, the shortest possible time for the implementation of reconstruction projects.
When implementing the comprehensive modernization program, a comprehensive approach is planned with the participation of the customer, representatives of research institutes and equipment manufacturers. For the first time, before the implementation of the program, a pre-project survey of the entire technological complex of the HPP is carried out, followed by the development of a project for its comprehensive modernization with the participation of the general designer of the Saratov HPP. This provides for "lifelong" service maintenance of replaced units by manufacturers.
Charity
Millions of funds are allocated annually to finance charitable programs. In particular, it provides sponsorship to the ROSTO Youth and Youth School in Balakovo, where children go in for scuba diving and orienteering, Children's Hospital No. 1, and other organizations. As part of educational projects, the HPP helped equip the laboratories of the Balakovo Polytechnic School. Traditionally, financial assistance is provided to veterans ineve of Victory Day.

Conclusions
Probably, there are no more ambitious projects than a hydroelectric power station. The photo of these concrete giants is amazing in size, and the units and technologies used reflect the latest achievements of industrial potential and scientific thought.
Hydropower plays a leading role in providing the population and industry with electricity. The accumulated experience in the construction and operation of hydroelectric power plants, the huge potential of Russian rivers, relative environmental safety and the use of renewable energy sources make it possible to increase capacity through the construction of new stations and the modernization of those already in operation. The Saratov HPP, which has been operating without failures for decades, is a vivid confirmation of this.
Recommended:
Volga-Ural oil and gas province: characteristics, deposits and strategic importance

The Volga-Ural oil and gas province is extremely important for Russia. Geographically, this is a rather large zone, which stretches from the great Volga to the Ural Range. It includes Bashkortostan and covers Tatarstan. VUNGP includes Udmurtia and several regions - near Volgograd, Saratov, Samara, Astrakhan, Perm. VUNGP covers the southern zones of the region near Orenburg
HPP is Shushenskaya HPP

HPP is an object erected on a river in order to convert the energy of its flow into electrical energy. One of the main structures of hydroelectric power plants in most cases is a dam that blocks the channel
Analysis of the real estate market in Russia on the example of the Volga region

Buy or rent real estate in the regions, of course, cheaper than in the capital. The cost differs significantly. But it also varies across regions. In order to understand how the price is formed, it is necessary to analyze the real estate market
HPP Ust-Ilimskaya: photo, address. Construction of the Ust-Ilimskaya HPP

In the Irkutsk region, on the Angara River, there is one of the few hydroelectric power plants in the country that has paid for itself even before construction was completed. This is the Ust-Ilimskaya HPP, the third stage in the cascade of stations on the Angara
LCD "Volga Park" (Yaroslavl): description, features

This time we will evaluate the residential complex "Volga Park" (Yaroslavl). Our task is to give the most objective assessment of the complex and the conditions that it can offer to potential residents

