2026 Author: Howard Calhoun | calhoun@techconfronts.com. Last modified: 2025-01-24 13:10:43
Bank corporate cards, as you know, are versatile. That is why calculations with them are widely used today. Corporate cards are convenient to use on business trips of employees both within the country and abroad, when paying for representative services, receiving cash at points of issue and ATMs. In the article, we will consider how corporate cards are taken into account in accounting.

General rules
To obtain a corporate card, a company signs an agreement with a banking structure. This opens a special bank account. The amounts that are formed on it are taken into account according to the account. 55.
To reflect the funds on the corporate card of the enterprise, a special subaccount to account 55 is used in accounting.
Analytics features
The construction of analytical accounting is carried out depending on the conditions for using the cards.
In some cases, the agreement with the bank provides for the presence of an insurance deposit on the company's account. It represents the minimum amount permanently in the account. It is also called the irreducible balance. This amount may be spent in exceptional cases. The deposit, in particular, is used in case of exceeding the payment limit.
In the accounting of corporate cards of legal entities, it is advisable to open sub-accounts of the 2nd order to the account. 55. These can be sub-accounts. "Payment limit" and "Insurance deposit".
The specified sub-accounts in the accounting of corporate cards of legal entities are opened without fail if several cards are linked to a single company account, using which any holder can make payment transactions within the specified limit. When crediting funds, the client submits to the bank a statement with the data of holders and card numbers, the amounts that must be transferred to each of them.
Reflection of enrollment
When replenishing the current account of a corporate card, an entry is made in accounting:
db ch. 55 subaccounts "Special account" Kd sc. 57 "Settlement accounts" (52 "Currency accounts")
For foreign currency on a special account, a revaluation should be carried out on the date of the transaction and the day of reporting. The resulting exchange rate differences in the accounting of corporate cards are reflected as follows:
- db ch. 55 subaccounts "Special account" Kd 91 subaccount. "Other income" (in the amount of positivedifference);
- db ch. 91, subch. "Other expenses" Kd c. 55 subaccounts "Special accounts" (by the amount of negative differences).

Transfers are on the way
When the bank receives primary documentation confirming the performance of transactions with a corporate card, an entry is made on the current account in accounting:
db ch. 10 (20, 25, 26, etc.) Cd count. 57 "Transfers are on the way".
The use of account 57 is due to the fact that the primary documents (receipts, slips, etc.) are received and processed by the accounting department before the formation of a card account statement confirming the debiting of funds.
A special sub-account should be opened for this account. It will reflect payments on a corporate card.
In accounting, operational control of the balance of funds can be carried out by subtracting the amount on the subaccount. "Operations on card accounts" (to account 57) from the balance of the sub-account "Special account" (to account 55).
Reflection of operations
It is carried out after receiving a bank statement, which confirms the actual write-off. In accounting, operations on corporate cards are reflected as follows:
db ch. 57 subaccounts "Operations on special accounts" Cd sc. 55 subaccounts "Special Account"
The list of operations allowed for implementation indicates that the holder has the right not only to make payments with the card, but also to use it to receive cash.

Cash withdrawal from a corporate card in accounting is executed on the basis of supporting documents. They are issued at the point of issue or at an ATM. The wiring will be like this:
db ch. 71 cd sc. 57 subaccounts "Operations on special accounts" (for the amount of funds received)
The use of cash is recorded according to the general rules in accordance with the primary documentation attached to the employee's expense report.
Important moment
In addition to the above model of workflow and accounting for corporate cards, in practice a situation may arise when an employee has not provided primary or other documentation confirming transactions during the reporting period. In this case, the bank statement may reflect the write-off of funds.
In such situations, you need to proceed from the following. Each card is assigned to a specific person - the holder. According to the procedure for generating reports on the movement of funds on special accounts, they must indicate the number of the card from which the debit was made. In such a situation, the importance of a competent organization of analytics on account 55.
Debiting from corporate bank cards in accounting is carried out on the basis of an extract not confirmed by documents, and is reflected as follows:
db ch. 73 cd c. 55 subaccounts "Special Account"
If the cardholder does not provide primary documentation or the costs incurred by him are not recognized as economically justified, he must returnspent funds according to the established rules. Reflection of the return is carried out on a credit account. 73 in correspondence with the accounting items of the enterprise's funds (for example, accounts 50, 51).

Accounting transactions in foreign currency
The specifics of accounting for corporate bank cards with foreign currency is determined by the conditions of its write-off and conversion, provided by the financial institution. In addition, the appearance of the card itself has a meaning.
According to the general rules, after returning from abroad, a seconded employee draws up an advance report, which he submits to the accounting department. He attaches the original documentation to it. It includes, among other things, papers drawn up during card payments.
All expenses made in foreign currency must be converted into rubles on the day the report is approved. In this case, entries are made:
- db ch. 08 (26, 44) Cd count. 71 (for the amount of the ruble equivalent of expenses at the exchange rate of the Central Bank);
- db ch. 71 cd sc. 57 subaccounts "Operations on special accounts" (for the amount of expenses paid by the card, in rubles at the exchange rate of the Central Bank).
Further entries depend on which corporate card (currency or ruble) was used. In accounting for foreign exchange transactions, the debt on the account. 57 is subject to revaluation and the date of their commission. When receiving a bank statement, an entry is made:
db ch. 57 subaccounts "Operations on special accounts" Cd sc. 55 subaccounts "Special bank account" - ruble equivalent at the exchange rateCentral Bank on the day of debiting funds
At the same time, according to the account. 57 determine the exchange rate difference. It is credited or debited. 91 (depending on the nature of the course correction).

When using a ruble corporate card in accounting, the entry will be made for the amount in rubles indicated in the statement. Usually its value differs from that reflected in the account. 57 subaccounts "Operations on special cards" on the day the report was approved. This is due to the fact that financial structures use an internal rate that does not coincide with the Central Bank rate when revaluing foreign exchange transactions.
The resulting difference is considered as a sum. Since the amount of payment made in rubles in the amount corresponding to the amount in foreign currency is adjusted for differences, they are reflected in the same account as the main amount of travel expenses. It could be c. 08, 44, 26 etc.
Fees
They are charged for servicing corporate cards. In accounting, commissions are included in other expenses and are reflected in the corresponding sub-account of the account. 91.
The amount and procedure for writing off remuneration are set in accordance with the tariffs of the banking organization. They are specified in the annex to the account service agreement.
Interest on balance
If the card account service agreement provides for their accrual, they are included in other income. In this case, the wiring is compiled:
db ch. 55 subaccounts "Special Account"Kd sc. 91 subaccounts "Other income"
Nuances
The above procedure for recording transactions applies mainly to enterprises that own card accounts and carry out settlements with commercial partners from them.
At the same time, the company can accept payment from cards of individuals and organizations. Issuers (card issuers) enter into agreements with merchants to sell products to cardholders.
The agreement fixes the rules for providing the point with technical devices, authorization of the operation, the terms of settlements with buyers, the amount of the commission of the servicing bank. The latter, as a rule, is withheld from the proceeds received from the sale of goods and credited to the account of the trade enterprise.
Collection of slips
Slip is a terminal check. The procedure and frequency of their collection is determined in the terms of the agreement signed with the acquiring bank (a credit company that organizes card acceptance points and provides services for servicing the entire range of operations in them). At the same time, a register of slips is mandatory. It indicates the number of checks and the total amount.
The register should be completed in two copies. One, together with the slips, is given to the collector, the second remains in the trading enterprise. In the latter case, the collector also gives a receipt.
As a basis for reflecting the amounts on the account. 57 is the second copy of the document. Prior to the transfer of slips to the collector, the enterprise does notcan treat amounts as "transfers in transit". Accordingly, account 57 is not reflected.
Before the slips are transferred to the bank (as long as they are at the cash desk of the trade enterprise), the funds for the goods sold are not debited from the accounts and are not credited to the account. Accordingly, it is believed that the buyers have formed receivables.
When the proceeds from the sale are credited to the account, a transaction is created:
db ch. 51 cd sc. 57
Accounting for corporate cards in C1
Reflection of operations is not currently accompanied by any difficulties. I must say that earlier the accounting of corporate cards in C1 7 7, for example, was done almost manually.
The software product 1C "Accounting" is constantly being improved. The first significant changes were noted by users of the C1 8 2 version of the program. Accounting for corporate cards in the newest application has become even easier. Consider some of the nuances of reflecting operations.
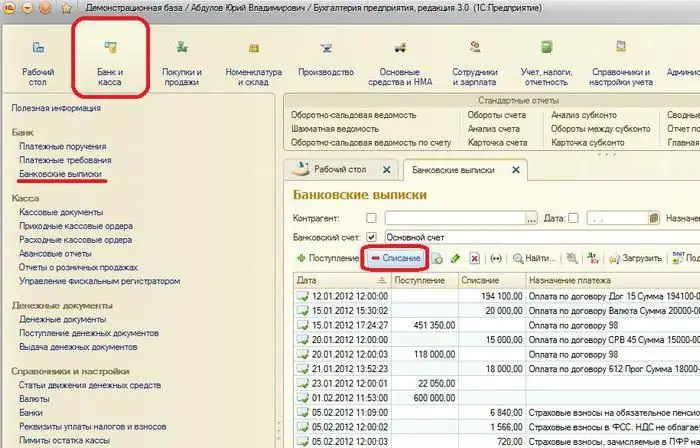
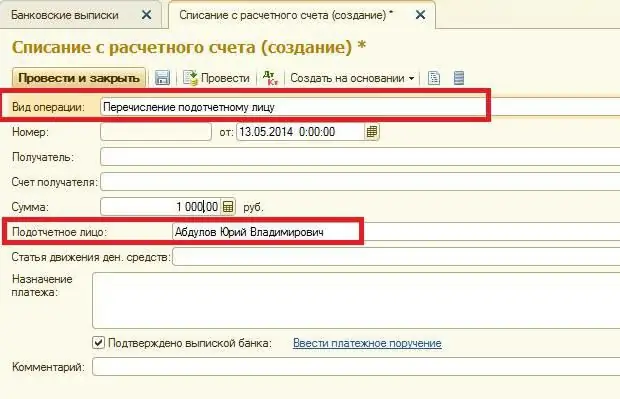
The operation of replenishing corporate cards in accounting in C1 8 3 is reflected using the document "Write-off from account". To open it, go to the "Bank and cash desk" section, then to "Bank statements" and click on the "Debit" button.
In the form of the document, the type of operation "Transfer to another account" is indicated. To select the beneficiary's account, open the "Bank accounts" directory. The debit item will be sc. 55.04.
In version 1C 8.2write-offs were made in the same way. At the same time, a separate document was not drawn up for the receipt of funds for the transfer from the settlement account - it was taken into account as the turnover of the movement of amounts.
Withdrawing cash from an ATM
When cashing funds, the employee actually accepts them under the report. Accordingly, he is obliged to provide documents confirming the expenses.
Suppose an employee cashed out a certain amount from the card and paid for the purchase of inventory items.
Withdrawal in 1C is reflected using the document "Write-offs from account". It is necessary to put down the type of operation: "transfer to an accountable employee", account 55.04. The bank account is the one to which the card is linked. The document also indicates information about its holder, i.e., about the accountable person.
When the operation is reflected, a record will be made:
db ch. 71.01 Cd count. 55.04
Withholding bank commission when withdrawing funds
This operation is reflected using the document "Write-off from account". Its type is "other write-off", accounting account - 55.04. The bank account is the account to which the card is attached.
The details indicate the account. 91.02. This is the debit account to which the commission is transferred. In the directory "Other expenses / income" you should select an item that includes the costs of paying for bank services. After that, a record will be generated:
db ch. 91.02 cd c. 55.04.
Expense confirmation operation
In 1C, expenses are reflected using the document "Advancereport".
When filling it out in the "Advances" tab, select "Debit from account".
In the "Goods" tab, fill in the data on the purchased inventory items, their invoice and VAT.
Recommended:
Accounting documents are The concept, rules for registration and storage of accounting documents. 402-FZ "On Accounting". Article 9. Primary accounting documents

Proper execution of accounting documentation is very important for the process of generating accounting information and determining tax liabilities. Therefore, it is necessary to treat documents with special care. Specialists of accounting services, representatives of small businesses who keep independent records should know the main requirements for the creation, design, movement, storage of papers
Corporate client. Sberbank for corporate clients. MTS for corporate clients

Each attracted large corporate client is considered an achievement for banks, insurance companies, telecom operators. For him, they offer preferential terms, special programs, bonuses for constant service, trying to attract and subsequently keep him with all his might
Accounting for working hours in the summary accounting. Summarized accounting of the working time of drivers with a shift schedule. Overtime hours with summarized accounting of wor

The Labor Code provides for work with a summarized accounting of working hours. In practice, not all enterprises use this assumption. As a rule, this is due to certain difficulties in the calculation
Corporate card report: example. Accounting for a corporate bank card
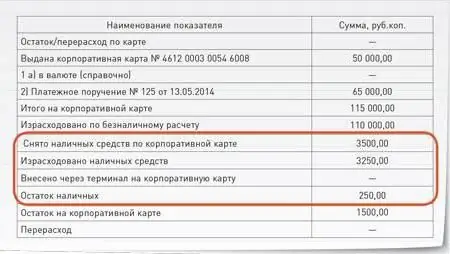
Accounting for corporate cards is quite simple. Experienced accountants, as a rule, do not have any problems recording transactions. Difficulties may arise when compiling a report on a corporate card by an employee to whom it was issued
Accounting and tax accounting at a manufacturing enterprise: definition, maintenance procedure. Normative accounting documents

In accordance with PBU 18/02, since 2003, the accounting should reflect the amounts arising from the discrepancy between accounting and tax accounting. At manufacturing enterprises, this requirement is quite difficult to fulfill. The problems are related to the difference in the rules for valuation of finished goods and WIP (work in progress)

