2026 Author: Howard Calhoun | calhoun@techconfronts.com. Last modified: 2025-01-24 13:10:47
The location of production facilities in new territories in the conditions of high demand for products in most cases turns out to be beneficial for modern enterprises. This increases the competitiveness of goods and allows you to optimize the logistics costs associated primarily with the organization of transport networks. Thus, the localization of production is carried out - this is the consolidation of the company's capacities in the territory of another state.
The concept of localization

In the field of manufacturing activity, localization should be understood as the transfer or expansion of an enterprise in the territory of another country. A key determining factor will be adaptation to the characteristics of the region in which the organization of the business is planned. In this context, we can say that the localization of production is a list of technological andorganizational measures, thanks to which the enterprise is built into specific economic, political and social conditions of work. Moreover, the degree of adaptation may be different depending on specific conditions and opportunities. For example, components for the assembly of industrial equipment may be supplied from the country where the production is located. That is, a partial process of manufacturing products of an incomplete cycle is organized.
Participants in the localization process
One should distinguish between the host company and its partners (often represented by the federal government of the host country). In the first case, we are talking about the so-called extender, and in the second - about the recipient. From the point of view of the extender, the localization of production is the expansion of positions in the world market by simplifying the processes of marketing products. Again, this is achieved due to the territorial approximation of the place of manufacture of products to the consumer and the reduction of transportation costs. Costs are reduced by an average of 25%. In turn, the recipient sees localization as an increase in the level of employment and an increase in investment attractiveness with an increase in tax revenues.
The most promising areas of localization

Theoretically, localization methods can be applied to any industry. The success of the project will depend on local conditions for conducting a particular activity, resources and other factors of the organization of the enterprise. In practice, the most active expansion of production can beattributed to the automotive, pharmaceutical, food and IT industries. As a rule, the more technologically advanced a company is and the higher the demand for its products in developed countries, the more successfully amenable to cross-border relocation of its capacity. Thus, among specific examples of the global localization of car production, one can note the expansion of the Volkswagen, Ford, Hyundai brands and a number of Chinese budget firms, which, thanks to cheap components, are flexible in adapting. The situation is more complicated in the chemical and metallurgical industries, since they are largely dependent on raw materials, which must be supplied in large volumes, passing through several stages of processing.
Development of an enterprise localization project
During the design phase, a full-fledged business model is created, and a plan is prepared to implement the cross-border relocation of the enterprise. Among the key organizational aspects that should be disclosed in the project, the following can be distinguished:
- What will be the procedure for finding and registering land as the property of the company.
- Construction and equipment of the production facility.
- Legal registration of activities.
- Creating a management system.
- Calculation of opportunities for local expansion of production capacities on the resources of the created infrastructure.
At the next stage of development of the production localization project, logistics tasks, issues of distribution and marketing of products are calculated. The business model should estimate the average annual production capacity, andalso reserve capacity. For more accurate calculations, statistical results of research centers are used that provide information on the investment climate, consumer activity, the economic situation in the local market, etc.

Criteria for localization of production
At the design stage, sufficient conditions are also calculated for the organization of production activities in a particular area. The following criteria are used to evaluate conditions:
- Sufficient technological capacity to process materials required by production.
- Availability of technical capabilities to organize production processes.
- Satisfiability of the ad valorem share rule. In essence, it means the potential profitability of the new site relative to the capacity of the expander company.
- Opportunities to increase capacity and complexity of production, also involving the abandonment of simple technological operations. For example, when localizing automotive production, a smooth transition from manual assembly of certain parts to automated layout is possible. The most advanced assembly lines of this type implement a complete cycle using robotic technology.
Also, at each stage, there are requirements for quality control of products on the way from raw materials to the final product. Designers should evaluate how quality control is possible in principle in accordance with the requirements of the extender.
Planmeasures to localize production
After the design decision is approved, a roadmap or a program for its direct implementation is drawn up. The plan is based on a priority scale with the parameters necessary for the localization of a particular production. A typical localization scenario can be represented as follows:
- Assessing the market potential of the target product.
- Modeling the production organization strategy.
- Preparing a financial plan for the most promising localization option.
- Equipment of the production site.
- Training staff.
- Organization of assembly production.
- Preparation of technical documentation.
- Product certification.
- Production optimization.
Each industry may have its own specifics of this process. For example, the localization of the production of industrial equipment largely depends on the components. In this case, you will need a separate prioritization program for each of the categories of elements in the assembly. So, it would be advisable to supply components with one set of properties from the extender, and with other characteristics - to be completely manufactured at our own facilities.

Degrees of localization
As well as the manufacturing process of a particular product, so the localization as a whole may be incomplete. For example, it is often implemented at 50% or 70%, that is, partially. The degree of localization of production is understood ascompleteness of the working cycle provided by the enterprise, and its independence from raw materials and technological support of the extender. An assessment of the independence of the enterprise and the completeness of its production cycle is given according to special calculation systems, which are also included in the design decisions on an individual basis. For example, there may be a points system in which a certain number of points are awarded for each item of a product. As a result, they are summed up and compared with a 100% production site of the extender.
Localization levels
This refers to a broader representation of localization based on common coefficients that are used in the global market. This makes it possible to compare the characteristics of localized extender enterprises not only among themselves, but also in a natural competitive environment. Criteria such as science intensity and technological development can be used. That is, the level of localization of production is a complex of aspects of the enterprise's activities that allow the production of products of one quality or another. Moreover, the level can also be expressed in quantitative and percentage terms, if the appropriate methodology is used, which can also be different depending on the specifics of the market.
Coefficients of localization levels

The main coefficients that give an idea of the levels of localization of various industries include the following:
- Product cost factor.
- Coefficientintellectual component of the enterprise. For example, the same localization of automotive production can be assessed by the degree of robotization and this will be an indicator of the intellectual component. Factories with 50-meter assembly lines serving only 10 people are considered high-tech.
- Coefficient of expenses and depreciation costs.
- Coefficient in which the availability of service points and customer service centers is calculated.
Modern localization issues
The main difficulties of localization processes in the industrial sector are due to the tightening of regulatory requirements for production. These include a high level of technological development, autonomy, flexibility in equipment placement, and logistics efficiency. Not every country or regional sites can fully provide the required level of such conditions. In addition, the localization of production means strict adherence to schedules for the delivery of raw materials with components, which, even if the requirements are met, is not always justified from a financial point of view. To this should be added the duties of the extender to the recipient, which may vary, but in any case, the partner of the expanding company should have its own benefit from providing the site.

Features of localization in Russia
Domestic industry is no exception in the global investment market, but has its own distinctive features. On the one hand, experts note the lag instrategies for applying localization in Russia, which is caused by flaws in the business climate and management in general. But, at the same time, the conservative approach to the distribution of financial resources and targeted support of the regions by the federal government are bearing fruit. Thus, the localization of car production in Russia is actively developing, which is especially evident in the Ulyanovsk, Kaluga and Leningrad regions. State support, coupled with preferential car loans, opened up wide opportunities for Italian manufacturers to deploy their capacities. Not so long ago, the Dutch auto giant DAF, as well as the Chinese corporation Dalian, placed their production.
Localization preferences
States provide new investors and extenders with a number of preferences that guarantee at least stable conditions for doing business. Among the most effective and widespread benefits of this type are:
- Decrease in premium rates.
- Relief of the tax burden (at least for the period of formation of the enterprise).
- Technical support in the modernization process.
- Stability of economic conditions at the time of the contract.
- Creating special conditions for customs policy for certain industries in the development of which the business entity is especially interested.
Conclusion

The concept of localization of large enterprises gives positive effects to both participants in the process andthe economic system as a whole. It should be noted that as technology develops, the methods of cross-border relocation of production become less and less costly. The range of tools is also expanding to more accurately manage the localization of production. Plans and strategies for the implementation of these processes are also becoming more complex, requiring ever deeper calculations involving huge arrays of primary information. The experience of many countries shows that the policy of the host state is still a key factor in successful localization. It can influence both a favorable economic environment for specific projects and the predictability of the investment climate, which is important for the future development of an enterprise.
Recommended:
Horizontal division of labor is The levels of management in the organization, the concept of goals and objectives

For the efficiency of the enterprise, horizontal and vertical division of labor is used in management. It provides for the detailing of the production process and the distribution of powers between managers of different levels. In order to improve the performance of the company, it is necessary to know the principles of the division of labor, as well as correctly determine the goals and objectives of the organization
Production and production systems: concept, patterns and their types
Production systems are structures that involve people and equipment working together. They perform their functions in a certain space, conditions, working environment in accordance with the tasks
Support and resistance level. How to trade support and resistance levels correctly?
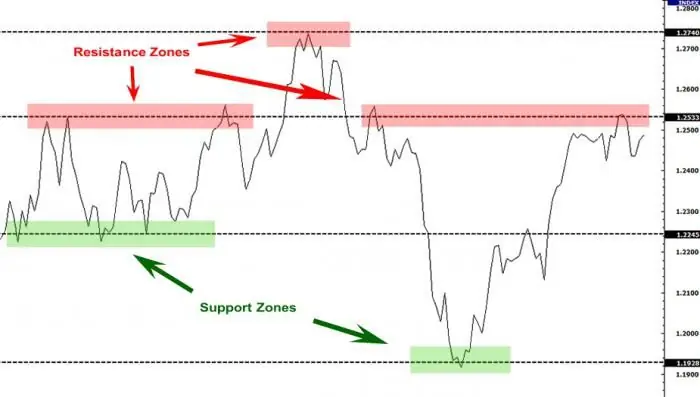
Support and resistance levels are the dominant concepts of the technical analysis of the foreign exchange market. Based on them, a large number of trading strategies have been developed, despite the fact that the lines belong to the category of inaccurate instruments
Inline production is Concept, definition, methods of organization and technological process

The production process is a complex technological action that can be organized in different ways and means. The work of an enterprise in the conditions of in-line production of products is today considered the most efficient, but at the same time demanding in terms of labor, organizational and material costs. In a general sense, in-line production is a format of production activity in which the principles of rhythm and repeatability of operations come to the fore
What does the dollar look like (photo). Degrees of dollar protection

The US dollar is the most widely used currency in the world. More than 60% of America's money supply is used outside the country. This makes it necessary for the government to provide a decent degree of protection for the dollar

