2026 Author: Howard Calhoun | calhoun@techconfronts.com. Last modified: 2025-01-24 13:10:47
In order to turn an ordinary blank into a suitable part for a mechanism, turning, milling, grinding and other machines are used. If milling is necessary for the manufacture of more complex parts, for example, gears, cutting splines, then turning is used to create simpler parts and give them the necessary shape (cone, cylinder, sphere). The cutting conditions in turning are very important, because, for example, for brittle metal it is necessary to use a lower spindle speed than for strong metal.
Features of turning
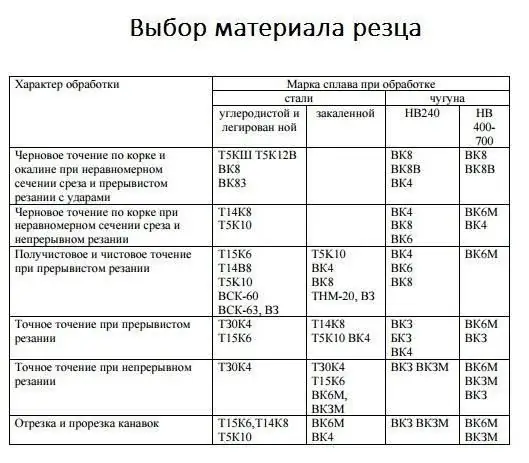
In order to turn a certain part on a lathe, as a rule, cutters are used. They come in a wide variety of modifications and are classified according to the type of processing, feed direction and head shape. In addition, the cutters are made of various materials: alloy steel, carbon steel, tool steel, high-speed cutting, tungsten,carbide.

The choice of one or the other depends on the material of the workpiece, its shape and the method of turning. Cutting conditions for turning necessarily take into account all these nuances. When turning, the workpiece is fixed in the spindle, it performs the main rotational movements. The tool for processing is installed in the caliper, and the feed movements are made directly by it. Depending on the machine used, both very small parts and large parts can be machined.
Basic elements
What elements of cutting data can be used in turning? Although turning is not always a very easy operation, its main elements are speed, feed, depth, width and thickness. All these indicators depend primarily on the material of the workpiece and the size. For very small parts, for example, choose the lowest cutting speed, because even 0.05 millimeters that are accidentally cut off can lead to rejection of the entire part.

In addition, very important indicators on which the choice of cutting conditions during turning depends are the stages at which it is performed. Consider the main elements and stages of metal cutting in more detail.
Roughing, semi-finishing and finishing
Turning a workpiece into a necessary part is a complex and time-consuming process. It is divided into certain stages: roughing, semi-finishing and finishing. If the part is simple, then the intermediate (semi-finishing) stage, as a rule, is not taken into account. At the first stage (draft), the details are given the necessary shape and approximate dimensions. At the same time, allowances must be left for subsequent stages. For example, given a workpiece: D=70 mm and L=115 mm. It is necessary to machine a part from it, the first size of which will be D1 =65 mm, L1 =80 mm, and the second - D2 =40mm, L2=20mm.
Roughing will be as follows:
- Cut the end 14mm.
- Turn the diameter along the entire length by 66 mm
- Turn the second diameter D2=41 mm to a length of 20 mm.

At this stage, we see that the part was not completely processed, but as close as possible to its shape and size. And the allowance for the total length and for each of the diameters was 1 mm.
Finishing this part will be as follows:
- Perform a fine end cut with the required roughness.
- Turn 80mm length to 65mm diameter.
- Perform fine turning from a length of 20 mm to a diameter of 40 mm.
As we can see, finishing requires maximum precision, for this reason, the cutting speed will be lower in it.
Where to start the calculation
In order to calculate the cutting mode, you must first select the material of the cutter. It will depend on the material of the workpiece, the type and stage of processing. In addition, incisors in which the cutting part is removable are considered more practical. In other words, it is only necessary to select the material of the cutting edge and fix it in the cutting tool. The most profitable mode is the one in which the cost of the manufactured part will be the lowest. Accordingly, if you choose the wrong cutting tool, it is likely to break, and this will cause losses. So how do you determine the right tool and cutting conditions for turning? The table below will help you choose the best incisor.

Cut layer thickness
As mentioned earlier, each of the processing steps requires some degree of precision. These indicators are very important precisely when calculating the thickness of the cut layer. Cutting data for turning guarantees the selection of the most optimal values for turning parts. If they are neglected and the calculation is not performed, then both the cutting tool and the part itself can be broken.
So, first of all, you need to choose the thickness of the cut layer. When the cutter passes through the metal, it cuts off a certain part of it. The thickness or depth of cut (t) is the distance that the cutter will remove in one pass. It is important to consider that for each subsequent processing it is necessary to perform a calculation of the cutting mode. For example, you should perform external turning of a part D =33.5 mm for a diameter of D1=30.2 mm and internal boring of a hole d=3.2 mm on d2=2 mm.

For each of the operations, the calculation of cutting conditions during turning will be individual. In order to calculate the depth of cut, it is necessary to subtract the diameter of the workpiece from the diameter after processing and divide by two. In our example, it will turn out:
t=(33.5 - 30.2) / 2=1.65mm
If the difference between diameters is too big, for example 40 mm, then, as a rule, it must be divided by 2, and the resulting number will be the number of passes, and the depth will correspond to two millimeters. With rough turning, you can choose a cutting depth from 1 to 3 mm, and for finishing - from 0.5 to 1 mm. If cutting the end surface is performed, then the thickness of the material being removed will be the depth of cut.
Setting the feed amount
Calculation of cutting conditions during turning cannot be imagined without the amount of movement of the cutting tool in one revolution of the part - feed (S). Its choice depends on the required roughness and the degree of accuracy of the workpiece, if it is finishing. When roughing, it is permissible to use the maximum feed, based on the strength of the material and the rigidity of its installation. You can select the desired feed using the table below.

After S has been selected, it must be specified in the machine's passport.
Cutting speed
Cutting speed (v) and spindle speed (n) are very important values that affect the cutting conditions in turning. Tocalculate the first value using the formula:
V=(π x D x n) / 1000, where π is Pi equal to 3, 12;
D - maximum part diameter;
n is the spindle speed.

If the last value remains unchanged, then the rotation speed will be the greater, the larger the diameter of the workpiece. This formula is suitable if the spindle speed is known, otherwise you must use the formula:
v=(Cv x Kv)/ (Tm x t x S),
where t and S are already calculated depth of cut and feed, and Cv, Kv, T are coefficients depending on mechanical properties and structure of the material. Their values can be taken from the cutting data tables.
Cutting Data Calculator
Who can help you calculate cutting conditions when turning? Online programs on many Internet resources cope with this task no worse than a person.

It is possible to use utilities both on a desktop computer and on a phone. They are very comfortable and do not require special skills. You must enter the required values in the fields: feed, depth of cut, material of the workpiece and cutting tool, as well as all the necessary dimensions. This will allow you to get a comprehensive and fast calculation of all the necessary data.
Recommended:
Machines for laser cutting of fabric. Criterias of choice

Laser machine for cutting fabric. Possibilities of the laser machine. Principle of operation. What is the versatility of laser machines. Equipment selection criteria: desktop area, laser tube power, fabric autoload, drawing scheme, manufacturer and service
Cutting speed for milling, turning and other types of mechanical processing of parts

Calculation of cutting conditions is the most important step in the manufacture of any part. It is very important that the calculation itself be rational. This is due to the fact that for various mechanical operations it is necessary to individually select the cutting speed, spindle speed, feed rate, and also the depth of cut. A rational mode is one in which production costs will be minimal, and the quality of the resulting product will be as accurate as possible
Cutting mode for milling. Types of cutters, calculation of cutting speed

One of the ways to finish materials is milling. It is used for processing metal and non-metal workpieces. The workflow is controlled by cutting data
Laser engraving on plastic: types of plastic, choice of pattern, necessary laser equipment and patterning technology

What types of plastic are used when applying laser engraving. Designs suitable for engraving and their types. How to edit and prepare photos for laser engraving. Necessary equipment for work, principles of its operation
Metal cutting machine. Plasma metal cutting machine
The article is devoted to the apparatus for cutting metal. The technology of plasma cutting, as well as the device and features of the equipment are considered