2026 Author: Howard Calhoun | calhoun@techconfronts.com. Last modified: 2025-01-24 13:10:28
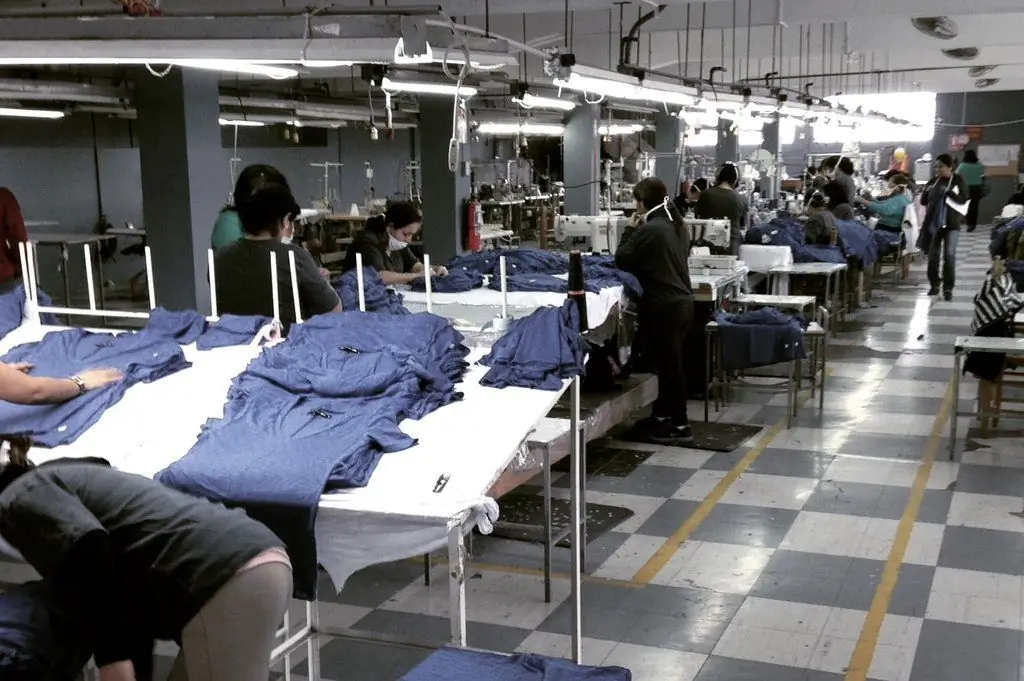
When thinking about what labor rationing is, many of us have associations of production, an uninterrupted workflow. This term is of great importance in economic planning. And although today one can often hear the opinion that labor rationing of workers is an echo of the Soviet system of production, most industrial enterprises are in no hurry to abandon the use of this tool.
Why set labor standards
It is impossible to imagine a modern management process without production costs, especially in the presence of such a component as payment for the work of employees. But what is the rationing of labor, what is meant by this concept? First of all, this is a mechanism for establishing the cost of working time for the implementation of a particular type of work in the production environment. The labor rate is a unit of measure that allows you to plan,analyze the total labor costs in organizational and technical conditions.
The urgent need for labor regulation arises during the crisis. The desire of entrepreneurs to reduce costs leads to the development of new, more efficient economic instruments. Labor cost regulation is one of them. All companies, industrial associations in the sectors of heavy and light industry, construction, transport, communications, wish not only to maintain their place in the niche of the domestic market, but also to achieve better results, which is impossible without using innovative approaches and increasing the level of competitiveness.
Management of labor rationing is an important element of production management, which is used by both domestic and foreign entrepreneurs. The experience gained in this segment extends not only to the production of material products, but also to the service sector. Economists find it expedient to work on labor rationing in budgetary institutions if the number of employees exceeds 50 people. In simple words, adherence to rational and efficient labor standards is necessary in any professional industry. It is quite risky to neglect them in the conditions of market economy instability.
What is the difference between norm and standard?
These two terms are often confused in non-professional environments. They are considered synonyms that have exactly the same meaning, but in fact, despite their apparent closeness, these concepts have different definitions. Standardis a scientifically sound, centrally developed measure of labor costs. At the same time, it can be implemented at the enterprise or serve as a kind of model for the organization to independently develop its own norm indicators. The use of standards can be repeated over a long period, and the norm is set only for one specific task and is replaced by another at the slightest organizational and technical adjustment.

The concept of normalization
Standards and norms are used everywhere, at any level, at any stage of the production process. What is labor regulation? This is a kind of way of rational distribution of labor resources and time costs. The norms are used in the process of main and auxiliary production. There is a certain sense in establishing labor standards for conveyor, manual (mixed), piece or large-scale, mass production. Moreover, recommendations are being developed on the rationing of the work of employees of the enterprise staff and management.
Setting labor standards and measures should be considered in a broad and narrow sense. First of all, it is an ordered set of special tools and methods that are intended to effectively determine the measure of labor. Its purpose is to obtain an objective assessment of the existing efficiency of the production process and the compliance of the applied labor costs with the amount of material reward.
In a broader senseto determine what labor rationing is, you can do this: this is an area of \u200b\u200bactivity of economic, engineering and social orientation. To implement labor process standards, such means are used as regulatory materials and the results of economic and theoretical studies using computer programs to calculate minimum, maximum and average values.
Classification of labor standards
This measure can be expressed by various indicators - volume, time, number of executive and serviced objects. In the applied labor rationing systems, great importance is given to the development of standards for the performance of one unit of product by one or a group of performers. As an example, let's take an assembly team that assembles one vacuum circuit breaker in 2 hours. In parallel with the time indicator, the reciprocal of labor rationing is taken into account - the production rate. In essence, this standard involves setting the amount of work, a kind of plan that workers need to complete in one shift. Since the assembly team assembles one circuit breaker in an average of two hours, they are faced with the task of assembling at least four of the same circuit breakers per shift.
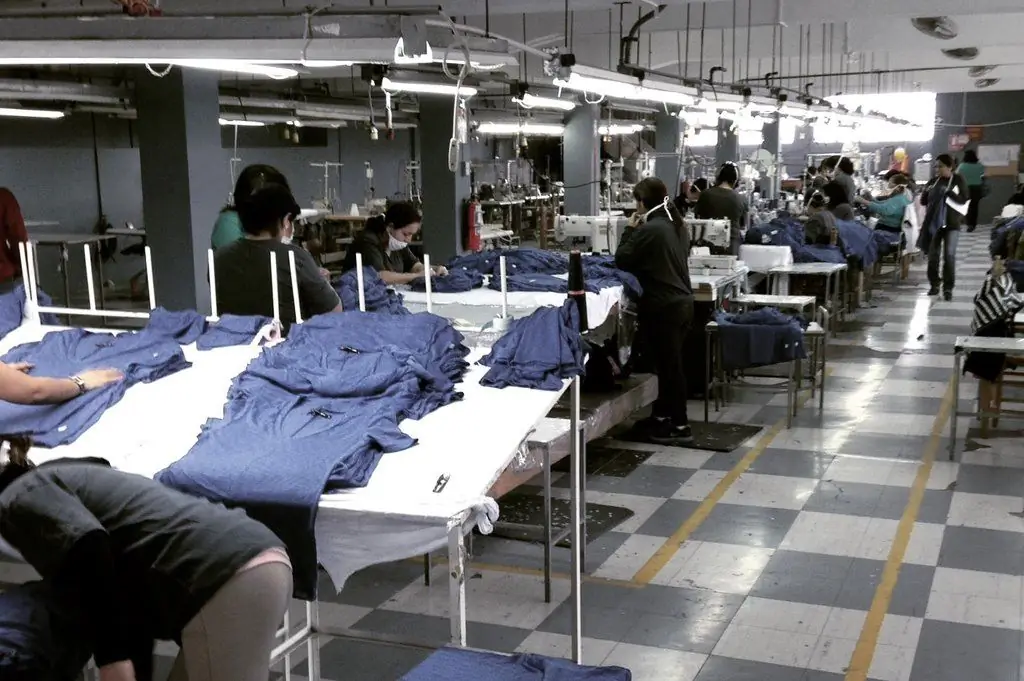

Another standard in labor rationing is the service rate. It is set for performers and determines how many objects they need to serve in a specific period of time. For example, an equipment adjuster needs to repair seven machines per shift. The reverse measure of the number allowscalculate how many workers need to be involved to perform a given amount of work or maintenance of a production facility per unit of time.
Labor rationing in budgetary organizations implies the existence of such a standard as a measure of manageability, reflecting the number of employees who can be under the direction of a director. The second name of this indicator is the norm of the number of subordinates. For example, a site foreman manages a workflow that can be limited to 35 people.
Under the norm of service time, a measure is assumed that approves the rational time spent on working with one object. We can talk not only about the maintenance of industrial equipment, but also about other service industries. For example, a specialist is given no more than 15 minutes to serve one visitor to a multifunctional center.
Calculation methods
Rationing of workers' labor is a separate scientific area of economics, which has its own tools and methodology. Conventionally, all methods for calculating the norms for completing work tasks can be divided into analytical and summary.
The second group includes techniques that do not provide for the need to differentiate production operations into several stages. Summary methods do not involve an analysis of the labor process, obtaining an assessment of the rationality of the resources used and labor costs. Such techniques make it possible to determine normalized indicators using statistical and operational information. And in this sense, it is of great importancehas the competence of a normalizer, so the so-called human factor plays an important role here.
Analytical calculation methods are more often used for labor rationing in budgetary institutions. They involve a deep analysis of the labor process, its differentiation into several stages of work performed by performers. At the same time, the specifics of job standards and instructions for the performance of professional duties are always taken into account. The category of analytical methods for calculating labor standards includes research, calculation and mathematical-statistical tools.

The research method involves conducting an analysis based on the information collected during the creation of chronometric production technologies and working time planning. Timing in the labor rationing system is a technique in which measures of multiple repetition of the same operational and technical elements are determined in machine or manual type of production. The task of timing is to establish the main and auxiliary time for the performance of individual operations for the implementation of the labor process. Timing is used as a direct tool for standardization in production and verification of the effectiveness of the applied standards by calculation or by choice.
Additionally, the method of momentary observations can be used, which allows you to estimate labor costs without measuring indicators directly related to them. This tool is based onProbability theory. There is no need for continuous recording of time, since the method allows you to cover several objects and areas of their activity at once.
Main Tasks
The main goal in labor rationing at a manufacturing or non-production enterprise, a budgetary institution is to provide satisfactory conditions for maximizing the efficiency of labor potential, increasing the competitiveness of products and occupying higher positions in the domestic or foreign market by reducing labor costs and introducing into the worker technology innovation process.
The primary task of labor rationing is to solve a number of problems:
- ensuring rational planning of labor costs and allocation of ready-to-use resources;
- establishing the optimal balance between the amount of equipment available and the number of employees who service it and perform production tasks;
- development of rules and regulations of labor activity within a particular enterprise.

The system of labor standards used in production is commonly understood as a set of strategic methods for organizing, coordinating and managing the work process. This complex also includes other important elements of rationing in production:
- selection of a methodological approach to setting standards for various activities and categories of hired personnel;
- algorithm for estimating normsaccording to quality criteria, as well as the use of an effective replacement procedure;
- maintaining relevant supporting documentation reflecting the tasks of labor rationing.
All of the above conditions are necessary for the effective rationalization of the resources used and the reduction of production costs. That is why managers are interested in improving the applicable labor standards on reasonable, progressive indicators, taking into account the characteristics of jobs and the intensity of labor activity.
Organizational and planning functions of labor standards
Each enterprise has its own provisions on labor rationing. How effective the system is, is evidenced by economic indicators, including sales growth, increased demand for products or services, increased competitiveness. Ideally, labor standards should cover the vast majority of production processes and categories of performers. It also matters how quickly and in a timely manner new normalized indicators are developed, reviewed and implemented.
The regulation on the system of labor rationing in production pursues the performance of two main functions - planning and organizational. The first is expressed by a set of necessary conditions, without which harmonious development and effective interaction of all divisions, departments, branches of the enterprise is impossible, taking into account consumer demand and supply in the market. The provision on labor rationing applied in a manufacturing company is the basic basisplanning processes for the main indicators of its core activities. Forecasts are used in all sectors of the economy to determine a long-term work plan. The value of effective planning today is difficult to overestimate. It is no coincidence that it is one of the requirements of the modern economy, because the introduction of the most advanced systems for evaluating indicators contributes to a stable increase in labor productivity and a more rational use of resources.

Rationing also performs an organizational function that allows you to establish progressive relationships between separate components of the production chain, to find effective use of unclaimed material and intangible resources of the enterprise. Thanks to labor standards, it is possible to form an overall system of production, consisting of capital, equipment and labor, and to support its efficiency and productivity in the future. Basically, labor rationing, or rather, its organizational function, is the main guideline in the placement of personnel, the implementation of processes for optimizing the structure of the enterprise and the number of personnel.
Economic and socio-legal expediency of rationing
In the work on labor rationing, great attention must be paid to the influence of natural economic processes and laws in force in our time. If we ignore a number of features that are inextricably linked with the model of modern market relations, it is impossible to plan and calculate the exact amount of labor costs,find out the degree of demand for finished products and their equivalent barter exchange.
The economic purpose of labor standards is to continuously stimulate productivity, increase the level of productivity with maximum time savings - these are the defining criteria for evaluating the effectiveness of the technologies used at the enterprise and progressive models of organizing the production process. Many recommendations on labor rationing imply a preference for an economical option for consuming resources in order to minimize overall costs.
In addition, modern labor standards are designed to ensure a more rigid impact of the market mechanism on the growth of the efficiency of work indicators and the improvement of quality characteristics. Given that labor rationing is the most convenient tool for comparing labor costs with finished products of activity, it is important for each of the business entities to ensure a stable and high level of profit.
The economic performance of production is also influenced by the managerial function of the rationing system. Without a well-coordinated work of management at an enterprise, it is difficult to achieve a consistent return on all elements of the production chain. If we study the mechanism of labor costs at a particular workplace, then we can no doubt say that rationing is involved in shaping the production behavior of personnel. The managerial function of labor standards is not only to determine the time spent on certain operations, but also to establish an algorithm for their implementation. Howthe more directions the model of labor organization used in production has, the more pronounced the manifestation of managerial functions seems, which subsequently determine the degree of effective management of all production processes.

You can not discount the social significance of labor standards. In the process of the emergence of labor processes and trusting relationships between management and personnel, a special role is played by the confidence of employees in the management's desire to maintain labor safety, increase the prestige, attractiveness of production work, satisfaction of performers with working conditions and material rewards. In addition, the regulation of labor in the legal field establishes the duties and rights of each employee, regulates the procedure for interaction between representatives of the managerial level and subordinates, ensuring legitimate mechanisms for resolving emerging conflicts in accordance with labor legislation. Also, the active use of labor standards allows you to establish exemplary discipline in production and stop its violations.
Labor standards in the outsourcing sector
Rationing of labor activity in production is wrong to consider a one-time event. This is a full-fledged activity that can have varying degrees of severity, depending on factors such as:
- production scale, organizational structure;
- line of business;
- features of manufactured products orservices provided;
- strategic goals and objectives of the company.
It is also impossible not to take into account the personnel issue, since only specialists, people who are competent in this industry, should deal with the issues of labor rationing. The trend of recent years has been the desire of entrepreneurs to move non-core business processes outside their company in order to free up resources for core business activities and get more time for the most efficient organization and management. Outsourcing is a prime example of this phenomenon. Today, the number of companies that have their own cleaners, logisticians, IT specialists, accountants, personnel officers, lawyers and representatives of other areas involved in the provision of basic production processes is decreasing. Instead of full-time staff, these functions are performed by employees of special offices for the provision of outsourcing services.
Can this model of cooperation be called effective for labor rationing? It is impossible to answer this question unambiguously. If the scale of the business does not imply a permanent presence in the workplace of any of the above specialists, the benefits of outsourcing are obvious:
- reducing the cost of performing these functions by saving on salaries and reducing the tax burden;
- minimizing the risks of "downtime" in work due to illness, employee vacation, etc.;
- the ability to control the actions of a third-party specialist.

The role of labor rationing in business
As already noted, in the modern manufacturing sector, labor standards serve as a tool for competent management, pursuing the goal of stable and consistent development of the company.
All processes in the economy are interdependent and interconnected. At the same time, the role of economic factors in the development of labor relations during the crisis is growing rapidly. Business owners try to do everything in order to get the maximum income with a minimum of expenses. Each entrepreneur is looking for his own formula for success, but in general the trend is noticeable:
- reduce staff;
- efficiently allocate and rationally use labor resources;
- save working time and avoid wastage;
- avoid factors that may negatively affect the quality of manufactured products or services provided.
At the same time, the workers themselves also strive to use their working time with the greatest efficiency, but they want to work in a safe environment with a satisfactory degree of intensity. Consequently, all parties to labor relations are interested in rationing.
Recommended:
Horizontal communication: basic concepts, types, management methods in an organization

What is communication? External and internal business communication. Characteristics of horizontal communication, possible problems and ways to solve them. Characteristics of vertical communication: hierarchical and inverse subgroups, their description, possible problems and their solution
Accounting documents are The concept, rules for registration and storage of accounting documents. 402-FZ "On Accounting". Article 9. Primary accounting documents

Proper execution of accounting documentation is very important for the process of generating accounting information and determining tax liabilities. Therefore, it is necessary to treat documents with special care. Specialists of accounting services, representatives of small businesses who keep independent records should know the main requirements for the creation, design, movement, storage of papers
Organization of labor is The system of labor organization

In modern conditions, the need for high labor organization is growing as the competitive environment and production efficiency grow. Organized labor has always provided and provides the highest results. The system of labor organization at a high level becomes a guarantee of effective activity in any field
Types of accounting. Types of accounting accounts. Types of accounting systems

Accounting is an indispensable process in terms of building an effective management and financial policy for most enterprises. What are its features?
Find an objective norm: what are the methods of labor rationing
Among the scientific organization of labor, rationing takes one of the places of honor, what are the methods of labor rationing, what advantages and disadvantages each of them has

